Special Report
27 Climate Emergencies That Are Happening Now and Can’t Be Stopped

Published:
Last Updated:

In September 2019, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, a U.N. body, released its latest report highlighting the dire consequences of failing to keep global warming to 1.5 Celsius above pre-industrial levels. To date, average global temperatures have already increased by 1 C. The report, like others before it, details how much worse the effects of global climate change would be should temperatures increase by 2.0 C or higher.
An earlier IPCC report on climate change stated that limiting the rise in global temperature to a 1.5 C increase — equal to roughly 2.7 F — “would require rapid, far-reaching and unprecedented changes in all aspects of society.” Indeed, some climate scientists estimate it would require massive reductions in greenhouse gas emissions almost immediately, and zero global emissions by 2050 to achieve that goal.
The global community is nowhere near to making that goal a reality, particularly as the United States, one of the largest carbon emitters, has announced its intention to withdraw from the Paris Climate Accord, which it will do in 2020. These are the countries that produce the most CO2 emissions.
Many experts are saying that temperature rise is already locked in at a 2.0 C increase — the equivalent of 3.6 F — the point at which the consequences will become much more severe.
But should a major change occur in the immediate future and global warming is halted at the 1.5 C target, it is important to note that this does not mean the effects of global climate change on the Earth and its population will not be serious. These are the places where weather is getting worse because of Climate Change.
Already, the approximately 1.0 C increase has had severe impacts on global weather, sea levels, and ecosystems. When 1.5 C is reached, the impacts, as determined by scientists and experts around the world, are projected to be disastrous.
24/7 Wall St. consulted reports by groups such as the IPCC, NASA, the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Association, the U.S. Global Change Research Program, and more, to identify the effects of global warming that either have already taken place or will occur even if warming is limited to a 1.5 C increase. If temperatures rise to 2.0 C or more, these are some of the more extreme disaster scenarios that will get worse if we do nothing.
Click here to see the 27 impacts of climate change
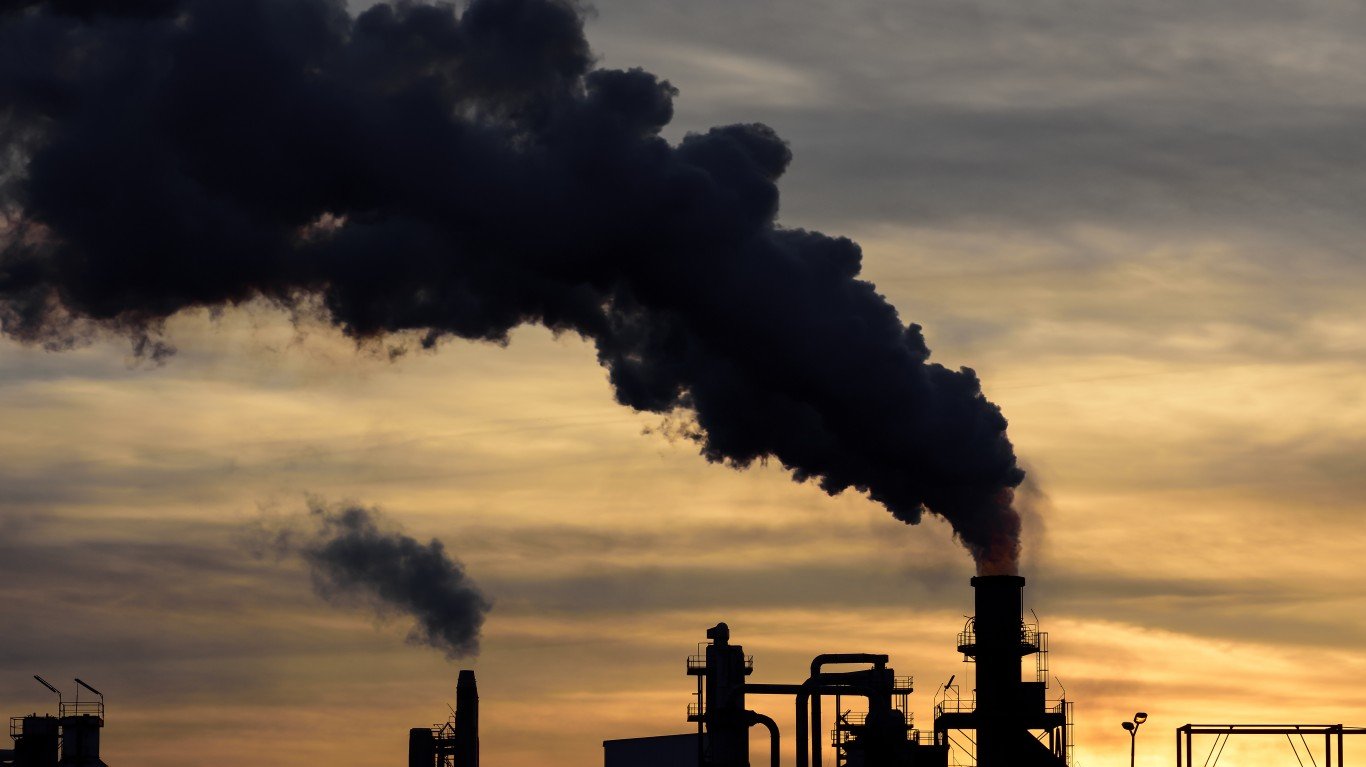

1. Carbon dioxide levels above 400 ppm
The concentration of global atmospheric carbon dioxide now exceeds 400 parts per million (ppm). The last time there was such a high levels of CO2 was about 3 million years ago, when temperatures were considerably higher.
[in-text-ad]

2. Global warming so far: 1.0°C
Since the beginning of the 20th century, surface temperatures have increased by approximately 1.0 C, or 1.8 F. Even such a small increase has had drastic effects.
3. Record heat
Since the year 2000, nearly every year has been one of the hottest on record. The last five years — 2014 through 2018 — have been the five warmest years in the NOAA’s 139 years of data.

4. Hotter in the US
In the United States, annual surface temperatures have been, on average, 1.5 F hotter than in the previous century.
[in-text-ad-2]
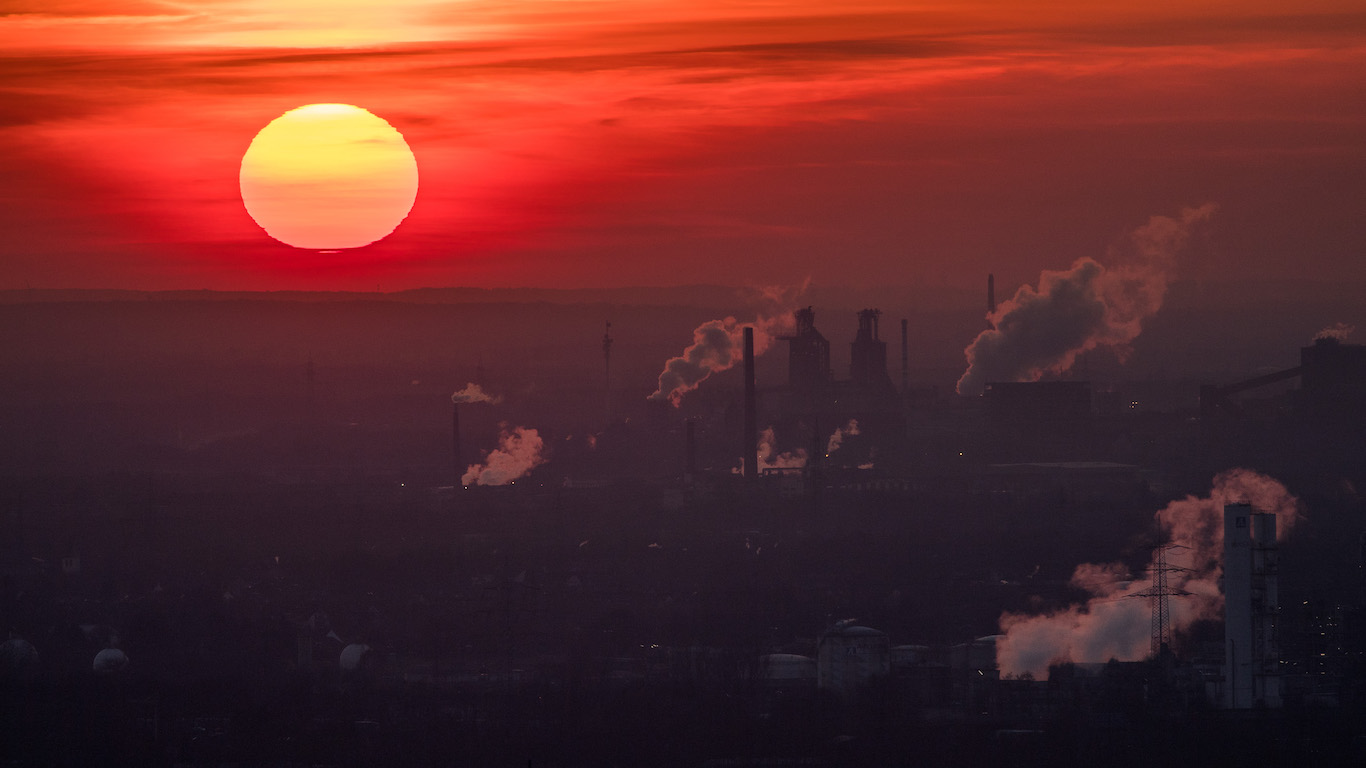

5. Hotter days ahead
In much of the contiguous United States, even under a conservative model, annual temperatures are expected to rise by 2-4 F by the middle of this century, with the biggest increases expected in the northern parts of the Midwest.
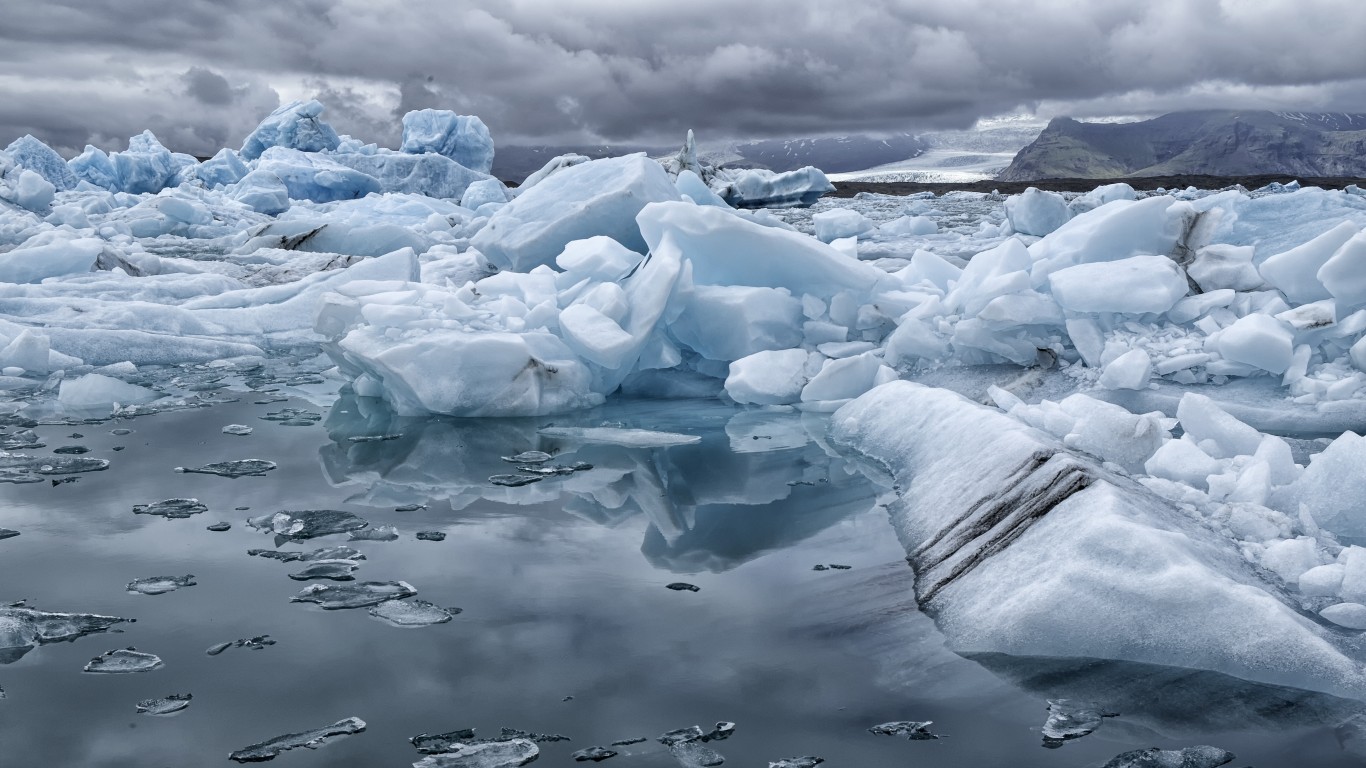

6. Sea ice vanishing
Since 1979, global sea ice coverage has declined at an annual rate of roughly 13,500 square miles, roughly equivalent to the size of Maryland.
[in-text-ad]
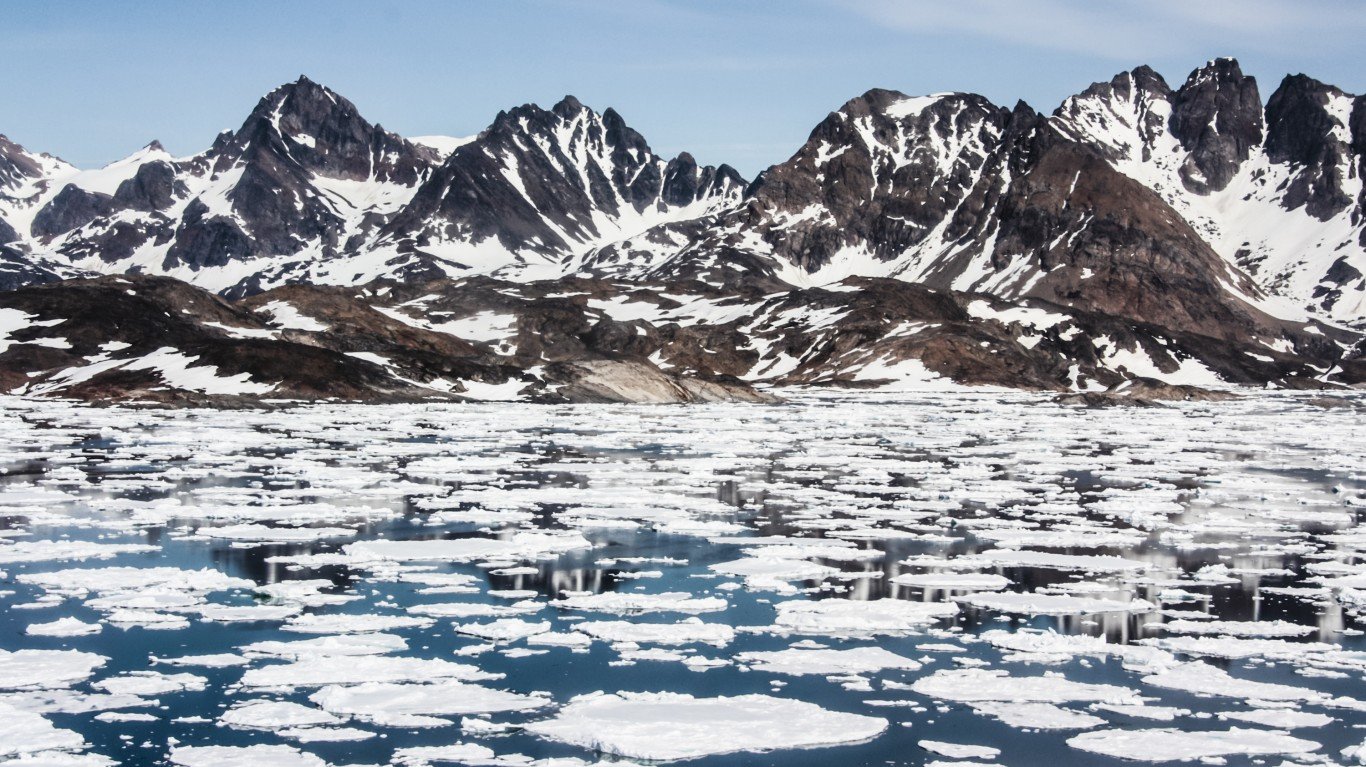

7. Greenland is melting
The Greenland ice sheet has been melting — and at an accelerating rate. On one day in July 2012, melt occurred across 98.6% of the ice sheet, affecting even the summit areas of the sheet, which are nearly two miles above sea level. It was the first time in the satellite record (which dates back to 1979) that snowmelt conditions had affected the entire ice sheet.
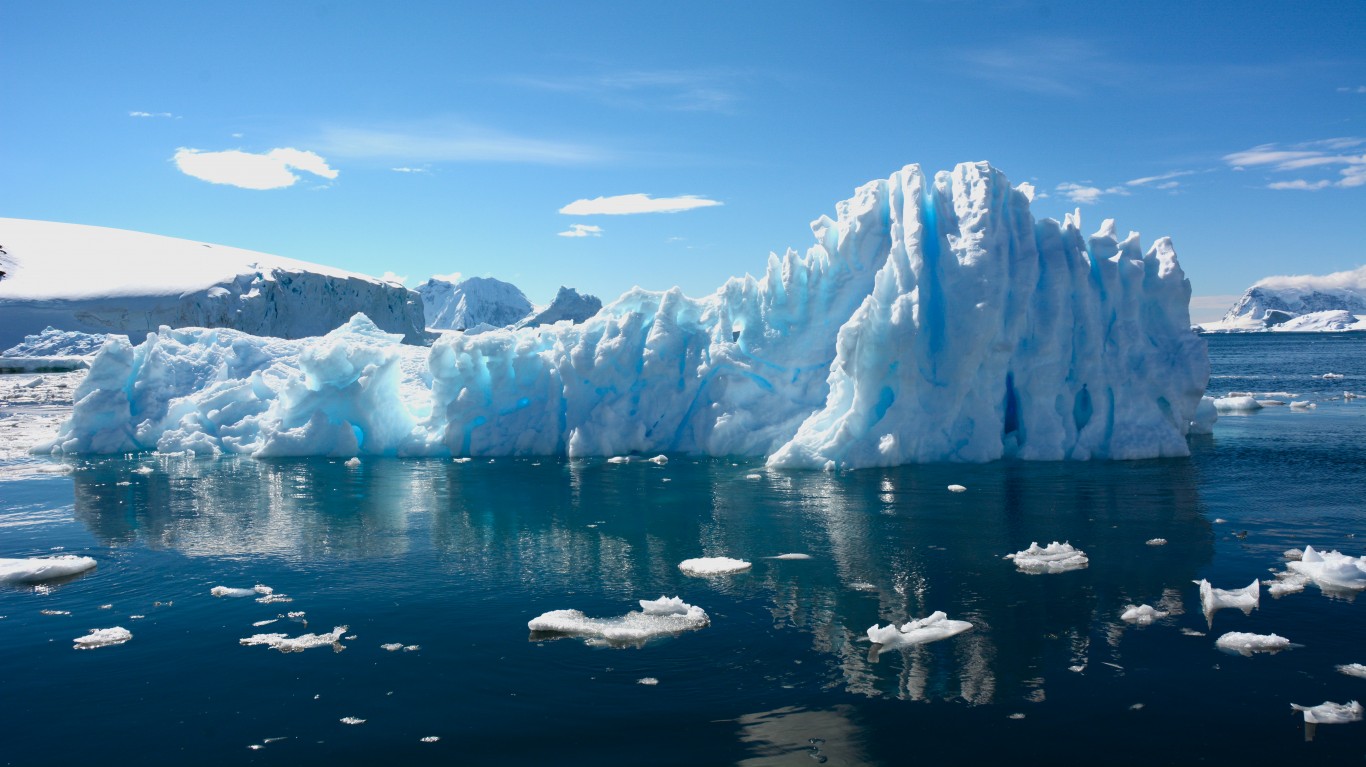

8. Antarctica is melting
Antarctic sea ice minimum levels in March 2017 were the lowest on record.
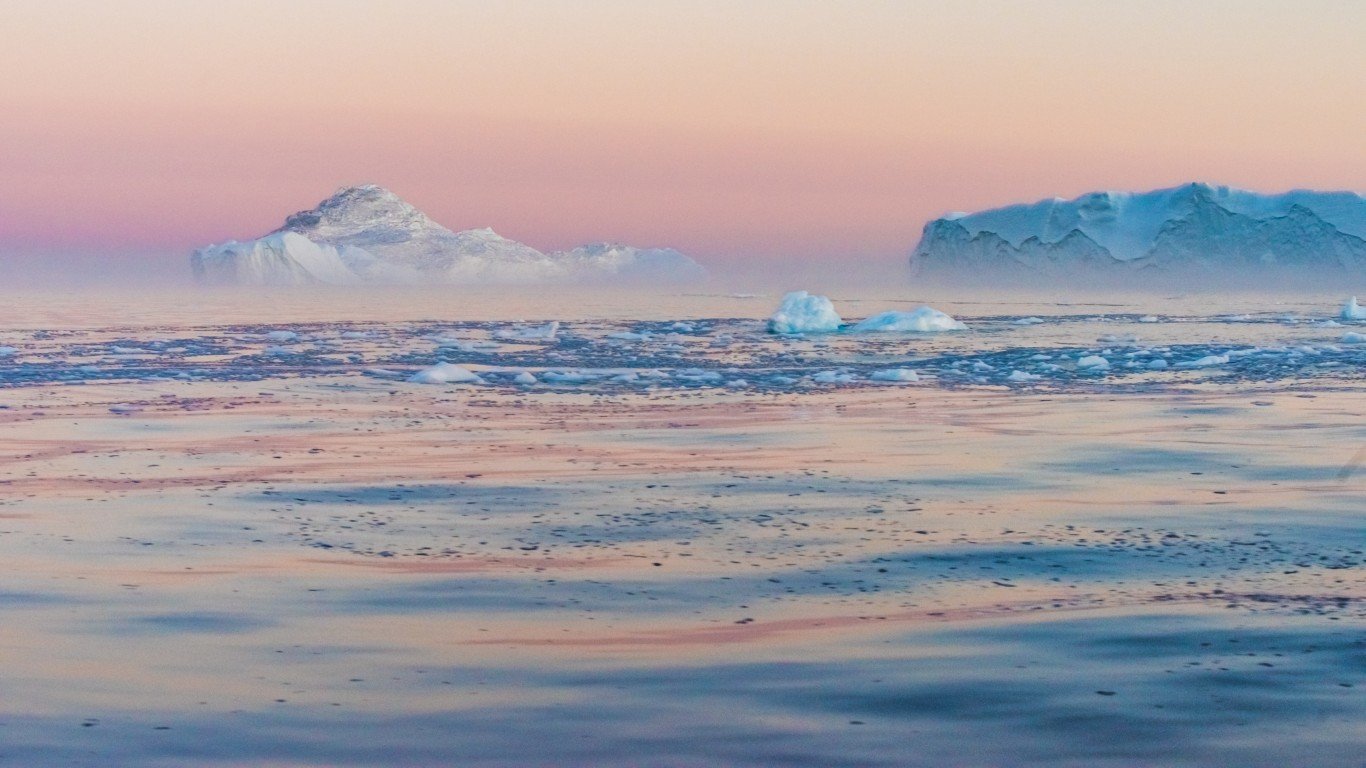

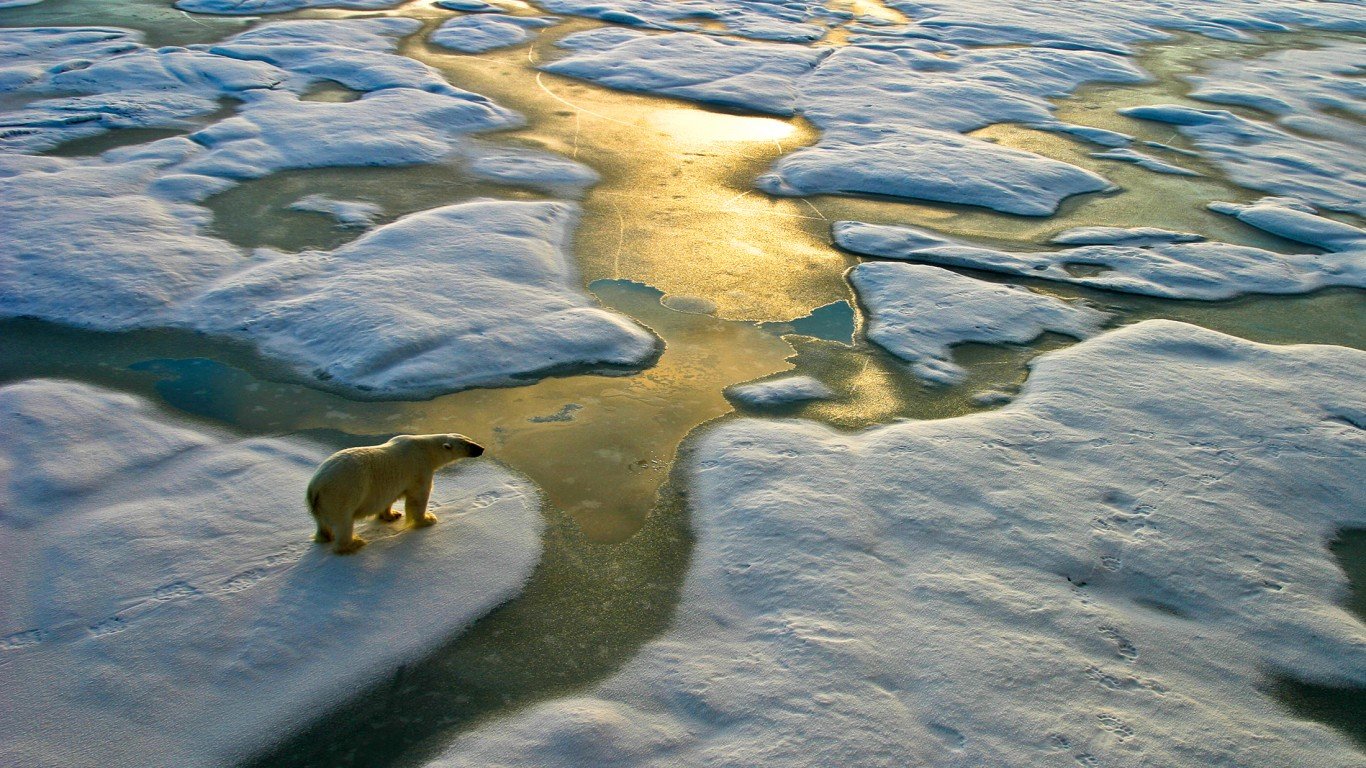
9. The Arctic is melting
Arctic sea ice has declined by 38.7% between 1979 and 2019. Climate models project the Arctic Ocean could be free of ice in the summers by mid-century.
[in-text-ad-2]
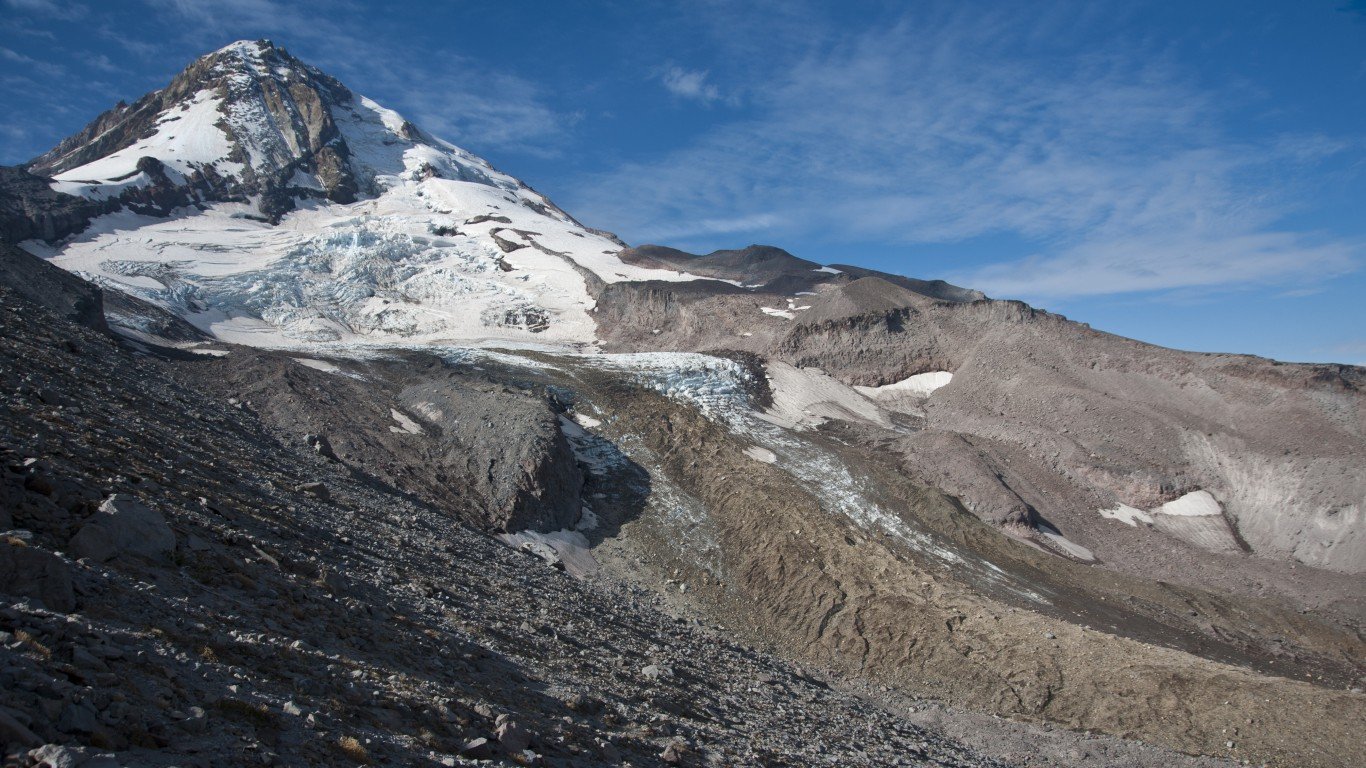

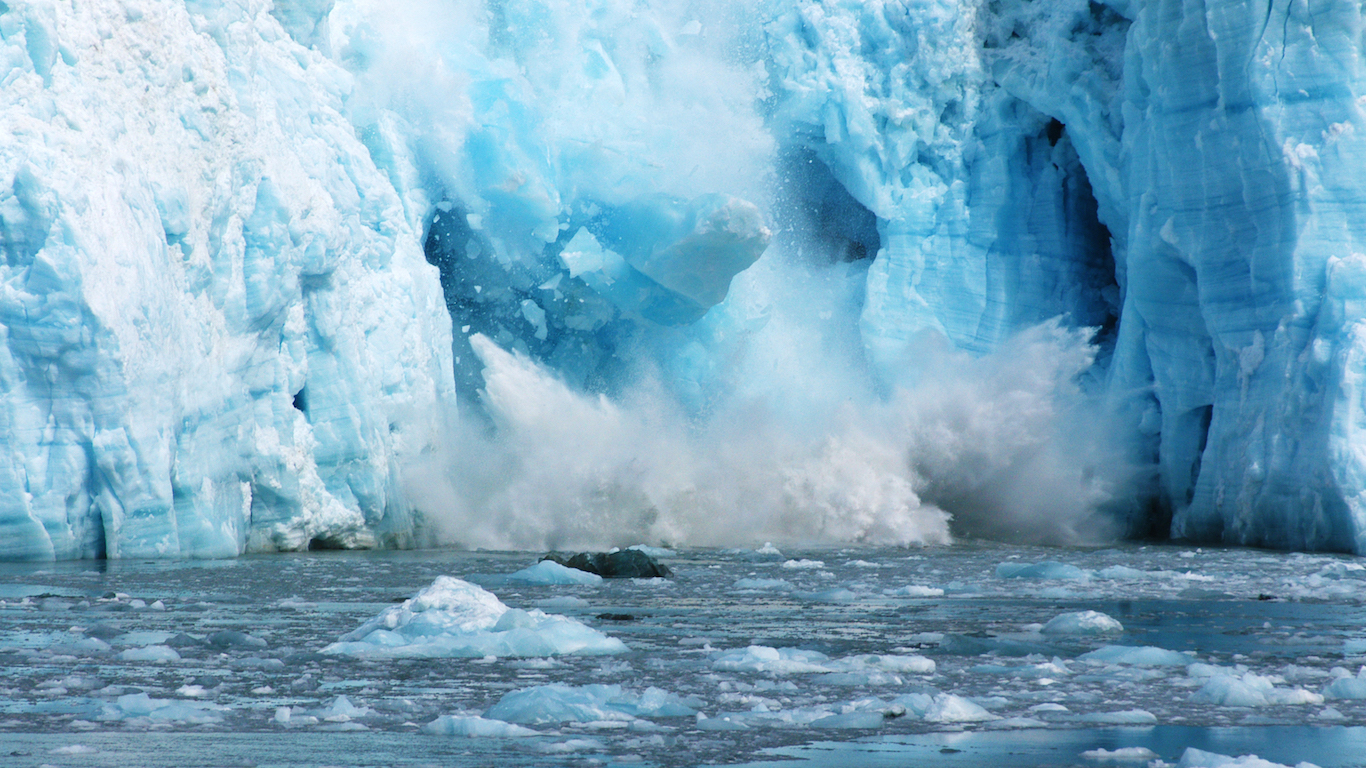
10. Glaciers are vanishing
The vast majority of glaciers on Earth are shrinking, many at alarming rates.
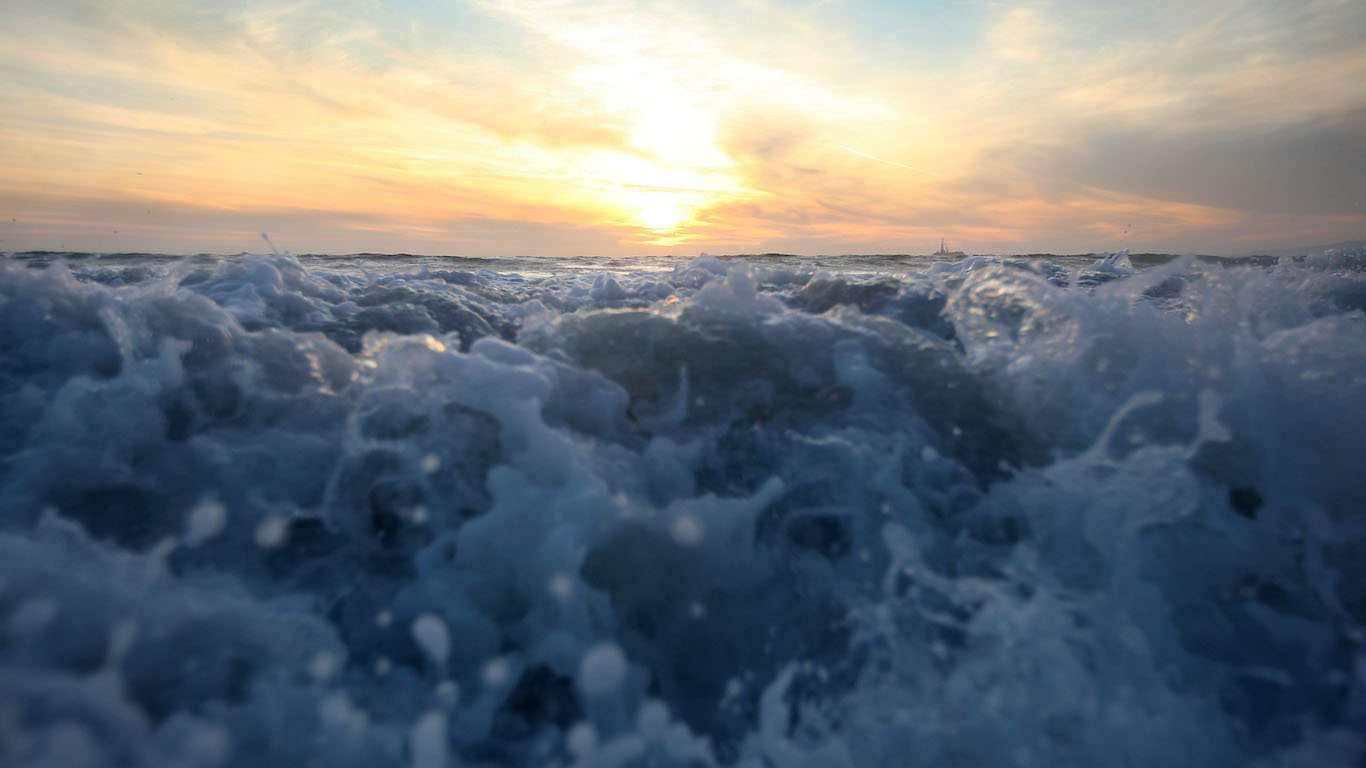

Average global sea levels have increased by about 8 inches since 1900.
[in-text-ad]
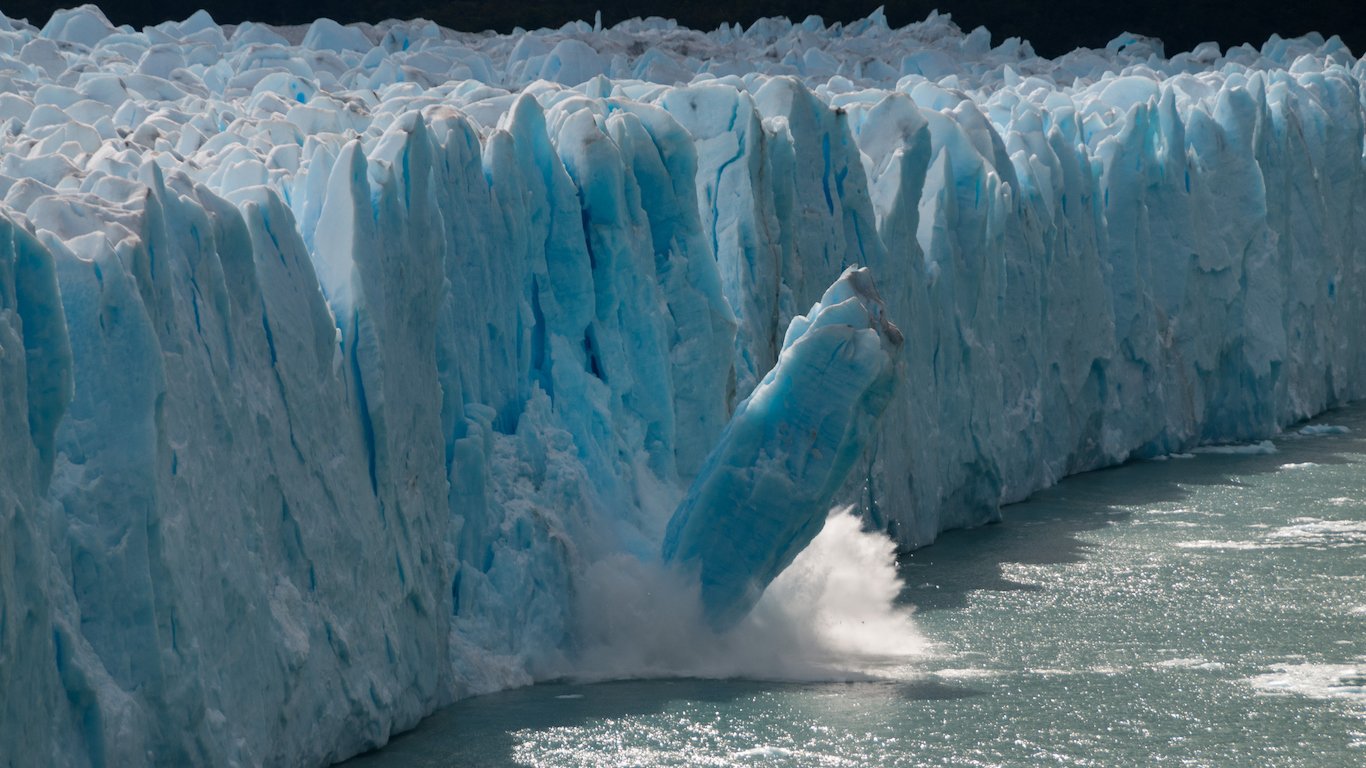

12. Sea level rise is accelerating
Since 1993 alone, sea levels rose 3 inches, or nearly half of the total rise since the turn of the 20th century.

13. Future sea levels
Under the best-case scenario, scientists are now concluding that average sea levels are expected to rise by an additional 1 to 4 feet by the end of the century. In a worst-case scenario, levels could rise by more than 8 feet.
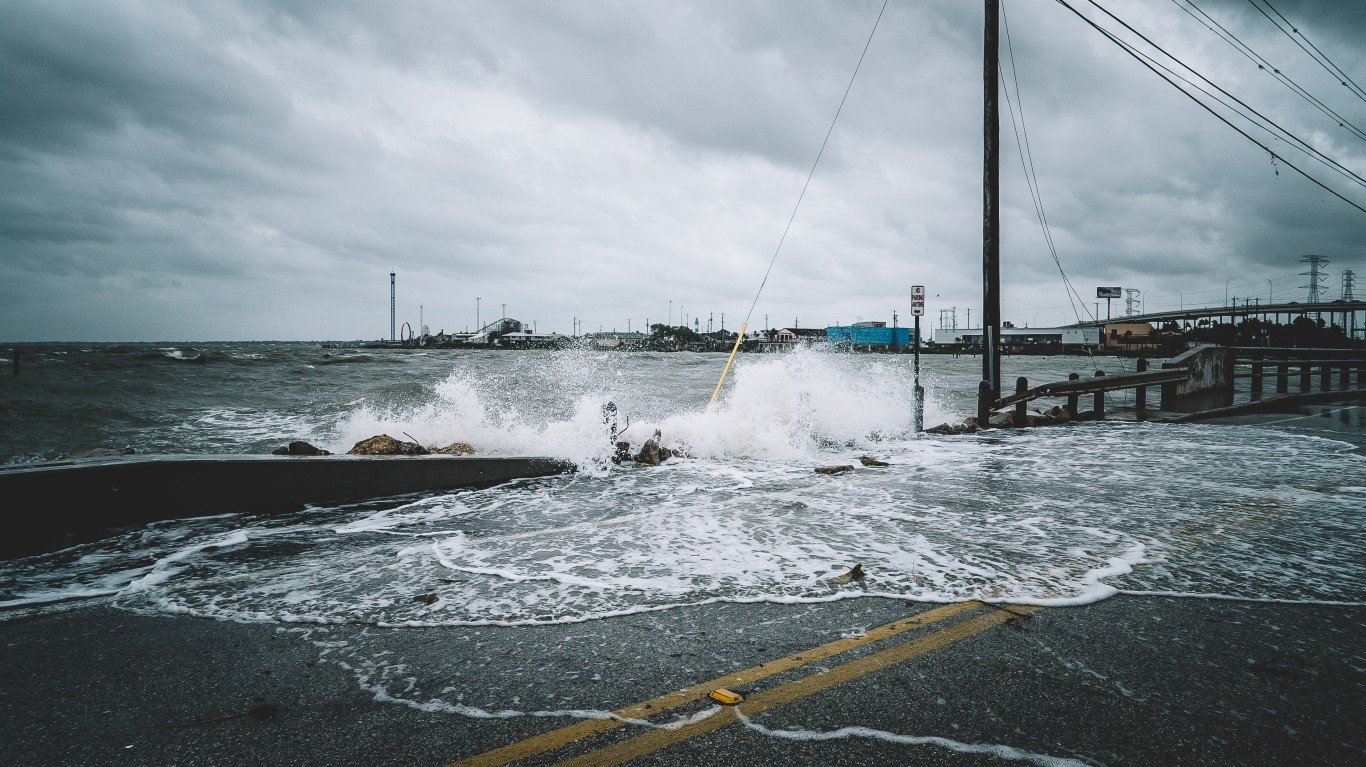

14. Flooding in the US
Rising sea levels may have already increased flooding in the United States. Today, dozens of American coastal communities flood at least partially 26 times per year. Within the next two decades, over 170 cities will be affected by chronic flooding.

15. Miami underwater
Large sections of major low-lying coastal cities like Miami will likely be regularly flooded this century without major structural changes to the city’s coastline.
[in-text-ad-2]

16. Growing seasons have changed
Agricultural growing season in the United States, particularly the West, has lengthened in recent years.

17. Allergy season has lengthened
Over the decade between 2001 and 2010, the average annual start of the pollen season was three days earlier than during the previous decade. The severity and frequency of illnesses tied to allergies — like asthma and hay fever — are expected to increase.
[in-text-ad]
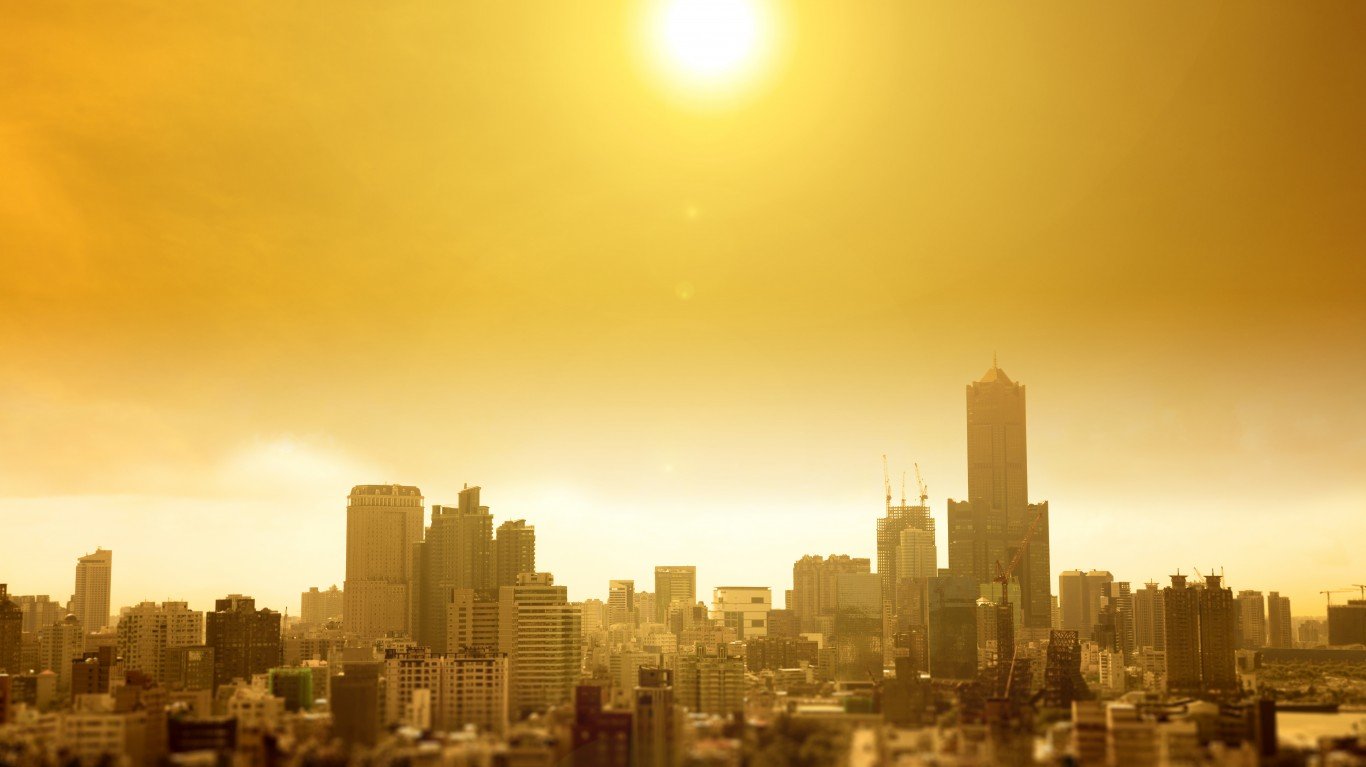

18. More heat waves
The total land area worldwide that has 30 days of extreme heat per year has roughly doubled since 1998.
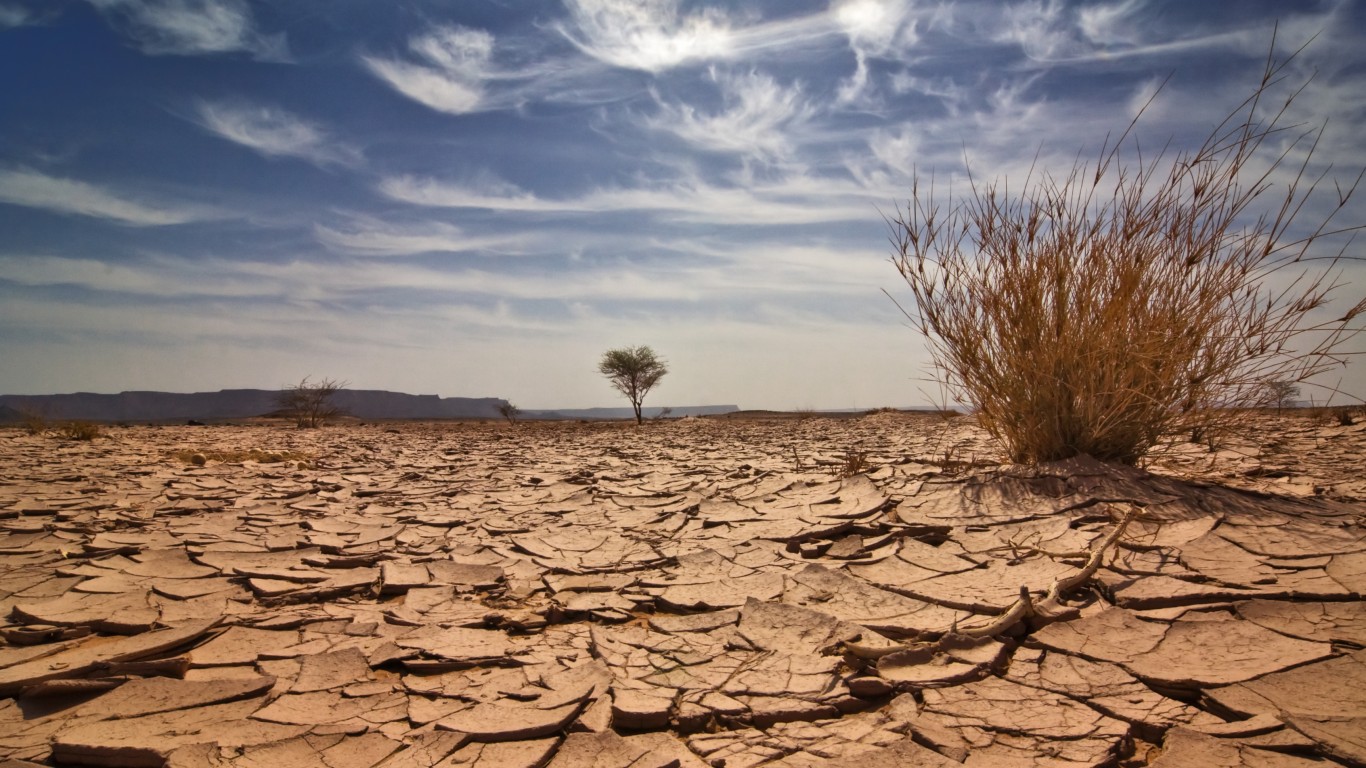

19. Increasing drought
If the increase in global average surface temperature reaches the 1.5 C mark, which it is almost certain to do, 350 million additional people will be exposed to severe drought regularly.
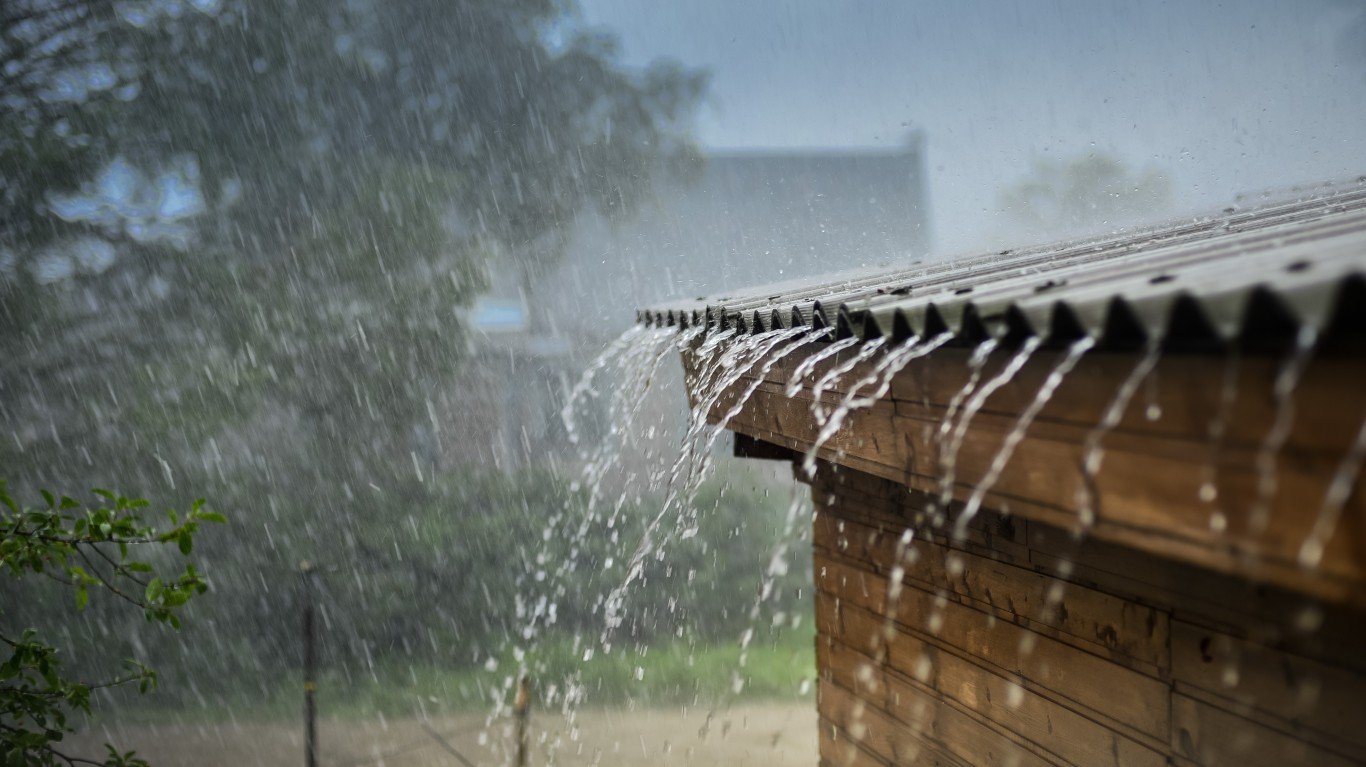

20. More global precipitation
More water vapor in the atmosphere as a result of global warming has led to an 8.5% increase in global precipitation since 1900.
[in-text-ad-2]
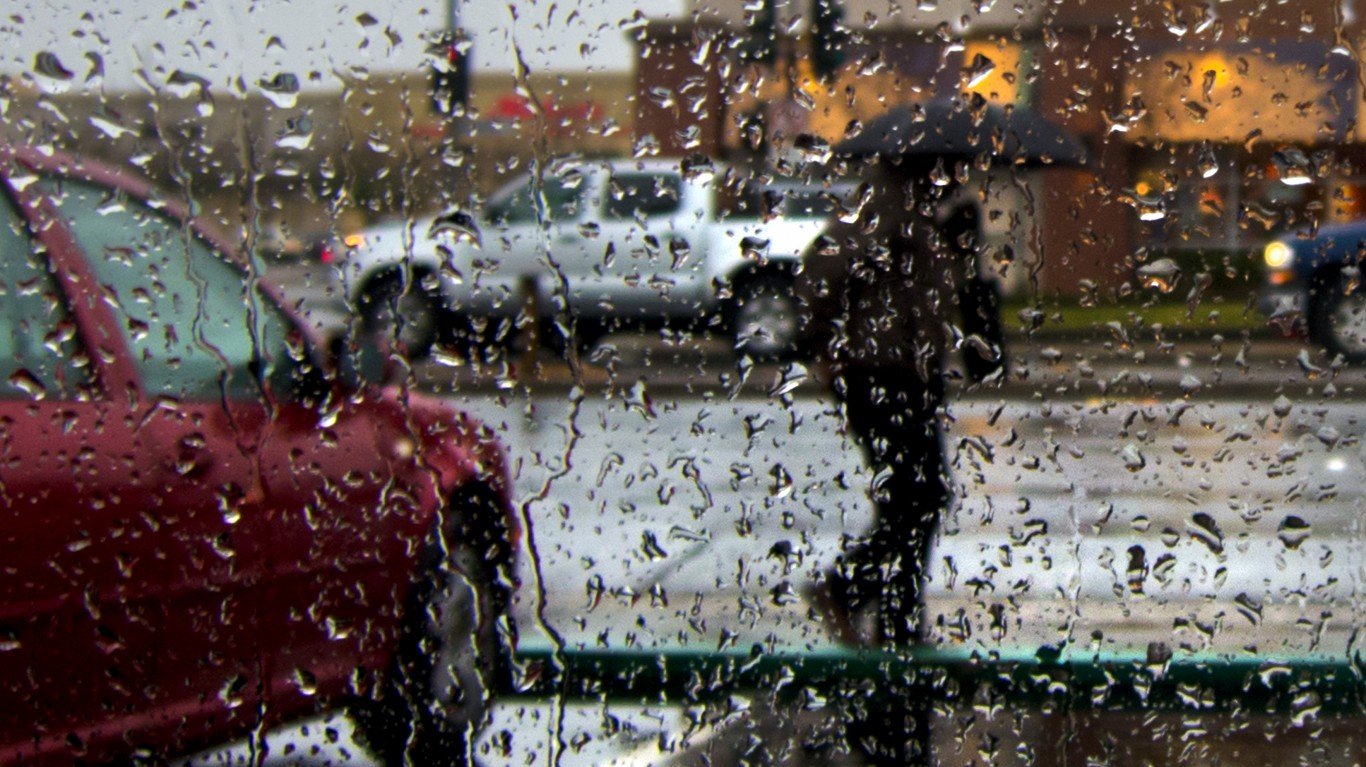

21. More precipitation in the US
Annual precipitation in the United States has increased by approximately 4% between 1901 and 2015.
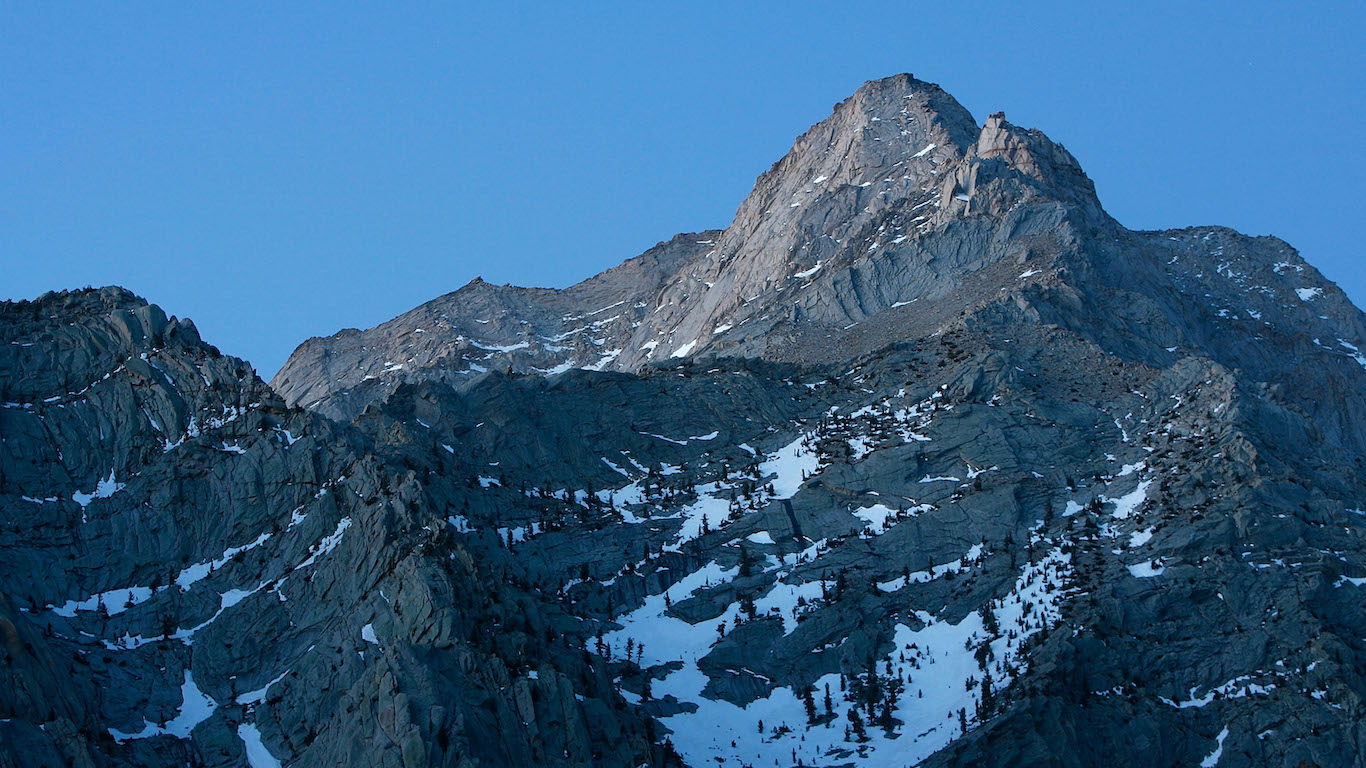

22. Less snow cover
Snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere has decreased by about 0.2 million square miles — slightly larger than the size of California — since the 1970s.
[in-text-ad]
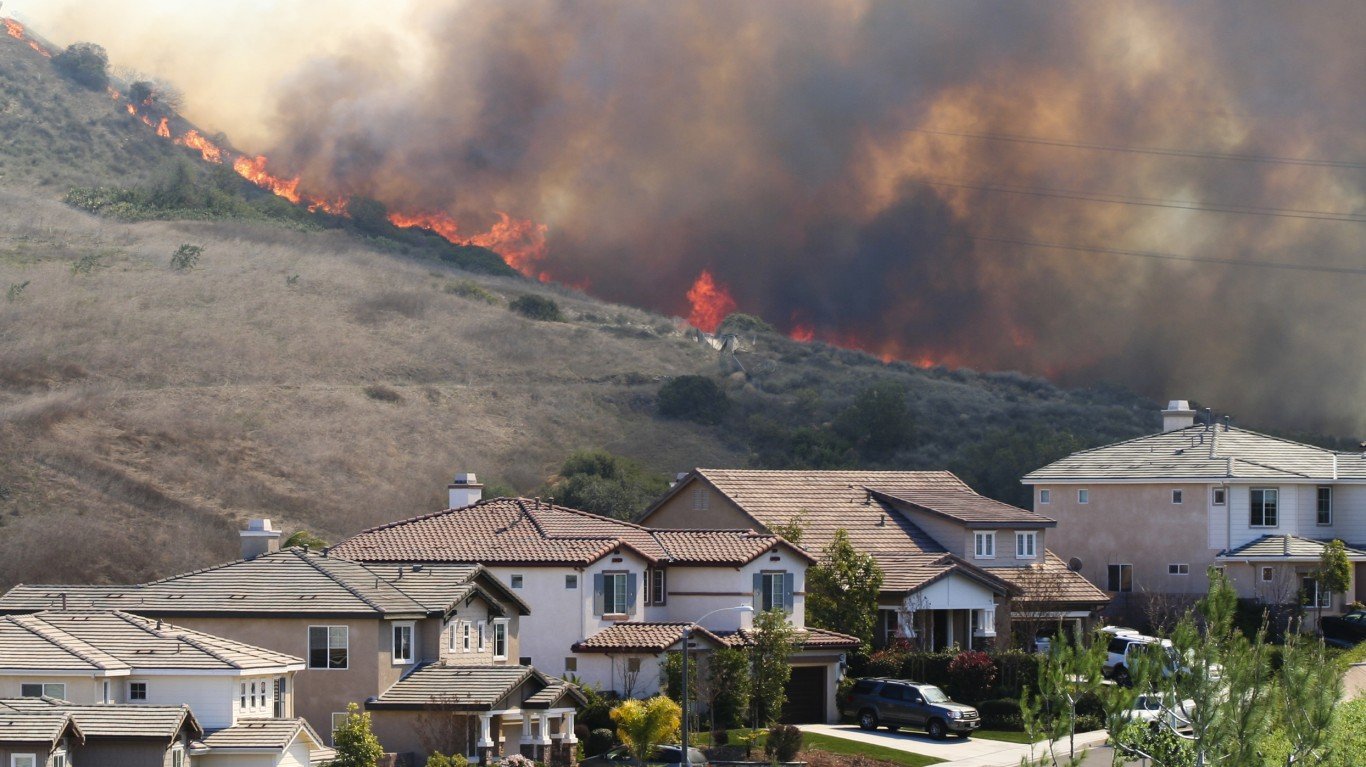

23. Forest fires more common
Since the turn of the century, there have been 10 years in which at least 7 million acres burned. This only happened in one year between 1956 and 1999.
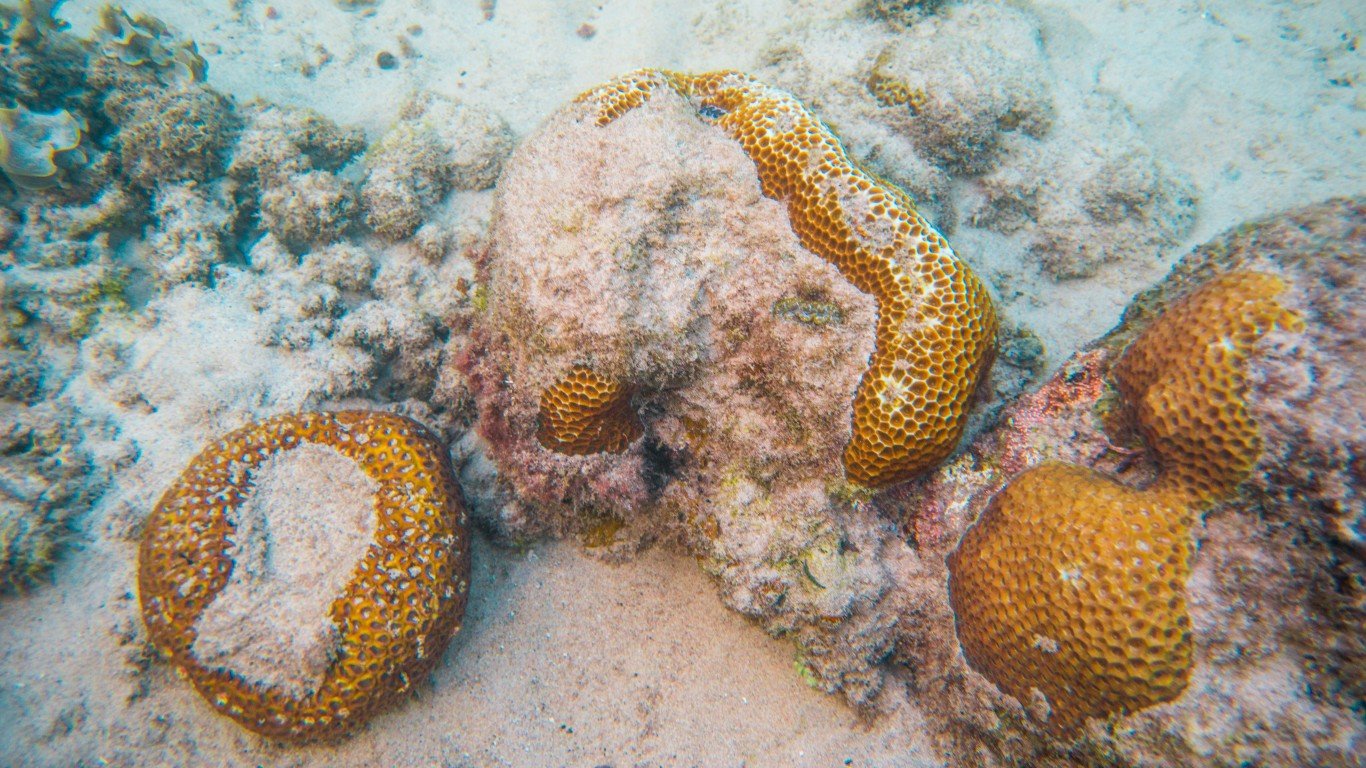

24. More acidic ocean
The ocean has absorbed carbon dioxide and become 30% more acidic in the past 200 years, the fastest increase in acidification in 50 million years.
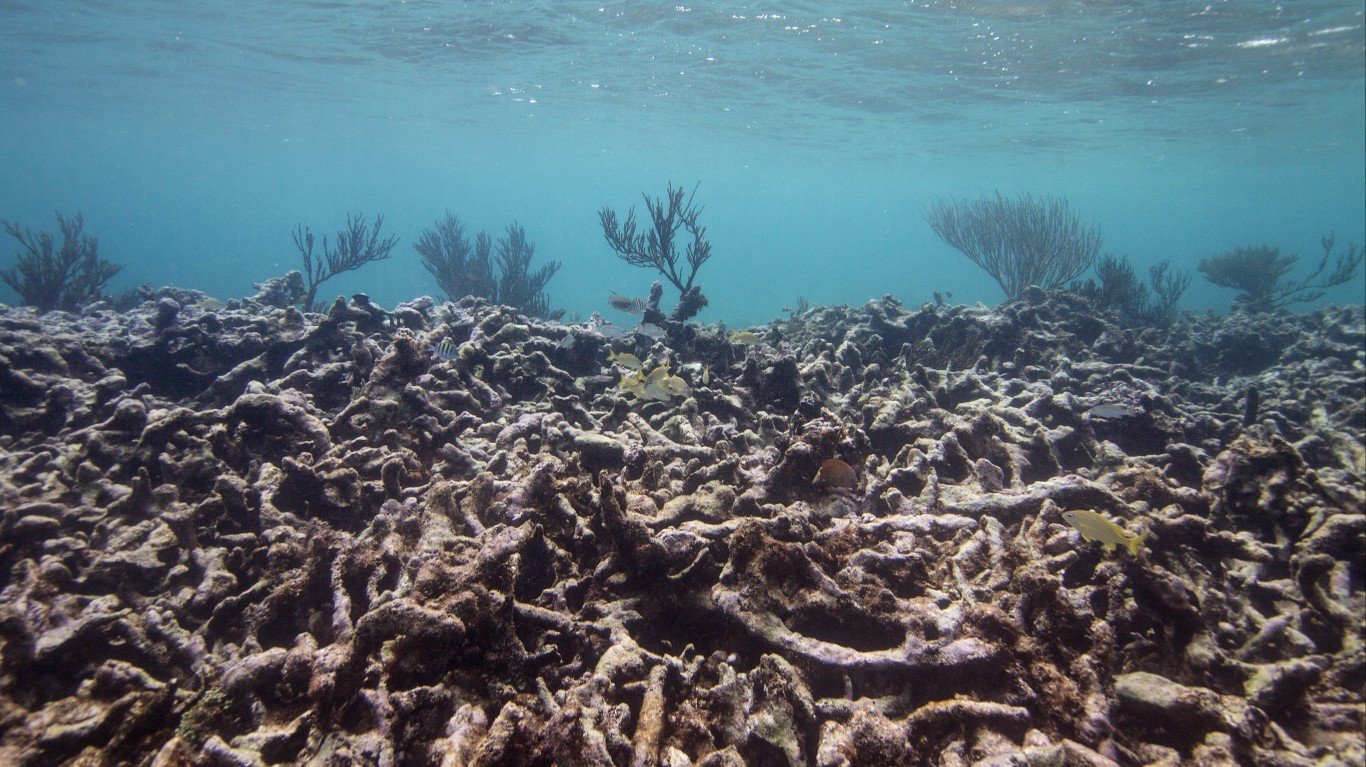

25. Dying coral reefs
Coral reefs are dying at alarming rates due to a number of reasons, including ocean water pollution, acidification, warming, overfishing, and other human activity.
[in-text-ad-2]
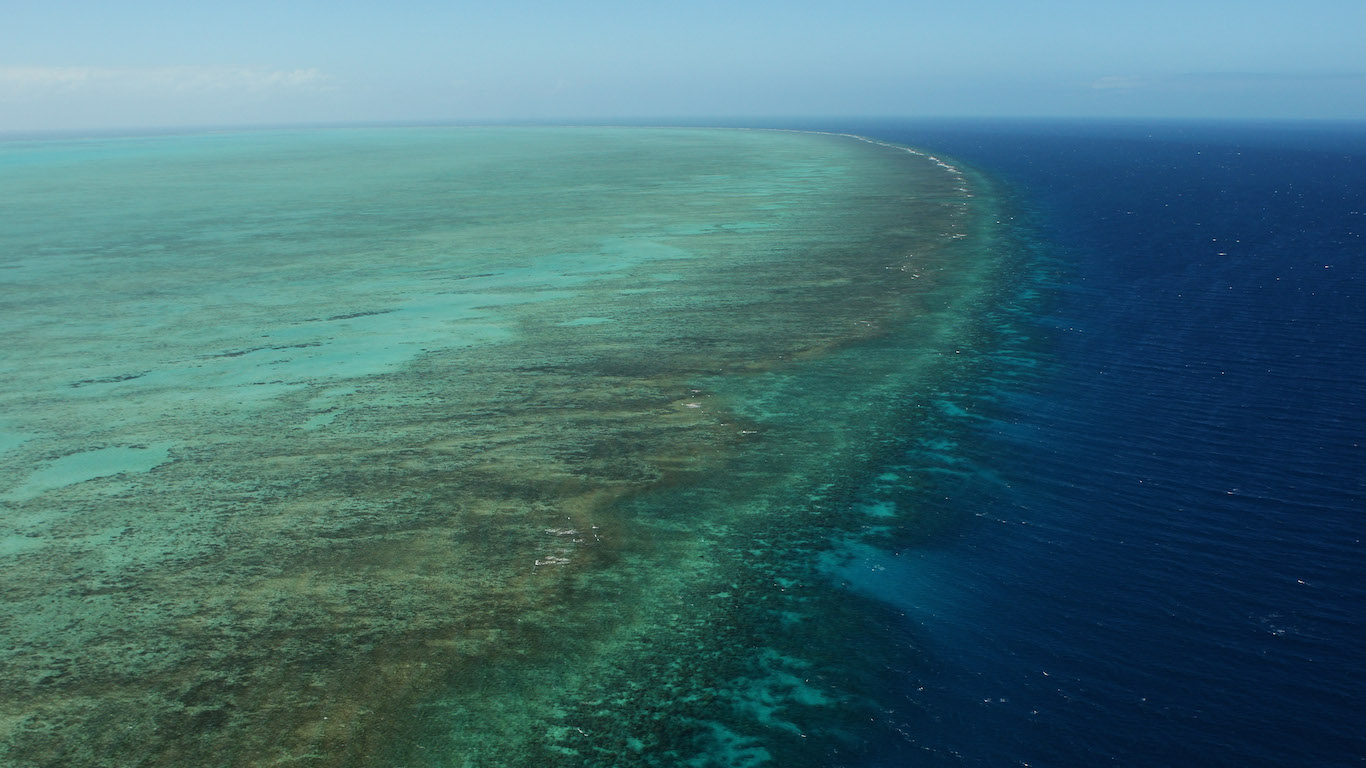

26. Coral extinction
Coral reef death will likely get much worse. Scientists estimate that an average surface temperature increase of 1.5 C will lead to a 70% to 90% loss of coral reefs in the coming years.
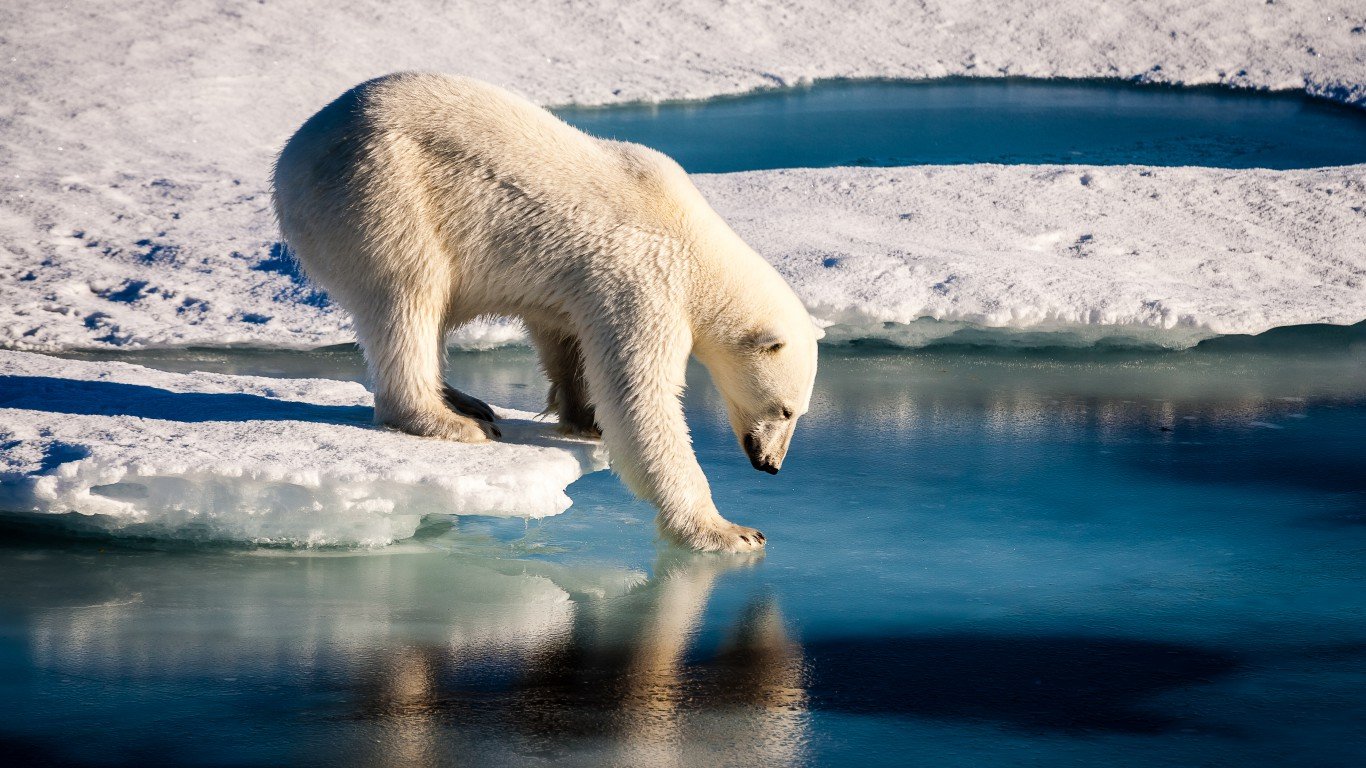

27. Widespread extinction
Global warming has already affected the habitats of numerous species, and as temperatures continue to rise, conditions will become even worse. An additional 0.5 C increase in global average temperature could put as much as 30% of all species on Earth at risk of extinction.
Are you ready for retirement? Planning for retirement can be overwhelming, that’s why it could be a good idea to speak to a fiduciary financial advisor about your goals today.
Start by taking this retirement quiz right here from SmartAsset that will match you with up to 3 financial advisors that serve your area and beyond in 5 minutes. Smart Asset is now matching over 50,000 people a month.
Click here now to get started.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.