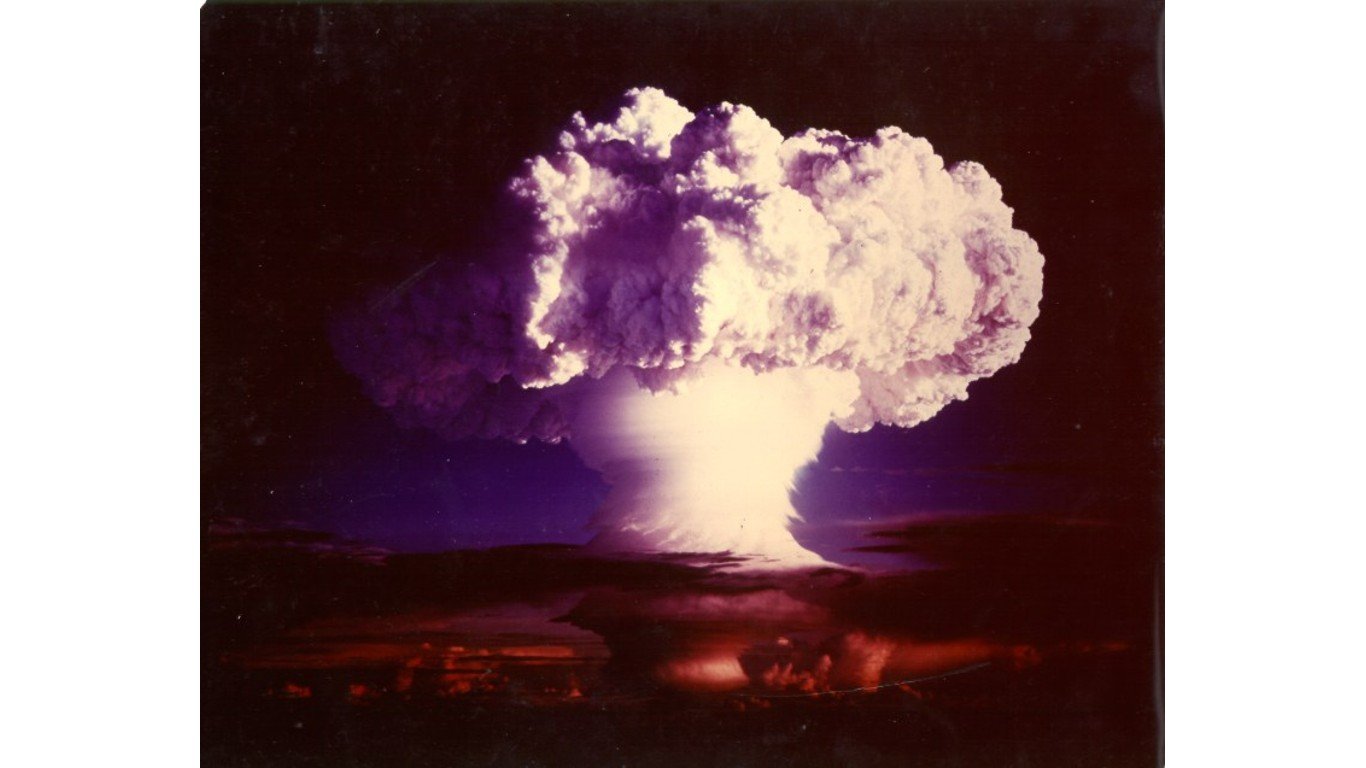

There are about 9,600 locked and loaded, or stockpiled, nuclear warheads in the world, more than 90% of them held by Russia and the United States, according to the Federation of American Scientists. And if the global supply of nukes were evenly detonated above the world’s large cities, the blasts would instantly kill 3 billion people, a recent report in Popular Mechanics estimates.
While today’s global stockpile of nuclear weapons has enough firepower to inflict staggering death tolls, today’s nukes are not even close to the most powerful ever developed. (This is what a nuclear war would do to the world.)
To determine the most powerful nuclear weapons ever built, 24/7 Wall St. reviewed data from defense industry news source Army Technology. Weapons were ranked on their explosive power in megatons – equivalent to the power of 1 million tons of TNT.
To get an idea of the difference in scale, the biggest human-made explosion was set off by the Soviet Union’s RDS-220, or Tsar Bomba, on Oct. 30, 1961. The Tsar Bomba, a 50-megaton hydrogen bomb yielding the equivalent of 50 million tons of TNT, was detonated in a test over an Arctic Ocean island. By comparison, the nuclear bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945 measured 15 kilotons and 25 kilotons, respectively, equivalent to 40,000 tons of TNT combined. (This is the country with the most nuclear weapons.)
The nuclear payloads of modern intercontinental ballistic missiles are typically measured in hundreds of kilotons, not in multiple megatons. The last of these super nukes was the B53, retired by the United States in 1997.
Nuclear weapons today may be less powerful than their predecessors, but they can be launched more easily, riding on the noses of high-speed missiles that can be launched from land or sea. Submarine-based nuclear ballistic missiles are particularly effective deterrents because they are more difficult to target than land-based sites.
Some of these nuclear warheads can hit any target in the world within 30 minutes, giving little or no warning to the populations living in the strike zones of these weapons.
Here are the most powerful nuclear weapons ever built

10. Mk-14 / TX-14
> Power: 6.9 megatons
> Circa: 1952-1956
> Country: United States
[in-text-ad]

9. Mk-16 (TX-16/EC-16) nuclear bomb
> Power: 7 megatons
> Circa: 1953-1954
> Country: United States
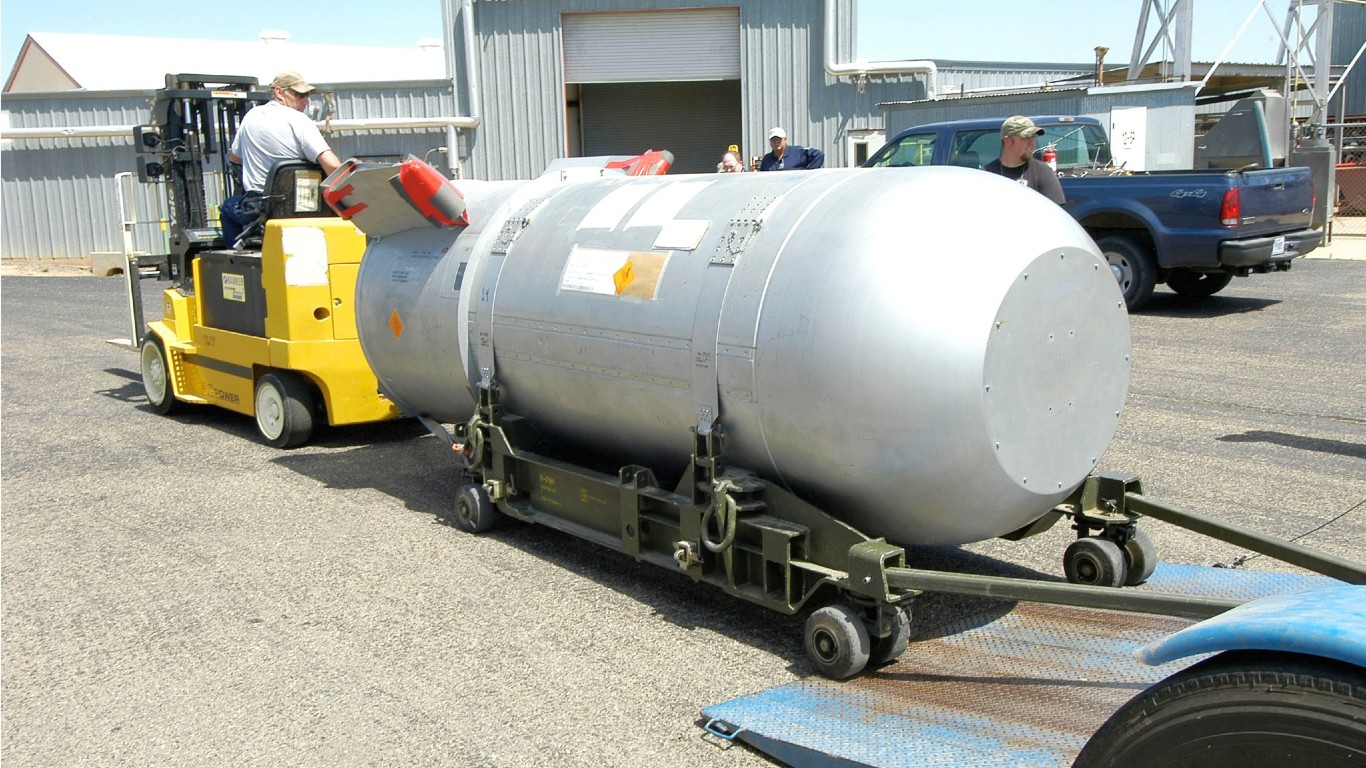

8. B53 (Mk-53)
> Power: 9 megatons
> Circa: 1997
> Country: United States
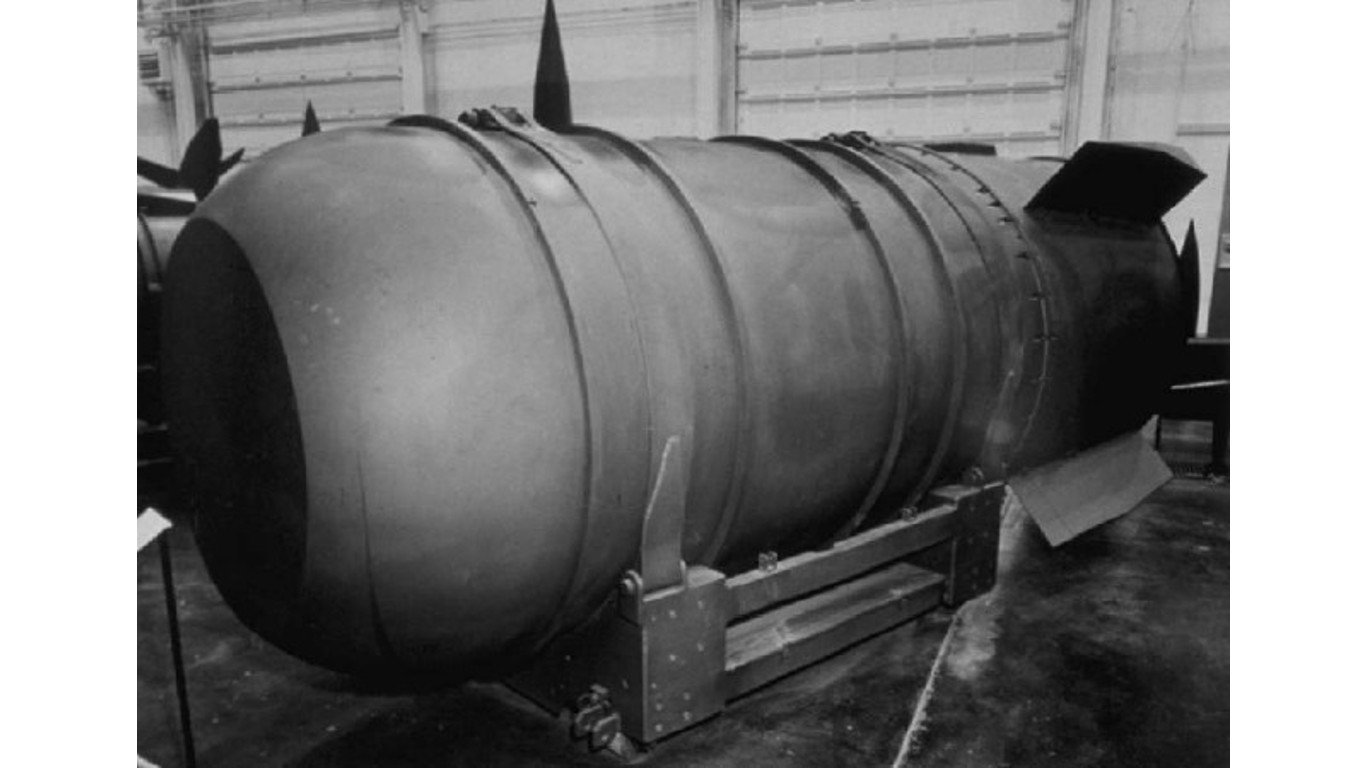

7. Mk-36 nuclear bomb
> Power: 10 megatons
> Circa: 1956-1962
> Country: United States
[in-text-ad-2]

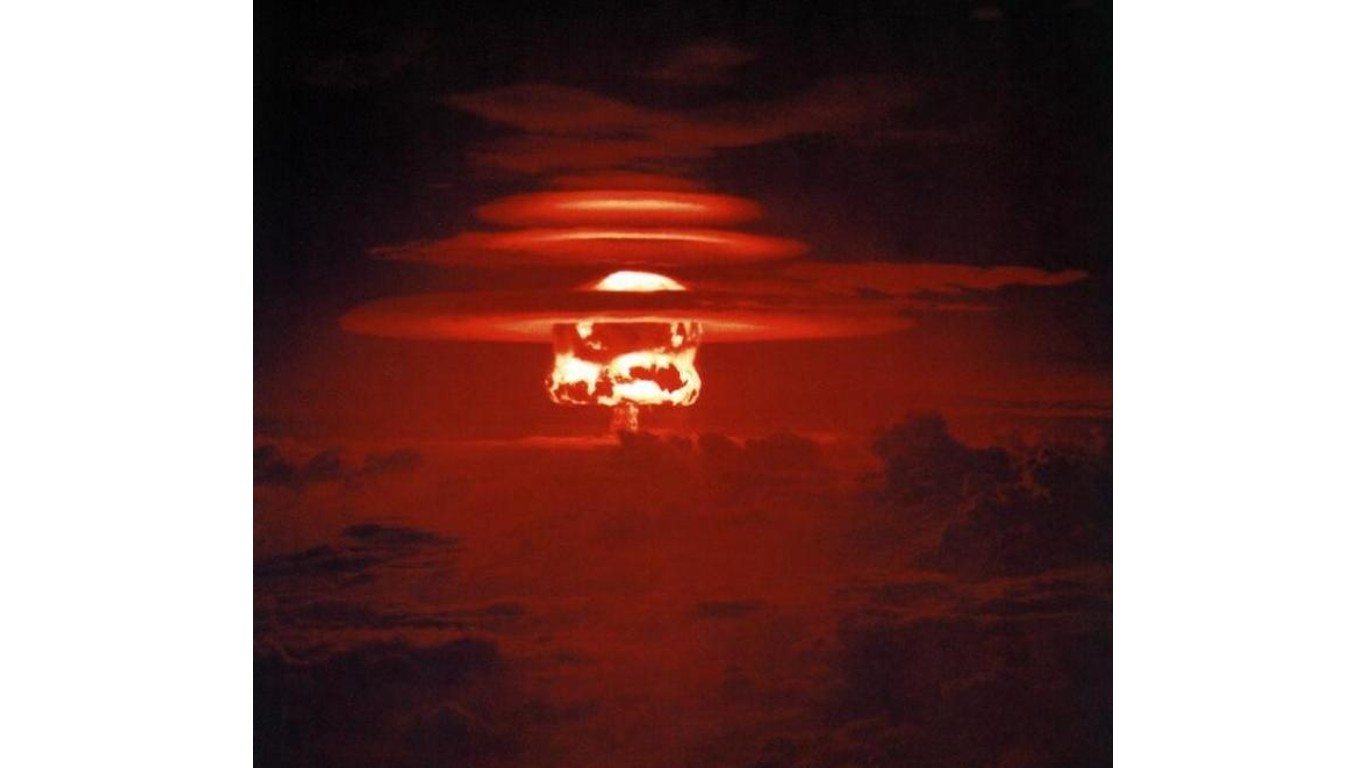
6. Ivy Mike H-Bomb
> Power: 10.4 megatons
> Circa: 1951
> Country: United States

5. MK 24/B-24
> Power: 10 to 15 megatons
> Circa: 1954-1956
> Country: United States
[in-text-ad]
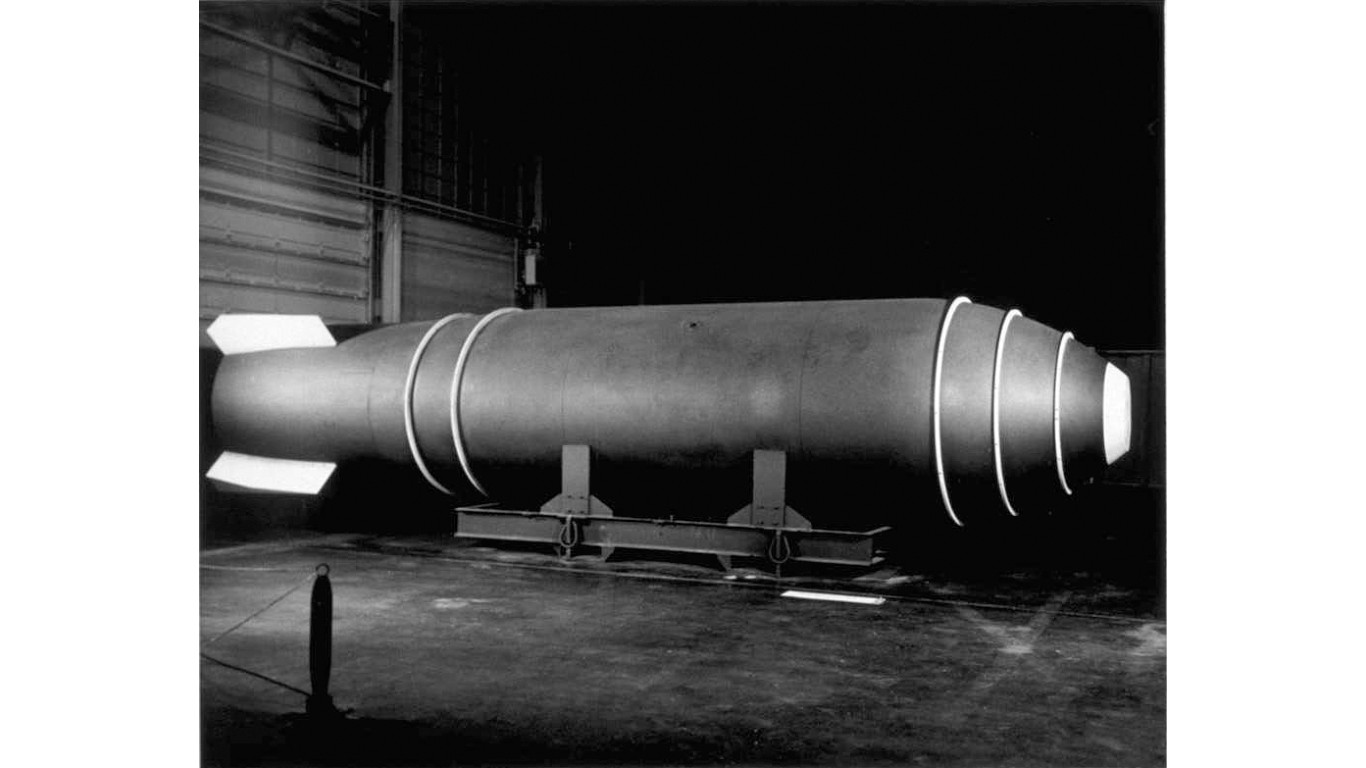
4. Mk-17/EC-17
> Power: 10 to 15 megatons
> Circa: 1955-1957
> Country: United States
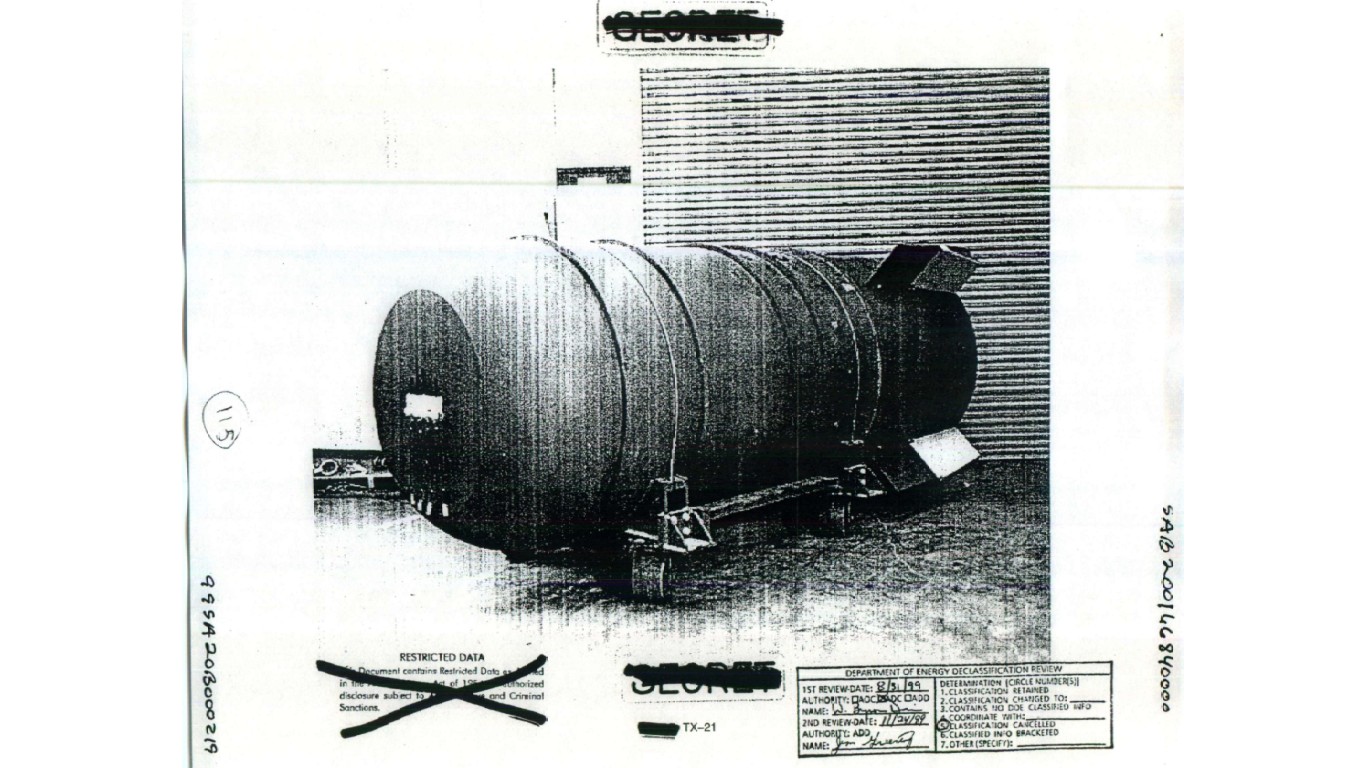
3. TX-21 “Shrimp” (Castle Bravo)
> Power: 14.8 megatons
> Circa: 1954
> Country: United States
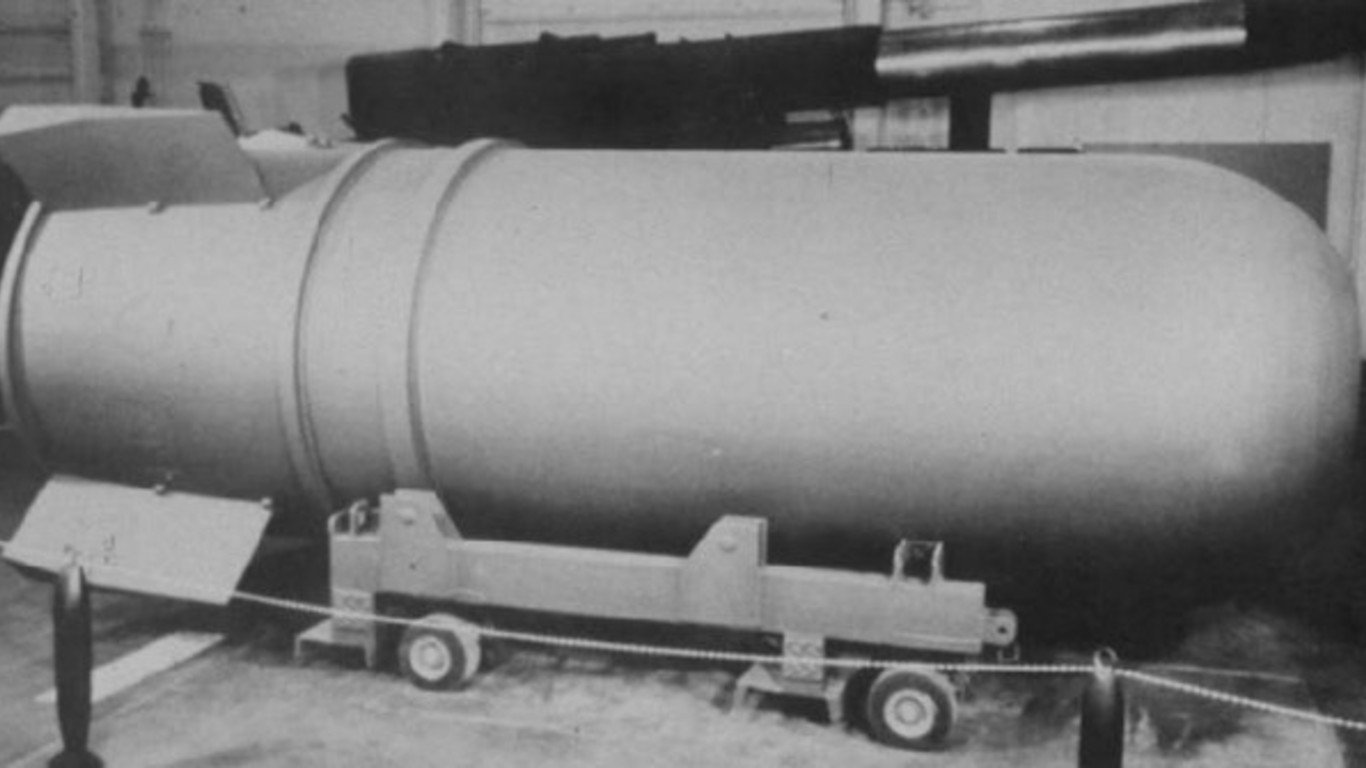

2. B41 nuclear bomb
> Power: 25 megatons
> Circa: 1960-1976
> Country: United States
[in-text-ad-2]
1. Tsar Bomba (RDS-220 hydrogen bomb)
> Power: 50 megatons
> Circa: 1961
> Country: Soviet Union
Take This Retirement Quiz To Get Matched With An Advisor Now (Sponsored)
Are you ready for retirement? Planning for retirement can be overwhelming, that’s why it could be a good idea to speak to a fiduciary financial advisor about your goals today.
Start by taking this retirement quiz right here from SmartAsset that will match you with up to 3 financial advisors that serve your area and beyond in 5 minutes. Smart Asset is now matching over 50,000 people a month.
Click here now to get started.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.
 24/7 Wall St.
24/7 Wall St.