
Fostering entrepreneurship has been the cornerstone of the U.S. economy and society from the country’s beginning. Many American businesses – those that began nearly 200 years ago as well as those that are barely a decade old – have expanded not only nationally but also globally. Names like Coca Cola, McDonald’s, Disney, and Apple are some of the most recognizable brands in the world.
But with global recognition came interest from companies abroad, and some of these iconic American brands are no longer in American hands. (Also see, these companies control over 50% of their industry.)
To find 25 classic American brands that are actually foreign-owned, 24/7 Wall St. reviewed data from various sources, with emphasis on company filings, sites, and press releases as well as financial media. After assembling an initial universe of some 50 brands, we used editorial discretion in choosing the final list with the aim of including the best-known, most iconic brands, as well as some of those you’d least expect to have foreign owners. (Our list is by no means comprehensive.)
Click here to see 25 classic American brands now owned by foreign companies.
Our list includes six companies that started in the 19th century, 12 companies born in the first half of the 20th century, another six companies that started later in the 1900s, and a relative newcomer from 2004.
The companies operate in diverse Industries, including food and drink, medicine, appliances, technology, oil and gas, pet food, even jewelry. It may be surprising to find that some of the brands on the list are foreign owned, but others, like Budweiser and Lucky Strike, made a big splash when they went to foreign hands. (These are the most valuable beer brands in the world.)
25. Alka-Seltzer
> Founded: 1931, launched by Miles Laboratory in Elkhart, Indiana
> Date first became foreign: 1978
> Current parent company: Bayer AG, Germany
> Product: Antacid
Alka-Seltzer was introduced in 1931, following reports that during the flu epidemic of 1928 a mixture of aspirin and baking soda was used to positive effect. Chemists at Miles Laboratories then created the antacid tablets – which include aspirin, sodium bicarbonate, citric acid, and flavoring agents in a form that reacts with water. The classic commercials of “Plop Plop, Fizz Fizz” followed, and Miles Laboratories sales soared.
In 1979, Bayer AG, at the time a big West German chemical company, offered to buy Miles in a deal worth $216 million, the New York Times reported. The iconic American brand, along with other Miles standbys, including One-a-Day and Flintstones vitamins, has been owned by Bayer since.
[in-text-ad]
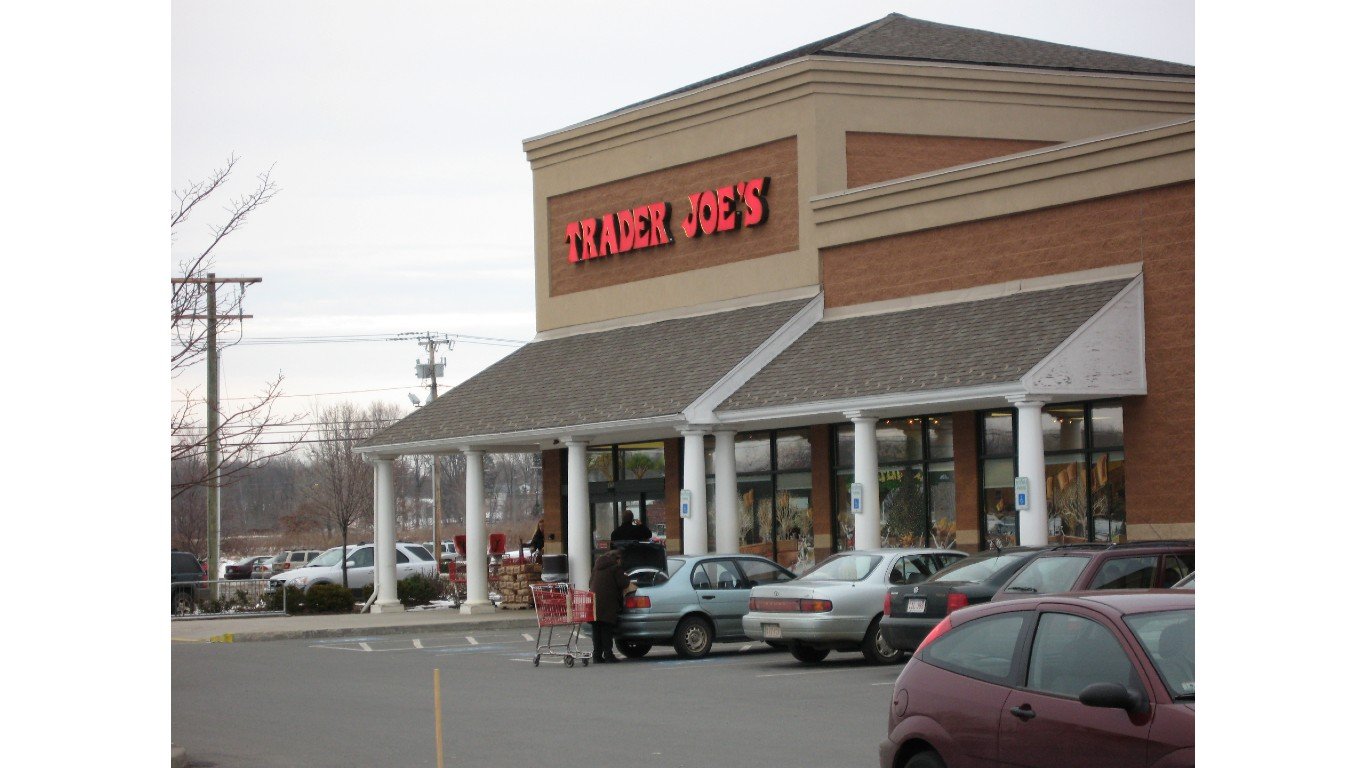

24. Trader Joe’s
> Founded: 1967, Pasadena, California
> Date first became foreign: 1979
> Current parent company: The Theo Albrecht family, Germany
> Product: Grocery store
The quirky grocery store chain that has almost a cult-like following is privately owned. As such, information is somewhat limited and we have largely relied on reported accounts. We know that founder Joe Coulombe (yes, there was an actual Trader Joe), who had launched a small chain of 7-Eleven competitors called Pronto Markets, opened the first Trader Joe’s in Pasadena, California, in 1967 with the aim of catering to the growing number of consumers that mainstream supermarkets were ignoring. In the 1970s, the chain began to capitalize on the health food craze, and developed an increasing number of private labels. It also sold bargain wines, eventually including the famous Two-Buck Chuck.
In 1979, Coulombe sold Trader Joe’s to the family of Theo Albrecht, who owned the German-based Aldi Nord grocery chain in Europe (not to be confused with the U.S.-operated Aldi Süd, owned by the family of Karl Albrecht, Theo’s brother.) According to the data company ScrapeHero, there are now 560 Trader Joe’s locations in 413 cities across 43 states and U.S. territories.

23. Citgo
> Founded: 1910, Bartlesville, Oklahoma
> Date first became foreign: 1986
> Current parent company: PDVSA, Venezuela
> Product: Gas stations
Citgo traces its beginnings to the founding of Cities Service Co. in 1910 by American businessman Henry L. Doherty. In 1965, Cities Service changed its name to Citgo. The company changed hands a number of times until in 1986, state-owned Petróleos de Venezuela, S.A. bought about 50% of Citgo, acquiring the other 50% in 1990.
Business had boomed during the 1990s, and oil revenue from PDVSA made up as much as half of Venezuela’s budget, according to the Washington Post. But political upheaval in the country and strained U.S.-Venezuela relations led to the Trump administration imposing additional sanctions, specifically on PDVSA, freezing its access to assets in the U.S. This may have contributed to the collapse of the country’s economy in 2019 and 2020, according to the Council of Foreign Relations. The Biden administration is considering easing some sanctions.
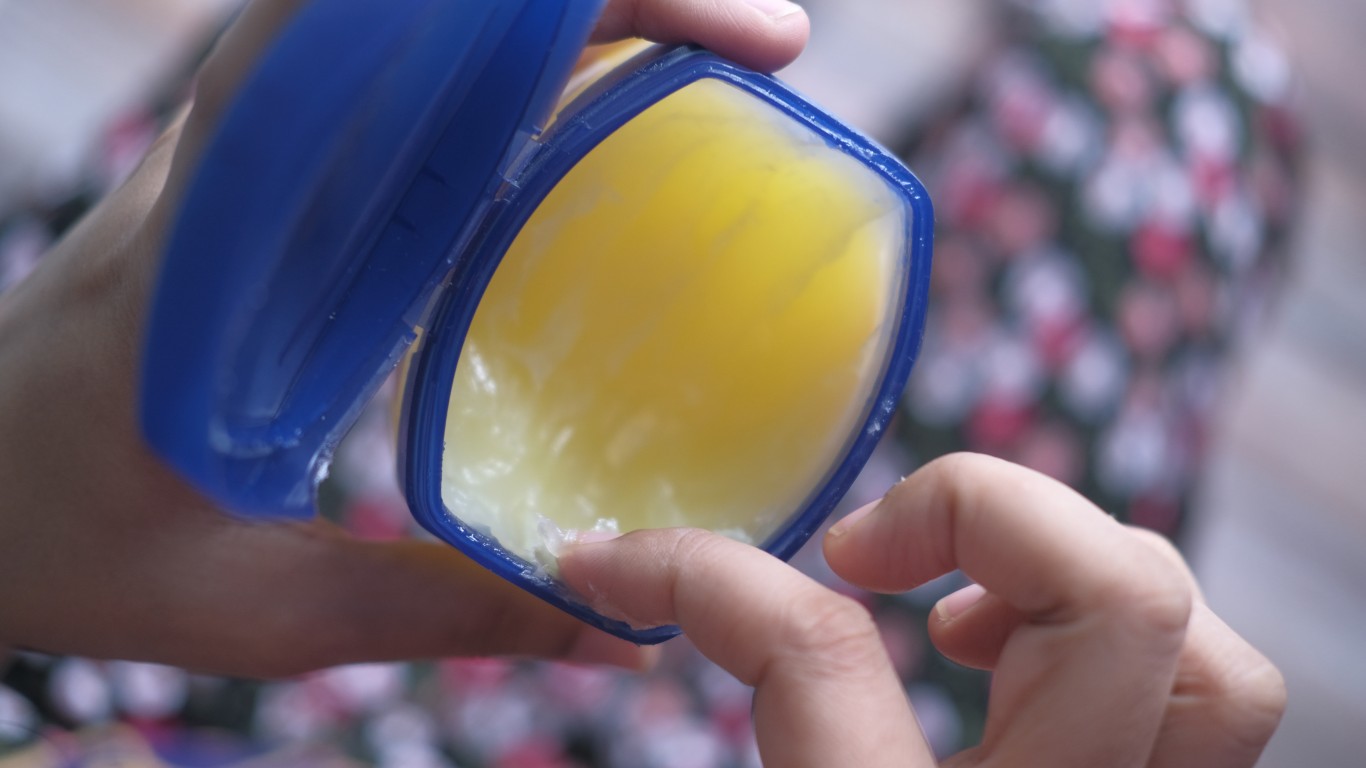

22. Vaseline
> Founded: 1870, Brooklyn, New York
> Date first became foreign: 1987
> Current parent company: Unilever, U.K.
> Product: Skin products
The Vaseline story begins in 1859, when young chemist Robert Augustus Chesebrough of Brooklyn discovers the skin-protecting properties of petroleum-based jelly on a trip to the oilfields of Pennsylvania. After years of testing extracting techniques, the brand was born in 1870. Soon, the product was selling across the U.S., and manufacturing and sales began in other countries as well.
In 1955, the Chesebrough Manufacturing Company acquired Pond’s Extract Company to become Chesebrough-Ponds, Inc., and in 1987, Unilever bought the company in a deal worth, $3.1 billion at the time, according to The New York Times.
[in-text-ad-2]

21. Firestone
> Founded: 1900, Akron, Ohio
> Date first became foreign: 1988
> Current parent company: Bridgestone Corporation, Japan
> Product: Tires
With its origin in 1900, Firestone has become a household name. The company was founded by Harvey Firestone in Akron, Ohio, growing from a small manufacturing plant to an enterprise with sales surpassing $1 million in 1906. In 1988, the Bridgestone Tire Company Ltd., founded in Japan in 1931, acquired what had become the Firestone Tire & Rubber Company in a $2.6 billion deal.
The company was involved in several large scandals – before and after its new ownership. In 1978, the company recalled 14 million Firestone 500 tires that caused at least 41 deaths through blowouts at high speeds. The company was also fined $500,000 for knowingly putting defective tires on the road. In 2001, the company recalled over 6 million of its tires, implicated in another 271 deaths.

20. Burger King
> Founded: 1954, Miami, Florida
> Date first became foreign: 1989
> Current parent company: Restaurant Brands International Inc., Canada; 3G Capital, Brazil and USA
> Product: Fast food
Burger King may not have the same deep roots as some of the other companies on the list, but it is without doubt a classic American brand. Founded in Miami in 1954, by 2013 it had become the world’s second largest fast food hamburger restaurant by the total number of restaurants (after McDonald’s), according to company filings. Still, the road has not been easy, and the company changed hands four times.
Burger King was sold in 1967 to Pillsbury, which in 1989 was acquired in turn by the U.K. spirits company Grand Metropolitan, now Diageo. Diageo sold Burger King to a group of American investors in 2002, which took Burger King public in 2006. In 2010, it was acquired by Brazilian investment firm 3G Capital and taken private. 3G announced a new deal in 2014, whereby Burger King would buy Canadian coffee and donut chain Tim Hortons, and form a new Canadian-based parent company named Restaurant Brands International. After unloading $3 billion worth of RBI shares in 1989, 3G Capital retained a 29% stake, according to an April proxy statement.
[in-text-ad]

19. Holiday Inn
> Founded: 1952, Memphis, Tennessee
> Date first became foreign: 1989
> Current parent company: IHG Hotels & Resorts, U.K.
> Product: Hospitality
Traveling with kids is never easy, and it was considerably more difficult – and expensive – before hotels such as Holiday Inn became the norm. In fact, that is what brought Kemmon Wilson, the founder of Holiday Inn, to create the chain back in 1952. At the time, hotels charged extra for his five children. He decided to build 400 family-friendly motels across the country, each within a day’s drive of each other, and each with standardized features, including no charge for kids under 12 that stayed with their parents. The chain quickly grew, expanding to Europe in the late 1960s.
In 1989, the renamed Holiday Corporation was purchased by U.K.’s Bass PLC, which paid Holiday’s shareholders $125 million in Bass stock and assumed about $2.1 billion of debt, according to the New York Times. Interestingly, the paper noted, Donald Trump was also interested in the hotels at the time. After a few iterations, Bass evolved into InterContinental Hotels Group (IHG), based on a chain originally developed by Pan Am founder Juan Trippe, in 2003.

18. 7-Eleven
> Founded: 1927, Dallas, Texas
> Date first became foreign: 1991
> Current parent company: Seven & I Holdings, Co., Japan
> Product: Convenience stores
7âEleven is another American brand nearly a century old that is actually foreign owned. The company can trace its origin to 1927, when John Jefferson Green began selling milk, bread, and eggs from an ice house. Though initially called Tote’m Stores, the name was changed to 7âEleven in 1946 to reflect the hours: 7 a.m. to 11 p.m., seven days a week. Today, the global brand claims to have more stores than any other retailer in the world – more than 81,000 across 18 countries.
Japanese company Ito-Yokado Co. acquired about 70% of Southland Corp., the operator of 7-Eleven, in 1991 in a $430 million deal. Following a reorganization where Ito-Yokado became part of Seven & I Holdings, it bought the remaining 27% of 7-Eleven in 2005 in a $1 billion deal.

17. Gerber
> Founded: 1927, Fremont, Michigan
> Date first became foreign: 1994
> Current parent company: Nestlé, Switzerland
> Product: Baby food
“Gerber is deeply saddened by the passing of Ann Turner Cook, the original Gerber baby, whose face was sketched to become the iconic Gerber logo more than 90 years ago,” the company announced in June 2022. Cook was 95 years old, and her face began adorning the brand in 1928. It became Gerber’s trademark in 1931.
It was Fremont Canning Company that began making Gerber baby food in 1927, growing it rapidly into a national brand. In 1994, Swiss pharmaceuticals company Sandoz A.G. completed the $3.7 billion acquisition of Gerber Products Company. Sandoz later became part of Novartis, which then sold the brand to Nestlé for $5.5 billion in 2007.
[in-text-ad-2]

16. Lucky Strike
> Founded: 1871, Richmond, Virginia
> Date first became foreign: 1994
> Current parent company: British American Tobacco PLC, U.K.
> Product: Tobacco
The Lucky Strike Cigarettes company was founded in Virginia in 1871. At the turn of the century, American Tobacco Company acquired the brand. The North Carolina company was one of the first to implement cigarette-manufacturing machines. During its heyday, through the first half of the 20th century, Lucky Strike was one of the top-selling tobacco brands in the country. In 1994, British American Tobacco PLC acquired the American Tobacco Company and all its subsidiaries for $1 billion, getting the Lucky Strike brand in the deal.
In 2017, Reynolds American – parent of the R. J. Reynolds Tobacco company, which was founded by its namesake in Virginia in 1875 – was also acquired by British American Tobacco, for $49.4 billion.
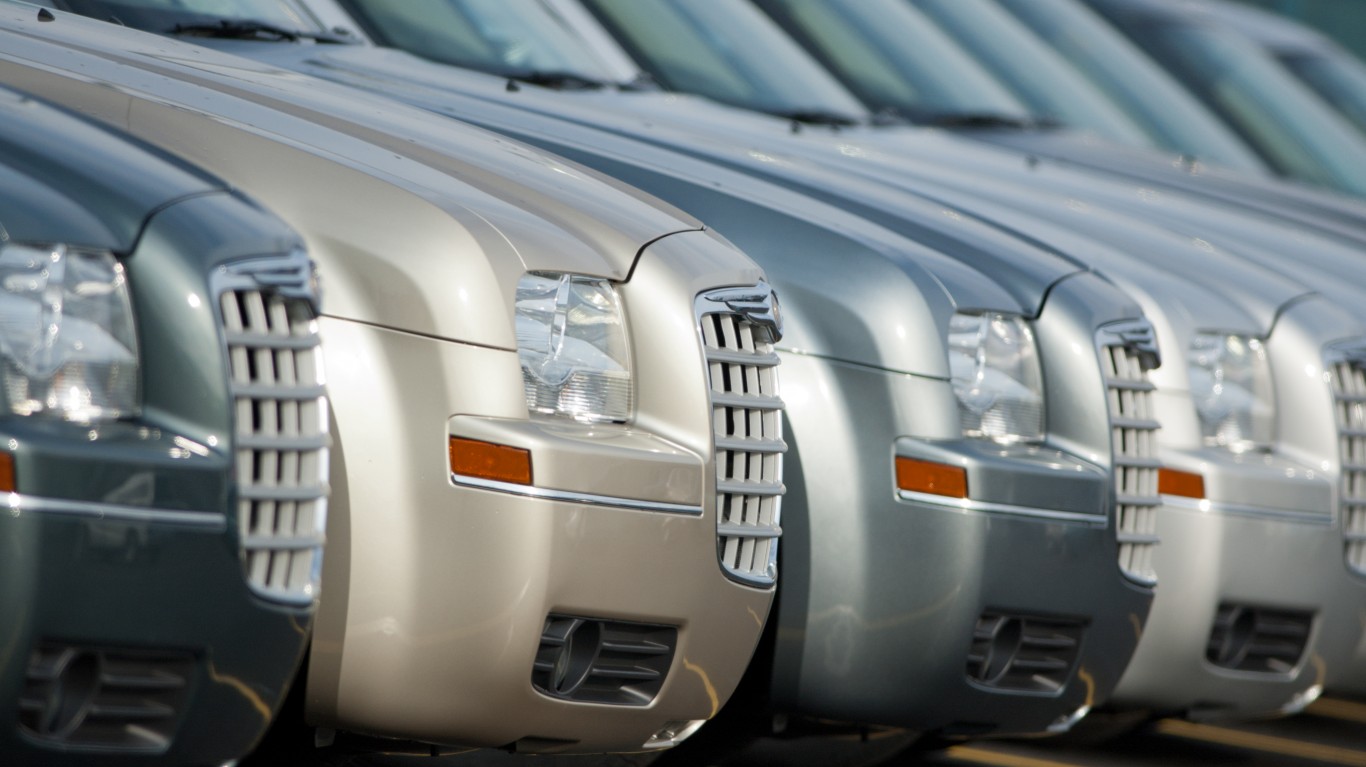

15. Chrysler
> Founded: 1925, Detroit, Michigan
> Date first became foreign: 1998
> Current parent company: Stellantis N.V., Netherlands
> Product: Autos
One of the Big Three American automakers, Chrysler was founded in 1925, but it has had a tumultuous history. In fact, it needed to be bailed out twice, in 1979 and 2008. In between, in 1998, Daimler-Benz of Germany acquired the car company, and it became DaimlerChrysler. It was the first time Chrysler was under foreign ownership.
The company returned to American hands when Daimler-Benz sold the company to investment fund Cerberus Capital Management in 2007. One of the parties involved in Chrysler’s second bailout deal, Italy’s Fiat S.p.A., gradually acquired the other parties’ shares, and the company in 2014 became Fiat Chrysler Automobiles, with a dual headquarters in Italy and the U.S. Following the 2021 merger of French company Peugeot S.A. with the Italian-American company, Stellantis N.V., which is headquartered in the Netherlands, was created.
[in-text-ad]

14. Hellmann’s
> Founded: 1913, New York, New York
> Date first became foreign: 2000
> Current parent company: Unilever, U.K.
> Product: Condiments
Though he did not invent the condiment, Richard Hellmann, a German immigrant, began selling his own mayonnaise in glass jars in his delicatessen in New York City as early as 1913. In 1927, Postum Cereal Company (which became General Foods) bought the Hellmann’s brand and later Best Foods. Together, the two brands of mayonnaise had a commanding market share.
Unilever bought the brand from the new iteration of the company, Bestfoods, in 2000 in a deal worth $20.3 billion. (Bestfoods also owned Skippy peanut butter, though it returned to American hands when Hormel Foods bought the brand from Unilever in 2013.) Hellmann’s had a 50% share of the U.S. mayonnaise market as of 2017.

13. Ben & Jerry’s
> Founded: 1978, Burlington, Vermont
> Date first became foreign: 2000
> Current parent company: Unilever, U.K.
> Product: Ice cream
The Ben & Jerry’s story began in 1978, when school friends Ben Cohen and Jerry Greenfield opened their first ice cream parlor in Burlington, Vermont, in time competing in the superpremium ice cream market. The quirky brand grew until it attracted the attention of London-based Unilever, which bought it in 2000 for $326 million.
When Unilever bought Ben & Jerry’s, it already owned several other American ice cream brands, including Popsicle, Good Humor, Breyers, and Klondike. All are still part of Unilever’s arsenal of ice cream brands, as the conglomerate continues to scoop up frozen dessert companies all over the world.
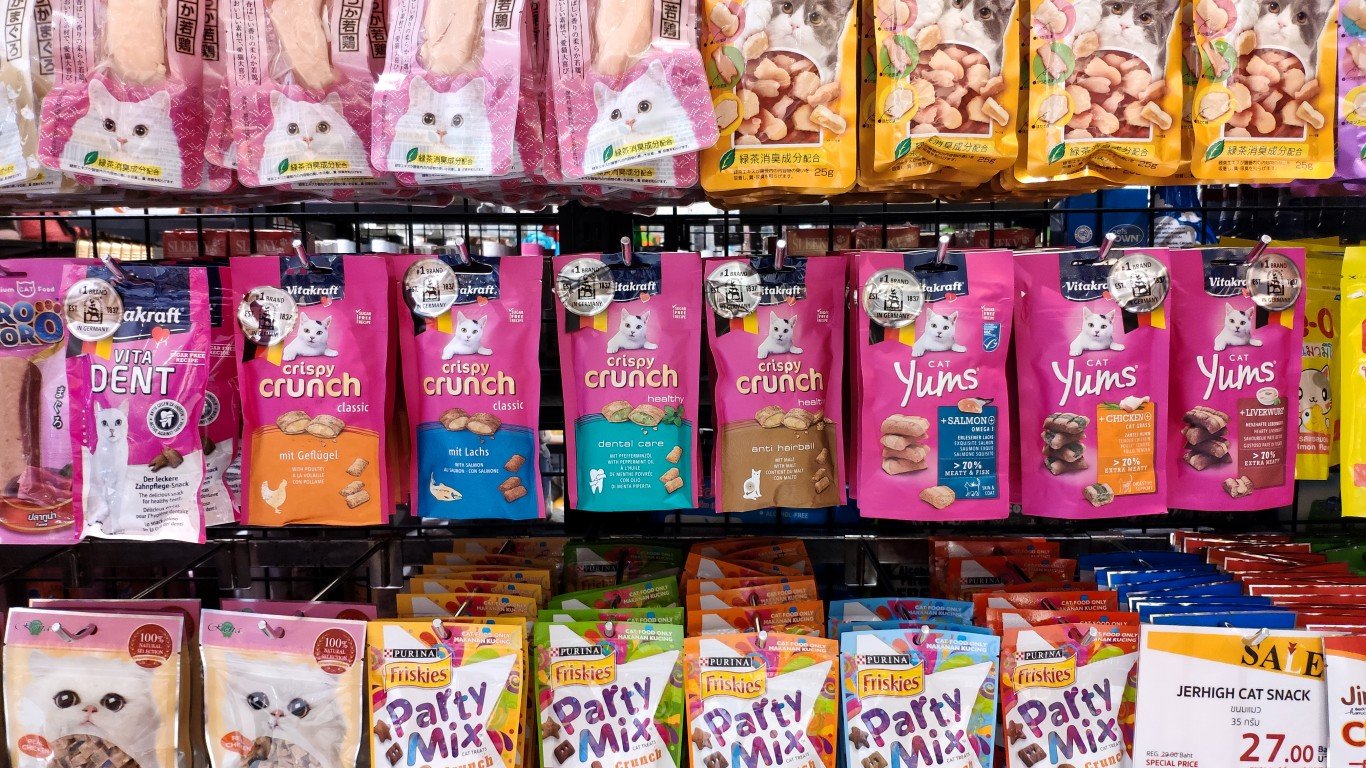

12. Purina
> Founded: 1894, St. Louis, Missouri
> Date first became foreign: 2001
> Current parent company: Nestlé, Switzerland
> Product: Pet food
In 1894, William H. Danforth, George Robinson, and William Andrews founded The Robinson-Danforth Commission Company, an animal food production company – the first company in the world to offer such products commercially, the company claims. The name was changed to Ralston Purina in 1902. The animal feed side of the business, Purina Mills, was sold to British Petroleum in 1986, but it returned to American ownership and is now part of Land O’Lakes.
The pet food side, however – Ralston Purina – was sold to Nestlé in 2001 in a $10.3 billion deal to form Nestlé Purina PetCare Company. The Swiss company also owns Gerber (No. 17). (General Mills acquired Ralston Purina’s breakfast cereal business in 1997.)
[in-text-ad-2]

11. John Hancock Life Insurance
> Founded: 1862, Massachusetts
> Date first became foreign: 2004
> Current parent company: Manulife Financial Corporation, Canada
> Product: Insurance
In what some might find ironic, the company named in honor of American Founding Father John Hancock is in Canadian hands. Not only that, but John Hancock is one of the oldest American companies, having been founded 160 years ago in 1862, a few years before Canada’s confederacy.
Still, in 2003, not long after John Hancock Financial Services was listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol JHF in 2000, Manulife Financial Corporation offered a nearly $11 billion all-stock takeover. The deal was completed in 2004.
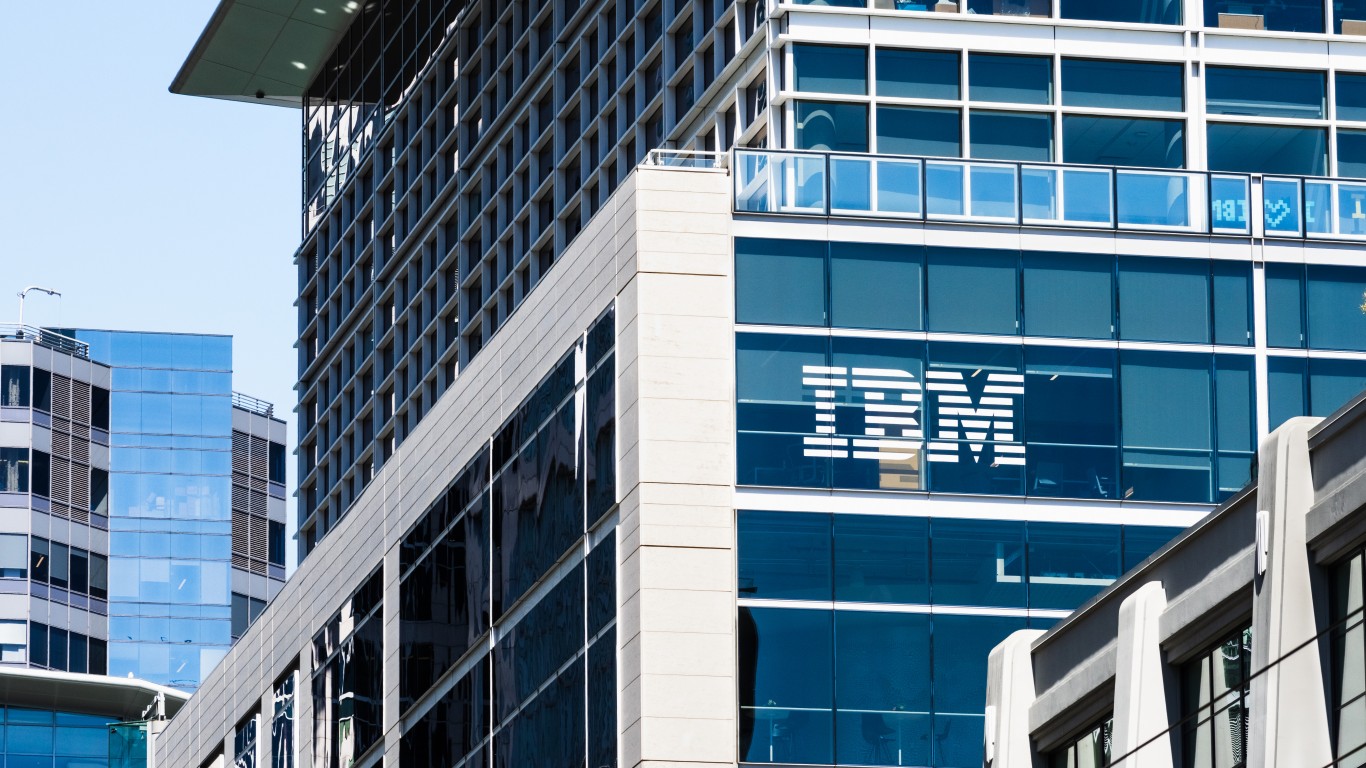

10. IBM PC
> Founded: 1981, New York City
> Date first became foreign: 2005
> Current parent company: Lenovo, China
> Product: Computers
IBM was founded in New York City in 1911 as the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (C-T-R), though two of C-T-R components can be traced further back, to the late 1880s. The company was renamed International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) in 1924. IBM grew quickly, establishing itself as the leader in business and scientific computing and helping to revolutionize computing.
The first IBM personal computer was introduced in 1981. The company was an integral part of the PC revolution, which helped shape the way we approach technology today. By 2004, IBM’s business had changed and it sought to divest the PC business. China’s Lenovo offered $1.75 billion at the time, and the deal closed in 2005.
[in-text-ad]

9. Hoover US
> Founded: 1908, North Canton, Ohio
> Date first became foreign: 2007
> Current parent company: Techtronic Industries, Hong Kong
> Product: Floor care (vacuums)
In 1908, visionary entrepreneur W. H. “Boss” Hoover took a risk and purchased a patent for the “electric suction sweeper,” even though fewer than 10% of U.S. homes had electricity, according to the Hoover Foundation. Sales soon soared and the company over the years changed hands from Maytag to Whirlpool Corporation to Techtronic Industries Co. Ltd. (TTI) of Hong Kong, which acquired Hoover in 2007. (Maytag had already sold Hoover Europe to Italian Candy SpA in 1995.)
TTI owns other American brands, including power equipment manufacturer Homelite Corporation, which it acquired in 2002; vacuum brand Dirt Devil, which it purchased in 2003; and Milwaukee Electric Tools, which it has owned since 2005, among others.

8. Greyhound Lines
> Founded: 1914, Hibbing, Minnesota
> Date first became foreign: 2007
> Current parent company: FlixMobility (parent of Flixbus), Germany
> Product: Transportation
After getting fired from the mines, Swedish immigrant Carl Eric Wickman unsuccessfully launched a car dealership business. But refusing to stay down, Wickman started driving passengers between the mining towns of Alice and Hibbing, Minnesota, in the lone car he owned – and Greyhound was born. Today, the bus line serves 2,400 destinations across North America alone.
Over the years, Greyhound also went through some turbulent times, filing for bankruptcy and changing hands several times. In 2007, it first became foreign-owned, when Britain’s bus company FirstGroup Plc bought Laidlaw International Inc., the owner of Greyhound at the time, in a $3.4 billion deal. In 2021, FirstGroup unloaded the intercity coach service to FlixMobility, parent of FlixBus, for an enterprise value of about $46 million.

7. Budweiser
> Founded: 1852, St. Louis, Missouri
> Date first became foreign: 2008
> Current parent company: Anheuser-Busch InBev, Belgium
> Product: Beverages
Though it was not yet owned by its eventual namesakes, Eberhard Anheuser and Adolphus Busch, Anheuser-Busch can trace its origin to a brewery that opened in 1852 in St. Louis. It was more than two decades until Budweiser was introduced to the American consumer, in 1876. The company greatly expanded in the 20th century, becoming the world’s largest brewer, a position it held until 2004. The brand remains popular in the U.S. with the light version the most shipped beer in 2020.
Consolidation in the industry led to the merger of Brazil’s AmBev and Belgium’s Interbrew to form InBev, which was to be headquartered in Brussels. The new company displaced Anheuser-Busch to become the world’s largest brewer. It was to become even larger when Anheuser-Busch agreed to sell itself to InBev in a $52 billion deal in 2008.
[in-text-ad-2]
6. Forbes
> Founded: 1917
> Date first became foreign: 2014
> Current parent company: Integrated Whale Media Investments, China
> Product: Publishing
By the time B.C. Forbes launched his namesake publication in 1917, he was already a renowned business writer. Though he believed in capitalism, he stated in the first issue of Forbes, “Business was originated to produce happiness, not to pile up millions.” It took some time – until 1982 – for the magazine to begin its famous ranking of richest Americans.
The business remained family controlled until 2014, when Forbes Media LLC announced that the Forbes family had sold a majority stake in the company to a Hong Kong investor group, Integrated Whale Media Investments, for more than $300 million, according to The Wall Street Journal. The deal valued the entire company at $475 million, The Forbes family was to retain minority ownership.

6. Motorola Mobility
> Founded: 1928, Chicago, Illinois
> Date first became foreign: 2014
> Current parent company: Lenovo, China
> Product: Consumer electronics (smartphones)
In 1928, two brothers incorporated Motorola’s founding company. One of the first products was the Motorola car radio, as founder Paul V. Galvin created the brand, linking “motor” (for motorcar) with “ola” (which implied sound), meant to convey sound in motion. In 1947, the company became Motorola, Inc., and in 1983, it introduced the world’s first commercial handheld cellular phone, the Motorola DynaTAC phone.
In 2011, Motorola, Inc. separated into two independent companies: Motorola Solutions, Inc., which served enterprises and government customers, and Motorola Mobility, Inc., which made mobile cellular devices and cable video management equipment. The latter was acquired by Google for $12.5 billion in 2011 and subsequently sold to Lenovo in 2014 for $2.9 billion. Lenovo also bought IBM PC (No. 10)
[in-text-ad]
4. GE Appliances
> Founded: 1907, Schenectady, New York
> Date first became foreign: 2016
> Current parent company: Haier, China
> Product: Appliances
In 1889, the company that Thomas Edison founded joined with two others to form Edison General Electric. The storied conglomerate, which would end up owning businesses in diverse industries, patented the first electric fan in the 1890s, and by 1905 was making electric refrigerators, irons, and sewing machines. It began manufacturing a line of cooking appliances in 1907.
But GE has been shifting its focus over time from traditional businesses such as appliances to higher-technology areas such as medical equipment and clean energy. It sold GE Appliances to Chinese home appliance maker Haier Group for $5.6 billion in 2016.

3. Popeyes
> Founded: 1972, New Orleans, Louisiana
> Date first became foreign: 2017
> Current parent company: Restaurant Brands International Inc., Canada; 3G Capital, Brazil and USA
> Product: Fast food
Founder Alvin C. Copeland Sr. opened the first Popeyes (named after detective “Popeye” Doyle of “The French Connection”) in the New Orleans suburb of Arabi in 1972, serving spicy, New Orleans-style chicken. By 1985, Popeyes opened its 500th restaurant, expanding internationally as well, and by 2011 it opened its 2,000th location.
Already the owner of American brand Burger King (see No. 20), Restaurant Brands International Inc. agreed in February 2017 to buy Popeyes Louisiana Kitchen Inc. for $1.8 billion. The deal closed two months later. At the time of the deal, Popeyes had more than 2,600 locations, most in the U.S. 3G Capital has a 29% stake of RBI, according to an April proxy statement.

2. Tiffany & Co.
> Founded: 1837, New York, New York
> Date first became foreign: 2021
> Current parent company: LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton, France
> Product: Jewelry
The oldest company on the list has relatively recently changed hands to foreign owners. The iconic brand dates back to 1837, when Charles Lewis Tiffany and his partner, J. B Young, opened a “stationery and fancy goods” store on Broadway in New York. Tiffany took control of the company in 1853 and renamed it Tiffany & Co. The company flourished, becoming one of America’s most iconic brands and arguably the world’s most famous jeweler.
Over 180 years after its beginning, France’s LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton, the world’s largest luxury goods company, agreed to buy Tiffany in a $16.2 billion deal, the largest ever in the luxury sector. The deal was to close in the middle of 2020, but then the COVID-19 pandemic hit and a dispute between the two companies ensued. In October that year, the two companies agreed to a reduced value, $15.8 billion, and the deal closed in January 2021. Interestingly, 2021 was reportedly a year of record-breaking growth for Tiffany, benefiting the new owners.
[in-text-ad-2]

1. GrubHub
> Founded: 2004, Chicago, Illinois
> Date first became foreign: 2020
> Current parent company: Just Eat Takeaway.com N.V., Netherlands
> Product: Food delivery
Though it may now seem like online food ordering was always around, especially throughout the pandemic, it is a very young business. And the youngest company on the list, GrubHub, has managed to build a recognizable brand in its relatively short existence.
Two web developers founded the company in 2004 to create an alternative to paper menus. Through funding and acquisitions in the budding business of online food ordering, the company debuted its platform in 2012. A year later, in 2014, GrubHub went public. In April 2020, Just Eat Takeaway.com agreed to buy Grubhub for $7.3 billion. The deal closed in June 2021. Since April 2022, however, there have been reports Just Eat Takeaway.com is looking to sell GrubHub at a much lower price.
Sponsored: Want to Retire Early? Here’s a Great First Step
Want retirement to come a few years earlier than you’d planned? Or are you ready to retire now, but want an extra set of eyes on your finances?
Now you can speak with up to 3 financial experts in your area for FREE. By simply clicking here you can begin to match with financial professionals who can help you build your plan to retire early. And the best part? The first conversation with them is free.
Click here to match with up to 3 financial pros who would be excited to help you make financial decisions.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.
 24/7 Wall St.
24/7 Wall St.
 24/7 Wall St.
24/7 Wall St.


