
Within weeks of taking office, President Joe Biden issued a series of executive orders aimed at making the U.S. carbon neutral by 2050. This goal hinges on eliminating greenhouse gas emissions in electricity production — which necessitate a shift away from fossil fuels, like natural gas and coal, toward clean renewable energy sources, like wind and solar.
It is important to note that not all renewable energy sources are carbon neutral, just as not all non-renewable energy sources emit greenhouse gases. Biomass, such as waste wood and crop residue is renewable, but when it is burned to produce electricity, it creates carbon. Similarly, though nuclear power plants are not classified as renewable sources, they do not produce air pollution. Still, some forms of biomass produce far less carbon emissions than fossil fuels.
Currently, only 17.7% of electricity produced in the United States comes from renewable sources. Nationwide, wind turbines generate the most electricity, followed by hydroelectric power plants and solar thermal power. Biomass, such as wood and agricultural waste, as well as geothermal energy, are renewable sources that account for a very small share of the U.S. energy mix.
Meanwhile, greenhouse gas-emitting coal and natural gas-fired power plants account for over half of all U.S. electricity production. Here is a look at the countries increasing carbon emissions the fastest.
While, as a nation, the U.S. has a long way to go to achieve carbon neutrality, at a state level, progress has been inconsistent. In some states, less than 5% of electricity production comes from renewable sources, while in others, fossil fuels have been virtually phased out. Here is a look at America’s most and least environmentally friendly states.
Using data from the U.S. Energy Information Administration, 24/7 Wall St. identified the states producing the most renewable energy. States are ranked based on the share of 2019 electricity production from renewable sources.
Click here to see how much renewable energy your state produces.
Click here to see our methodology.

50. Delaware
> Electricity from renewables: 2.3% of total (120,466 MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Other biomass (61,389 MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (4.8 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: -0.3 ppt. (8th lowest)
Only 2.3% of electricity produced in Delaware comes from renewable sources, the smallest share of any state in the country. The state’s renewable energy comes from a mix of solar, wind, and biomass.
Over 90% of electricity in Delaware is generated through natural gas-burning power plants. Over the last decade, the state has reduced its reliance on coal considerably while ramping up use of natural gas. Delaware does not produce enough electricity to meet in-state demand and buys anywhere from one-third to one-quarter of its electricity from other states.
[in-text-ad]

49. Mississippi
> Electricity from renewables: 2.6% of total (1.7 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wood and wood derived fuels (1.4 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (48.8 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: -0.3 ppt. (7th lowest)
Mississippi is one of only four states where renewable sources account for less than 3% of electricity production. A largely agricultural state, Mississippi has considerable biomass resources such as logging residue, crop residue, and livestock manure. Biomass accounts for the largest share of renewable electricity in Mississippi followed by solar.
Natural gas is by far the largest contributor to the state’s power grid, accounting for 74% of electricity production. Of the 10 largest power plants in the state, nine are natural gas-burning. Mississippi is also home to the Grand Gulf Nuclear Power Station, the largest nuclear reactor in the United States. Nuclear power accounts for about 17% of the state’s electricity production.

48. Ohio
> Electricity from renewables: 2.7% of total (3.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (2.0 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (51.3 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +1.9 ppt. (16th lowest)
Only 2.7% of electricity produced in Ohio comes from renewable sources, the third smallest share of any state in the country. Like many Midwestern states, the largest renewable electricity source in Ohio is wind. The state’s largest wind farm has 152 wind turbines. In the coming years, the state plans to increase electricity production from wind substantially.
Ohio has about 5% of the nation’s recoverable coal supply. Coal has historically been the largest electricity source in the state. However, in 2019, it was overtaken by natural gas for the first time. Natural gas-fired power plants account for about 43% of electricity production in Ohio compared to coal, which accounts for 39%. A decade ago, coal-burning plants generated 83.6% of electricity in the state, compared to just 3.4% generated by natural gas-burning power plants.

47. New Jersey
> Electricity from renewables: 2.8% of total (2.0 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Solar thermal and photovoltaic (1.2 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (40.4 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +1.2 ppt. (13th lowest)
New Jersey generates just 2.8% of its total electricity production through renewable sources. Over half of that is generated through solar power, and the rest is from biomass.
The bulk of electricity production in New Jersey happens in natural gas-fired power plants. There are also three operational nuclear power plants in the state that account for 37.5% total electricity production. Nuclear power shouldered a larger share of the state’s electricity production not long ago. However, the state in 2018 shuttered its Oyster Creek nuclear power plant, which at the time was the oldest operational nuclear reactor in the country.
[in-text-ad-2]

46. Connecticut
> Electricity from renewables: 3.3% of total (1.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Other biomass (480,951 MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (21.3 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: -0.7 ppt. (5th lowest)
Connecticut is one of eight U.S. states in which less than 4% of the electricity comes from renewable sources. It is also one of just three states in which biomass sources, like plants such as corn and soy, provide more renewable energy than any other renewable source.
In a break from the broader national trend, Connecticut is one of just 10 states in which the share of renewable sources declined over the last decade, falling from 4.1% of the state’s energy production to 3.3%.

45. Florida
> Electricity from renewables: 3.5% of total (8.6 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Solar thermal and photovoltaic (3.9 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (182.0 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +1.4 ppt. (14th lowest)
In Florida, only 3.5% of electricity is generated through renewable sources. Solar thermal and photovoltaic is the largest renewable contributor to the power grid in the Sunshine State. One solar energy production facility in the state uses nearly 200,000 mirrors to concentrate sunlight and generate electricity. It is the only facility of its kind in the eastern United States. Biomass such as sugar cane waste, citrus pulp, wood pellets, and yard waste is also widely used for electricity production in Florida.
The state is one of 25 where natural gas-fired plants generate the most electricity. Florida also has two nuclear power plants that generate about 12% of electricity in the state.
[in-text-ad]

44. Louisiana
> Electricity from renewables: 3.6% of total (3.6 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wood and wood derived fuels (2.2 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (69.5 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: -0.3 ppt. (6th lowest)
Just 3.6% of Louisiana’s energy comes from renewable sources, less than a quarter of the comparable national share. Louisiana does not use wind or geothermal sources. The bulk of its renewable energy production comes from wood and wood-derived sources, one of just a handful of states in which this is the case.
Nationwide, a larger share of electricity comes from natural gas than any other single source, at 38.4%. Louisiana, which has among the largest natural gas reserves of U.S. states, is also one of the largest natural gas-producing states. More than two-thirds of the state’s electricity comes from natural gas, at 69.4%, the sixth highest share of any state.

43. Pennsylvania
> Electricity from renewables: 3.9% of total (8.8 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (3.5 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (98.0 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +1.1 ppt. (12th lowest)
Pennsylvania generated nearly 229 million MWh of electricity in 2019 — and only 3.9% of it came from renewable sources. Most renewable energy production in the Keystone State is from hydroelectric power plants and most of the rest from wind turbines. The state has two pumped storage plants, which operate by moving water from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir and then releasing the water to power turbines. The state also had 26 operational wind farms as of mid-2020 and added two additional wind farms at the end of that year.
Electricity generated from natural gas power plants has expanded considerably in Pennsylvania in recent years as reliance on coal-fired plants has declined. As of 2019, 42.8% of electricity in the state came from natural gas, compared to 13.3% a decade earlier. Over the same period, reliance on coal fell from 48.1% of electricity production to 16.6%.

42. West Virginia
> Electricity from renewables: 5.2% of total (3.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (1.7 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (58.2 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +1.8 ppt. (15th lowest)
Only 5.2% of electricity in West Virginia is produced from renewable sources — namely hydroelectric and wind. The state is home to a dozen hydroelectric plants, the oldest of which began operating in 1909, while the newest has been generating electricity since 2016.
Far and away, the largest source of electricity in West Virginia is a non-renewable resource that has been integral to the state’s history and economy — coal. Coal accounted for over 90% of electricity production in the state in 2019, and that same year, West Virginia had more recoverable coal reserves in active mines than every state except for Wyoming and Illinois. Much of the electricity produced in West Virginia is sold to other states.
[in-text-ad-2]

41. South Carolina
> Electricity from renewables: 6.0% of total (6.0 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (3.0 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Nuclear (56.1 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +1.9 ppt. (17th lowest)
Just 6.0% of the 100.1 million MWh of electricity produced in South Carolina in 2019 came from renewable sources. The state has about 30 utility scale hydroelectric plants and is ramping up its solar power production capacity.
The largest power source in South Carolina is nuclear. There are four nuclear power plants in the state with seven nuclear reactors, including the Onconee plant, which is the largest power plant in the state. Only Illinois and Pennsylvania produced more nuclear power than South Carolina in 2019.

40. Rhode Island
> Electricity from renewables: 6.2% of total (472,344 MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Other biomass (207,796 MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (7.1 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +4.3 ppt. (24th lowest)
Virtually all of Rhode Island’s non-renewable energy — and 93.7% of its energy overall — comes from natural gas, accounting for over 7.1 million MWh. This is by far the largest share of any state.
Just 10 states produce a lower share of their electricity using renewable sources than Rhode Island’s share of 6.2%. Rhode Island’s top renewable energy source is biomass, which produced nearly 208,000 MWh or 2.7% of the state’s total electricity. Biomass sources just narrowly edged out wind sources as the state’s top renewable electricity source.
[in-text-ad]
39. Virginia
> Electricity from renewables: 6.4% of total (6.2 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wood and wood derived fuels (2.7 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (58.0 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +0.9 ppt. (11th lowest)
Just 6.4% of electricity produced in Virginia is from renewable sources, less than most states and up by less than 1 percentage point from a decade ago. Renewable energy production in the state comes from a mix of wood and other forms of biomass, hydropower, and solar thermal.
The largest electricity source in the state is natural gas, which accounts for nearly 60% of production. Virginia is also home to two nuclear power plants, which generated 30.5% of electricity in 2019. That same year, coal’s contribution to the power grid amounted to just 3.5%, marking the first time in the state’s history that renewable sources generated more power than coal.

38. Kentucky
> Electricity from renewables: 6.5% of total (4.7 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (4.2 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (51.7 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +2.4 ppt. (18th lowest)
Kentucky produced 71.8 MWh of electricity in 2019. Just 6.5% of that, 4.7 MWh, came from renewable sources, mostly from hydroelectric sources. Other renewable energy sources in the state include wood derived fuels, other biomass sources, and solar, thermal, and photovoltaic sources.
Kentucky produces the fifth-most coal of any state, and coal ranks as the state’s largest energy source, accounting for 72% of all electricity production in the state. The second major source of electricity in the state is natural gas, which accounts for 21.4% of the state’s power.

37. Missouri
> Electricity from renewables: 6.8% of total (5.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (2.9 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (55.7 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +4.1 ppt. (22nd lowest)
Only 6.8% of the 78.3 million MWh of electricity produced in Missouri in 2019 came from renewable sources. The state’s 500 wind turbines generated over half of all renewable energy. Much of the rest of the state’s renewable energy comes from hydropower plants.
The majority of electricity produced in Missouri comes from coal. Though the state has its own coal deposits, the coal it uses for electricity is lower sulfur content coal shipped in from Wyoming. Locally-mined coal is hotter burning and is primarily used for industrial production. Texas and Indiana are the only states that burn more coal than Missouri, and eight of the state’s 10 largest power plants are coal burning.
[in-text-ad-2]

36. Indiana
> Electricity from renewables: 7.1% of total (7.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (6.2 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (60.8 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +5.2 ppt. (22nd highest)
In Indiana, only 7.1% of the power supply comes from renewable sources, the largest of which is wind. The first utility-scale wind farm in the state came online in 2008, and now, wind turbines are spread across central Indiana.
As one of the largest coal-producing states in the country, Indiana’s power grid also relies primarily on coal. Indiana burns more coal than every other state except for Texas, and eight of the 10 largest power plants in the state are coal fired. In the last decade however, like many other states, the state has increased its usage of natural gas, and over that period, coal went from supplying 93% of the state’s electricity to 59%. Indiana has set a goal to derive 10% of its energy supply from clean sources by 2025.

35. Illinois
> Electricity from renewables: 8.2% of total (15.1 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (14.5 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Nuclear (98.7 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +6.3 ppt. (19th highest)
Only 8.2% of electricity production in Illinois comes from renewable sources — the largest of which is wind. Nearly all renewable energy generated in the state comes from wind turbines, while hydropower, biomass, and solar account for a very small share of total energy production.
Though not a renewable energy source, Illinois’s largest power supplier is not a carbon emitter either. Nuclear reactors generate nearly 100 million MWh electricity in Illinois, more than in any other state and over half of the state’s total power production. There are currently six nuclear power plants with a combined 11 reactors operating in the state. With high production capacity, Illinois exports about 20% of the electricity it produces to other states.
[in-text-ad]

34. Michigan
> Electricity from renewables: 8.5% of total (9.9 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (5.8 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (37.3 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +4.6 ppt. (25th highest)
Power plants in Michigan churned out 116.7 million MWh of electricity in 2019 — and only 8.5% of it was produced using renewable resources. Wind accounted for most of the state’s renewable energy generation, as Michigan has over two dozen wind farms, largely located in the eastern part of the Lower Peninsula.
The largest share of electricity in the state is produced in coal-fired power plants. Though Michigan has no active coal mines, it ships in coal from ports on the Great Lakes and by rail from a number of other states, including Colorado, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Wyoming. Natural gas-burning plants are also a major supplier to Michigan’s electrical grid.

33. Arkansas
> Electricity from renewables: 8.8% of total (5.7 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (4.1 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (23.3 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: -1.2 ppt. (4th lowest)
Like nearly every other Southern state, Arkansas has a relatively low share of its electricity coming from renewable resources, at 8.8%. The bulk of Arkansas’ renewable energy comes from hydroelectric sources, accounting for 6.4% of the state’s overall energy production. Also, the state uses wood and wood-derived fuels to produce 1.9% of its energy, more than double the comparable national share.
Coal and natural gas each account for over a third of electricity production in Arkansas. The share of the state’s electricity that comes from natural gas has expanded significantly from 2009 to 2019. Arkansas is one of just a handful of states with a lower share of its energy coming from renewable sources in 2019 than 10 years prior.

32. Georgia
> Electricity from renewables: 8.9% of total (11.5 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wood and wood derived fuels (5.1 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (58.6 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +4.2 ppt. (23rd lowest)
In Georgia, wood and wood-derived fuels account for 3.9% of electricity production, a larger share than in all but three other states. Of the 25 million acres of forest in the state, 24 million are available for commercial use. There are seven wood pellet manufacturing plants in the state that churn out 1.5 million tons of wood fuel per year. Accounting for hydropower, solar, and other biomass, renewable sources account for 8.9% of Georgia’s annual electricity production.
The state’s largest electricity source is natural gas, which accounted for 45.6% of electricity production in 2019. The state’s two nuclear power plants produced over one-quarter of Georgia’s electricity output that year.
[in-text-ad-2]
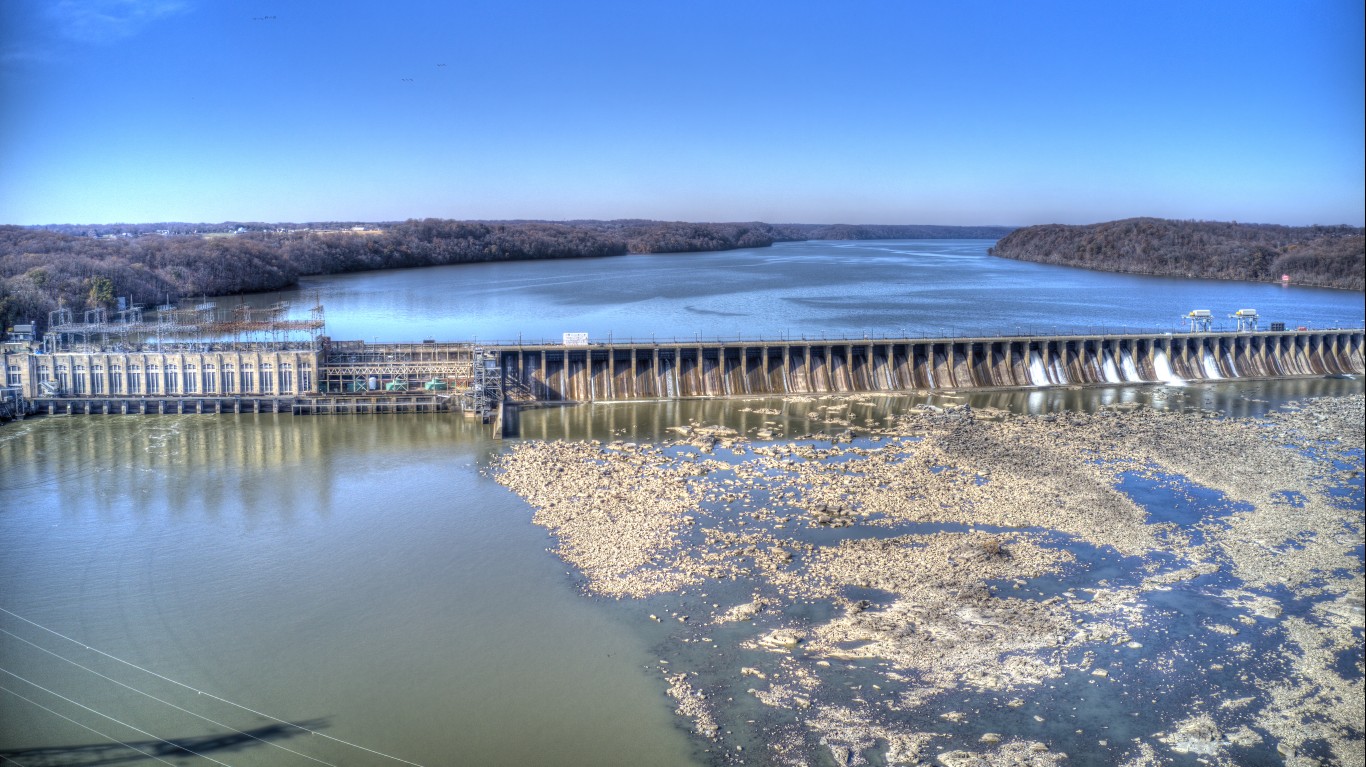

31. Maryland
> Electricity from renewables: 9.1% of total (3.6 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (2.2 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Nuclear (15.0 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +3.6 ppt. (21st lowest)
Maryland does not produce nearly enough power to meet demand, and as a result buys electricity from other states in the mid-Atlantic region. Still, through a variety of channels, the state generated 39.3 million MWh of electricity in 2019 — 9.1% of which came from renewable sources. Nearly half of renewable energy in the state comes from hydroelectric plants — one of which, the Conowingo plant on the Susquehanna River. The plant was the largest power plant ever built when it came online in 1928 and is still one of the largest in the state by output.
Nuclear power accounts for the largest share of power generation in Maryland, followed closely by natural gas. The state has one nuclear power plant with two reactors and, with a standing ban on hydraulic fracturing, it imports natural gas by pipeline from other states.

30. Wisconsin
> Electricity from renewables: 9.4% of total (5.9 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (2.6 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (26.3 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +3.2 ppt. (20th lowest)
Wisconsin is one of 21 states that gets less than a 10th of its total electricity from renewable sources. The state’s renewable energy supply includes several sources — 4.2% of the state’s energy production comes from hydroelectric, 3.0% from wind sources, 1.3% from wood fuel, and 0.8% from other biomass sources.
Though the use of coal power has waned in Wisconsin and the U.S. in recent years. Still, it remains as the largest source of electricity in the state, accounting for 26.3 million MWh, or 42.0%, of the state’s total electricity production.
[in-text-ad]

29. Alabama
> Electricity from renewables: 10.6% of total (15.1 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (11.4 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (57.2 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: -0.3 ppt. (9th lowest)
Despite being the 24th most populous state, Alabama produces the sixth most electricity, at 142.7 million MWh. This is due in part to the fact that the state’s large industrial sector requires a significant amount of power. The state ranks in the top 10 states for hydroelectric, wood-derived, natural gas, and nuclear energy electricity production.
In Alabama, 10.6% of the state’s electricity comes from renewable sources, lower than the majority of other states. Some 8.0% comes from hydroelectric sources, 2.3% from wood and wood-derived fuels, and 0.3% from solar thermal and photovoltaic sources.

28. Arizona
> Electricity from renewables: 10.8% of total (12.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (6.2 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (46.1 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +4.9 ppt. (23rd highest)
Renewable energy sources in Arizona accounted for 10.8% of electricity production in 2019. Nearly all renewable energy in the state comes from one of two sources: hydroelectric power plants and solar energy farms. One of the top solar energy producers in the nation, the state has a solar thermal power plant in Maricopa County and is also home to the nation’s largest solar PV plant in Yuma County. Additionally, the Glen Canyon Dam and the Hoover Dam on the Colorado River in northern Arizona are major producers of hydroelectricity.
The largest sources of electricity in Arizona are not renewable, however. In 2019, natural gas-burning plants supplied 40.6% of electricity produced in the state, and coal-burning power plants generated 20.4%.

27. Utah
> Electricity from renewables: 10.9% of total (4.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Solar thermal and photovoltaic (2.2 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (25.2 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +7.9 ppt. (17th highest)
Utah is one of just six states where solar thermal and voltaic sources account for a larger share of renewable energy sources than all others, at 5.6% of its total electricity production — the fifth highest share of all states. Hydroelectric and wind sources each supply more than 2% of the state’s energy
Utah produces more energy than it consumes, and sells some of its electricity to neighboring states. Though Utah accounts for just 2% of the nation’s coal production, coal provides 64.5% of the state’s electricity — a larger share than all but four other states.
[in-text-ad-2]

26. Hawaii
> Electricity from renewables: 12.1% of total (1.2 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (529,310 MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Petroleum (6.9 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +4.7 ppt. (24th highest)
Hawaii is by far the most petroleum-dependent state in the U.S. Over 70% of the state’s electricity comes from petroleum — no other state gets even 15% of electricity from that source. Located in the Pacific Ocean, the state must import the petroleum, making its electricity prices much higher than those of any other state.
However, Hawaii’s location does provide some advantages. The state has relatively high shares of its electricity supply coming from biomass sources, at 3.0%, and solar thermal and voltaic sources, at 2.8%. Hawaii also gets 5.4% of its electricity from wind sources.

25. Wyoming
> Electricity from renewables: 12.7% of total (5.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (4.2 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (35.4 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +5.7 ppt. (20th highest)
In Wyoming, 12.7% of electricity is produced from renewable sources. Wind accounts for the largest share of renewable energy production in the state.The state’s geography of mountains and prairie lands contribute to wind forces across the plains. Wind power will continue to expand in Wyoming as several wind farms are being developed, including a 900 turbine project in the south-central part of the state.
Despite increasing wind energy production, the bulk of electricity in the state comes from coal-fired power plants. Wyoming is home to over a third of recoverable coal reserves in operating mines in the U.S. and has six of the 10 largest coal mines in the country. Coal accounted for about 84% of electricity production in Wyoming in 2019.
[in-text-ad]

24. North Carolina
> Electricity from renewables: 12.7% of total (16.7 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Solar thermal and photovoltaic (7.5 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Nuclear (41.9 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +6.8 ppt. (18th highest)
North Carolina produces 12.7% of its electricity from renewable sources. The largest source of renewable energy in the state is solar thermal and voltaic sources, which accounts for 5.7% of energy production, the fourth highest share of any state in the country.
Renewable energy is taking up an increasingly larger share of North Carolina’s energy production. In 2009, renewable sources accounted for just 6.0% of the state’s energy production.

23. Tennessee
> Electricity from renewables: 13.9% of total (11.4 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (10.1 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Nuclear (35.7 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: -0.1 ppt. (10th lowest)
Renewable sources account for 13.9% of power production in Tennessee — and the vast majority of that energy comes from hydroelectric plants. The state is home to 28 hydroelectric power plants, the largest of which is the TVA Raccoon Mountain, a pumped storage plant that has been in operation for over four decades.
Tennessee relies most heavily on non-renewable sources. Coal and natural gas each account for a little over one-fifth of the state’s electricity production. The largest share, however, comes from nuclear power plants. There are two nuclear power facilities in the state that account for 43.4% of electricity production. The largest single power plant by capacity in Tennessee is the Cumberland facility, a coal-fired plant. However, the plant is not operating at full capacity and both nuclear plants generate more output than Cumberland.

22. Massachusetts
> Electricity from renewables: 15.6% of total (3.4 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Solar thermal and photovoltaic (1.2 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (15.4 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +9.4 ppt. (16th highest)
Massachusetts derives 15.6% of its electricity from renewable sources. Solar power accounts for 5.4% of electricity production, making the state one of only six where the largest renewable power source is solar thermal and photovoltaic. Hydropower and biomass each account for just over 4% of electricity production in the state as well. Increased renewable energy production will be critical for the state to reach its goal of net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.
Of all energy sources, natural gas is the largest source of electricity production in Massachusetts. The state also has the highest natural gas energy production capacity in New England.
[in-text-ad-2]

21. New Hampshire
> Electricity from renewables: 17.2% of total (3.1 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (1.5 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Nuclear (10.9 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +3.0 ppt. (19th lowest)
Hydropower, biomass, and wind account for 17.2% of electricity production in New Hampshire. Though the vast majority of electricity production in the state comes from non-renewable sources, New Hampshire still generates relatively little carbon emissions from its power plants.
Nuclear reactors are far and away the largest contributor to the state’s power grid. The largest power plant in New Hampshire is the Seabrook nuclear generating station, and nuclear reactors account for 60.5% of electricity production in the state.

20. Texas
> Electricity from renewables: 18.8% of total (90.9 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (83.6 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (255.6 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +13.2 ppt. (13th highest)
Energy production, namely oil and gas extraction, is an economic pillar in Texas. Yet the state is also one of the largest producers of electricity from renewable resources in the country. Nearly 19% of electricity production in the state comes from renewable sources, such as wind.
The largest contributor to the state’s electric grid, however, is natural gas. Texas is home to about a quarter of all U.S. natural gas reserves, and natural gas accounts for nearly 53% of electricity production in the state. Texas also has an estimated 9 billion tons of recoverable coal reserves and is the nation’s largest producer of lignite coal — a type used almost exclusively for electricity production. Coal generates about as much electricity in the Lone Star State as all renewable resources combined.
[in-text-ad]

19. Nebraska
> Electricity from renewables: 23.2% of total (8.7 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (7.2 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (20.4 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +20.6 ppt. (8th highest)
In Nebraska, renewable sources generate 23.2% of the state’s electricity. As is typically the case in Midwestern states, wind turbines are the largest renewable contributor to Nebraska’s energy grid. The second largest renewable source is hydro power, which accounts for 3.6% of electricity production.
Though not a major coal producer itself, Nebraska generates over half of its electricity from coal — nearly all of which is shipped in from Wyoming. The state also has one nuclear power plant in operation. The Cooper Nuclear Station along the Missouri River generates about 19% of Nebraska’s electricity.

18. New Mexico
> Electricity from renewables: 24.2% of total (8.5 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (6.9 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (14.7 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +19.5 ppt. (9th highest)
Renewable energy production has ramped up in New Mexico in recent years. A decade ago, renewables accounted for less than 5% of the state’s power grid, compared to 24.2% today. The increase was driven primarily by growing use of wind turbines, which now total 1,100 in the state and are the largest renewable electricity source.
While parts of New Mexico are ideal for utility-scale wind farms, the state is also rich in non-renewable resources that can be used in electricity production. New Mexico is home to about 3% of recoverable coal in the U.S. and over 5% of the nation’s natural gas reserves. Both of these resources are a significant part of New Mexico’s energy mix, but coal is substantially less important today than it has been in decades past. Today, coal accounts for 41.8% of electricity in the state, down from 90% in 1990.

17. Minnesota
> Electricity from renewables: 24.3% of total (14.5 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (11.0 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (17.8 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +10.0 ppt. (14th highest)
In Minnesota, renewable energy sources account for 24.3% of electricity production. Most renewable energy in Minnesota comes from wind turbines located in the prairies in the southwestern part of the state.
Other primary energy sources in Minnesota include coal and nuclear. The largest power plant in Minnesota is coal-fired, and the second largest is a nuclear power plant — one of the two in the state. Though coal use has been declining in the state, it still accounts for about 30% of electricity production. Nuclear accounts for about 24%.
[in-text-ad-2]

16. Colorado
> Electricity from renewables: 24.9% of total (14.0 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (10.9 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (25.3 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +14.8 ppt. (11th highest)
Nearly one-quarter of electricity generated in Colorado comes from renewable sources,the vast majority from wind. Hydropower and solar power also account for a small share of the state’s energy mix.
More than any renewable source, coal-burning power plants contribute the most to Colorado’s power grid. The state is a major coal producer and has both underground and surface mines. Demand for electricity often exceeds production in Colorado, and as a result, the state typically also buys power from nearby states like New Mexico and Wyoming.
15. Nevada
> Electricity from renewables: 28.4% of total (11.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Solar thermal and photovoltaic (4.8 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (25.8 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +17.1 ppt. (10th highest)
Nevada is one of only 15 states that derives over 25% of its electricity from renewable sources. Reliance on renewables in power generation is due in part to the state’s investment in solar power infrastructure. Between 2015 and 2019, solar electricity production tripled in Nevada. Hydro electricity also accounts for a significant share of Nevada’s energy mix, as the Hoover Dam, which sits on the Arizona border, powers hydro plants in both states.
Despite rapidly increasing renewable electricity production, natural gas accounts for the bulk of electricity production in the state. Nearly two-thirds of electricity produced in Nevada comes from natural gas — and eight of the state’s 10 largest power plants are natural gas burning.
[in-text-ad]

14. New York
> Electricity from renewables: 28.5% of total (37.5 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (30.6 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (47.6 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +4.4 ppt. (25th lowest)
Renewable power sources account for 28.5% of electricity production in New York state. The state is one of the top four producers of hydroelectricity in the country, as over one-fifth of its net power generation comes from hydro plants — the largest of which is the Robert Moses Niagara plant near Niagara Falls. New York also has about two-dozen wind farms, which, together, account for the bulk of the remaining renewable energy production in the state.
Though it is not a renewable energy source, nuclear power does not have the kind of carbon emissions that sources like coal or natural gas do. Just over a third of New York’s electricity was generated by nuclear power plants in 2019. That share will likely soon drop, however, as Indian Point, one of four nuclear plants in the state, closed a reactor in 2020 and is slated to stop its second reactor in 2021.

13. Alaska
> Electricity from renewables: 29.7% of total (1.8 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (1.6 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (2.7 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +9.8 ppt. (15th highest)
Though it is one of the top oil-producing states, nearly 30% of electricity generated in Alaska is from renewable sources — a larger share than in all but a dozen other states. Nearly all of Alaska’s electricity generated from renewable sources comes from hydroelectric plants. These plants are located largely in the southern part of the state in mountainous areas that tend to have high precipitation throughout the year.
The largest source of electricity in Alaska is natural gas-burning power plants. Alaska also derives about 15% of its electricity from petroleum, a larger share than nearly every other state.

12. North Dakota
> Electricity from renewables: 35.0% of total (14.4 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (11.2 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (25.2 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +21.9 ppt. (7th highest)
North Dakota is one of only 12 states where over a third of electricity is produced using renewable sources. The state’s largest renewable source and second largest overall electricity source is wind. Only three states generate more electricity through wind turbines than North Dakota.
Still, coal is the primary source of electricity in the state. Half of the 10 largest power plants in the state are coal fired. With a small population, North Dakota produces more electricity than it consumes, and as a result, it exports about half of the electricity it generates to other states in the region, including Minnesota, Montana, and South Dakota.
[in-text-ad-2]

11. Oklahoma
> Electricity from renewables: 39.1% of total (33.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (29.0 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (44.2 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +30.4 ppt. (3rd highest)
Nearly 40% or electricity produced in Oklahoma comes from renewable sources, a larger share than in all but 10 other states. Like many other states in the Great Plains region, Oklahoma’s power grid relies substantially on wind. Over one-third of all electricity in Oklahoma comes from wind alone, the third largest share among states. Hydro power also accounts for nearly 5% of electricity generation in the state.
Oklahoma is also home to many of the largest natural gas fields in the United States. And although the largest power plant in the state is coal fired, natural gas is Oklahoma’s largest source of electricity, accounting for over half of all annual production.

10. Kansas
> Electricity from renewables: 41.7% of total (21.2 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (21.1 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (17.3 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +35.5 ppt. (2nd highest)
Electricity production from renewable sources has surged in Kansas over the last decade. As recently as 2009, just 6.2% of electricity produced in the state came from renewable sources. As of 2019, the state was one of only 10 nationwide where over 40% of electricity production was from renewable sources.
As is often the case in Great Plains states, Kansas’s largest renewable power source is wind. The state has nearly 3,200 wind turbines, which generate 41.5% of its electricity, a larger share than in every other state except Iowa. After wind, the second largest source of electricity in the state is coal. Coal, a carbon-producing, non-renewable resource generates about one-third of the state’s electricity. Though the state does have coal reserves, its last coal mine was shuttered in 2016, and most of the coal now used to generate electricity is shipped in from Wyoming.
[in-text-ad]

9. Iowa
> Electricity from renewables: 43.6% of total (27.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Wind (26.3 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (22.2 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +27.1 ppt. (5th highest)
Many states in the Midwest have power grids that rely heavily on wind turbines — but none as much as Iowa. Of the 62.6 million MWh of electricity produced in the state in 2019, 42% was generated from wind. There are about 5,100 wind turbines in the state. Electricity production from other renewable sources in Iowa is relatively low.
Energy production from wind has ramped up considerably in Iowa in recent years — and 2019 was the first time that coal accounted for a smaller share of electricity generation — 35.4% — as wind in the state.

8. Montana
> Electricity from renewables: 44.7% of total (12.4 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (10.0 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (14.1 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +5.7 ppt. (21st highest)
Montana is home to about 30% of the nation’s recoverable coal deposits. Despite abundant non-renewable resources, the state derives nearly 45% of its electricity from renewable sources, more than all but seven other states. Far and away, the largest renewable energy source in Montana is hydro, followed by wind.
Still, six utility-scale coal-burning power plants generate about 51% of all electricity produced in Montana. With vast resources and a relatively small population, Montana consumes only about half of the electricity it produces. The rest is sold to other states — primarily Washington and Oregon.

7. California
> Electricity from renewables: 48.2% of total (97.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (38.4 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (85.8 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +22.1 ppt. (6th highest)
Nearly half — 48.2% — of electricity produced in California is from renewable sources. Though hydroelectric power plants account for the largest share of renewable power generated in the state, droughts in recent years have made hydroelectric output less predictable.
The state has been able to meet demand for electricity during drought years, in part, through increased production of solar energy. Electricity generated through solar panels now accounts for 14.0% of electricity production in the state. A decade ago, solar generated just 0.3% of electricity. No state reported a larger increase in solar electricity production over the last 10 years than California.
Still, meeting electricity demand in the country’s most populous state is no small task, and to do so, California also relies heavily on fossil fuels. Nearly 43% of the state’s electricity production comes from natural gas-burning power plants.
[in-text-ad-2]

6. Oregon
> Electricity from renewables: 62.2% of total (38.7 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (30.3 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (20.9 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: -3.6 ppt. (3rd lowest)
Of the 62.3 million MWh of electricity produced in Oregon in 2019, 62.2% came from renewable sources — making the state one of only six nationwide where half of all electricity is produced from renewables. Like many states that rely heavily on renewable energy, the largest share of electricity produced in Oregon is from hydroelectric plants. The four largest power plants in the state are hydroelectric plants on the Columbia River. As is the case with other states in the region, however, hydro production has dropped in recent years due to a drought.
Meanwhile, wind production in the state has increased substantially. There are now about 1,900 wind turbines in Oregon that generated 10.6% of the state’s electricity in 2019. A decade ago, wind accounted for only 6.1% of electricity production in Oregon.

5. Washington
> Electricity from renewables: 69.8% of total (74.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (66.0 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (15.7 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: -4.9 ppt. (2nd lowest)
In Washington, about 70% of electricity is produced through renewable sources. Though renewables account for a far larger than typical share of electricity production in the state, Washington’s reliance on renewable power production has fallen by nearly 5 percentage points in the last decade. The decline is due in part to a regional drought, which has resulted in reduced output in the state’s Grand Coulee Dam. The dam, which sits on the Columbia River, is one of the world’s largest hydroelectric plants.
Reduced hydroelectric production capacity has resulted in an increased reliance on wind, as well as natural gas, which is the state’s largest non-renewable source of electricity.
[in-text-ad]

4. South Dakota
> Electricity from renewables: 73.8% of total (10.7 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (7.9 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Coal (2.6 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +14.5 ppt. (12th highest)
In South Dakota, renewable sources, primarily hydropower, account for 73.8% of electricity production. Three of the largest power plants in the state are hydro plants located on the Missouri River. In total, hydropower accounts for nearly 55% of electricity production in the state. The second largest renewable power source in South Dakota is wind. There are more than 800 wind turbines in the state, generating nearly 20% of electricity production.
The largest non-renewable source in South Dakota’s energy mix is coal, followed by natural gas. Though the state has some recoverable coal reserves, those resources are not mined, and the coal used in electricity production is shipped in from other states, primarily Wyoming.

3. Idaho
> Electricity from renewables: 76.3% of total (14.1 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (10.3 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (4.3 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: -9.9 ppt. (the lowest)
More than three-quarters — 76.3% — of electricity in Idaho is produced from renewable sources, the third largest share of any state. Unlike most states, however, Idaho is less dependent on renewables now than it was 10 years ago, when a nation-leading 86.3% of its electricity was generated from renewable sources.
Hydroelectricity production, the largest renewable energy source in the state, has declined precipitously in 2009, due in large part to drought. Though wind production has picked up over the same period, the state now relies more heavily on natural gas than it has in the past.

2. Maine
> Electricity from renewables: 78.6% of total (8.2 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (3.5 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (1.8 million MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +28.8 ppt. (4th highest)
Nearly 80% of Maine’s electricity comes from renewable sources — and that renewable energy mix is highly diversified. About one-third of the state’s electricity comes from hydropower, about a quarter comes from wind, and one-fifth from wood. The bulk of the remainder of electricity production in Maine comes from natural gas-burning power plants.
Electricity production in Maine has changed considerably in recent decades. In the early 1990s, over 30% of electricity in the state was generated by the Maine Yankee nuclear power station. However, the plant was shuttered in 1997, and now Maine is one of 20 states that does not generate electricity through nuclear power.
[in-text-ad-2]

1. Vermont
> Electricity from renewables: 99.9% of total (2.3 million MWh)
> Largest renewable energy source: Hydroelectric conventional (1.3 million MWh)
> Largest non-renewable energy source: Natural gas (1,851 MWh)
> 10-yr. change in share of renewable energy: +73.6 ppt. (the highest)
Virtually all electricity in Vermont is generated through renewable sources. There are almost 50 hydroelectric plants throughout Vermont that account for over half of all in-state electricity production. The state also has five utility scale wind farms, which together generate 16.5% of all electricity.
As recently as 2009, nuclear reactors accounted for nearly three-quarters of all electricity production in the state. However, following the permanent closure of the Vermont Yankee Nuclear Power Station in 2014, natural gas accounts for the bulk of what little electricity is generated in the state from non-renewable sources.
Methodology:
To determine the states producing the most renewable energy, 24/7 Wall St. reviewed data on electricity generation by source in 2019 from the Energy Information Administration. States were ranked based on the electricity generated from renewable sources — which include conventional hydroelectricity, wind, wood and wood-derived fuels, other biomass, geothermal, and solar thermal and photovoltaic — as a percentage of electricity generated from all sources. Data on electricity from non-renewable sources and historical electricity data also came from the EIA. Data on the average sale price of electricity came from the EIA and is for 2019.
Data on population size used to calculate electricity generation per capita came from the U.S. Census Bureau’s Population and Housing Unit Estimates program and is for 2020. Supplemental data on educational attainment and median household income came from the Census Bureau’s American Community Survey and are for 2019.
Sponsored: Attention Savvy Investors: Speak to 3 Financial Experts – FREE
Ever wanted an extra set of eyes on an investment you’re considering? Now you can speak with up to 3 financial experts in your area for FREE. By simply
clicking here you can begin to match with financial professionals who can help guide you through the financial decisions you’re making. And the best part? The first conversation with them is free.
Click here to match with up to 3 financial pros who would be excited to help you make financial decisions.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.
 24/7 Wall St.
24/7 Wall St. 24/7 Wall St.
24/7 Wall St.




