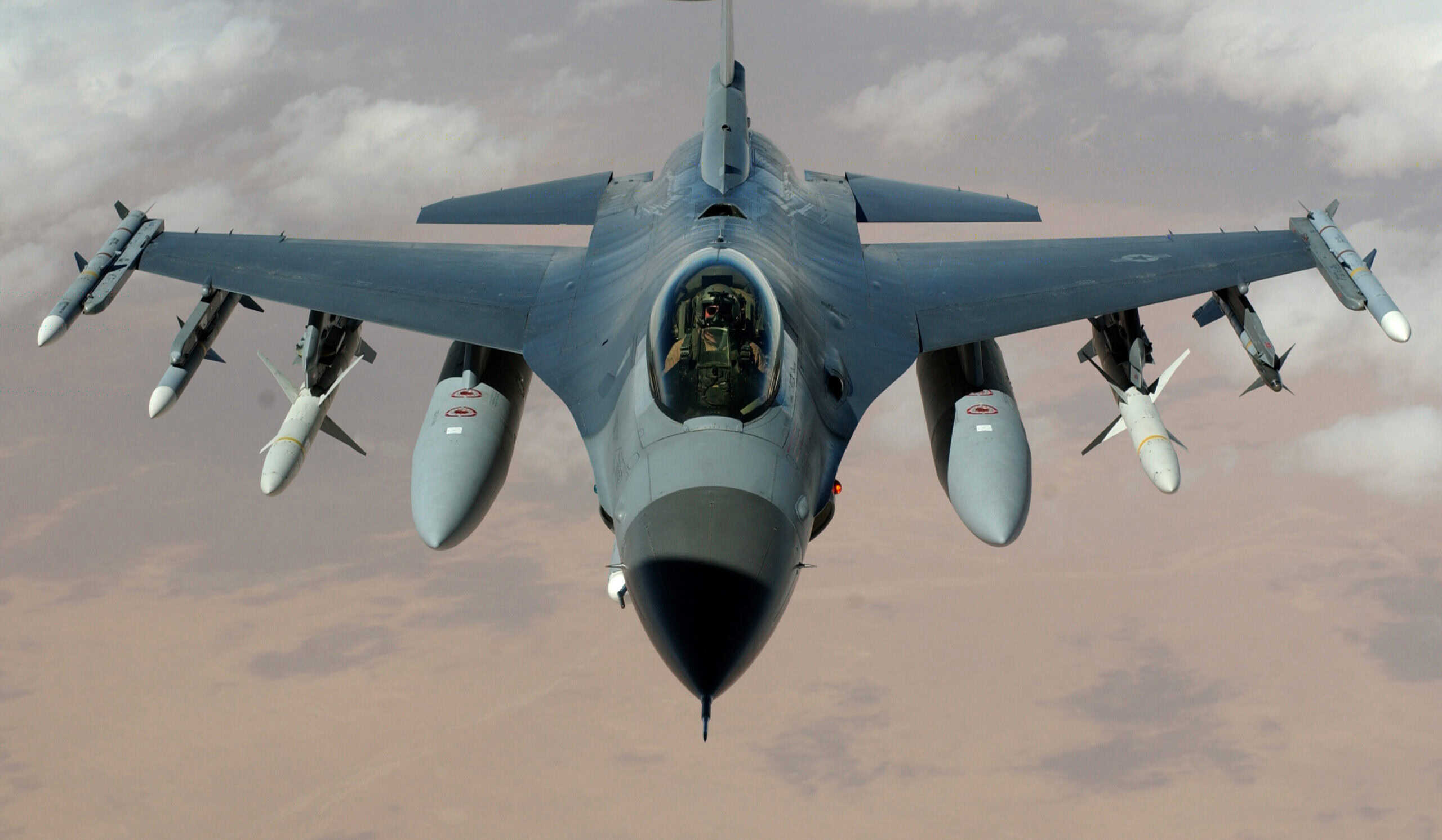

In 1972, the United States Air Force made their original order for the F-16 air-to-air fighter jet. As of last year, there were approximately 800 still in service for the USAF. This summer, some of those F-16s will head to Ukraine to aid in their continued efforts to combat a Russian invasion. Training for the Ukrainian pilots has lasted six months, and their government has waited for quite some time longer to gain access to this air power. Despite many concerns about the age of the equipment, range of fired missiles, and effectiveness against newer technology, the first dozen will be delivered as soon as the pilots complete their training.
Over the years, the United States has sold old combat aircraft to other countries and for scrap. Civilians are even able to purchase demilitarized fighter jets for personal use. The military occasionally finds itself in the position of having too much inventory following a war or long-term occupation; after WWII, there were nearly 300,000 aircraft, and they only needed a fraction of these pieces. Retiring and selling off old units is a way to make room for better, modern technology. Throughout the Air Force’s history, there are countless planes that hold a special place in the collective hearts of the service men and women who have flown them. The lasting legacy of these flying machines can be observed in museums and in private collections around the world.
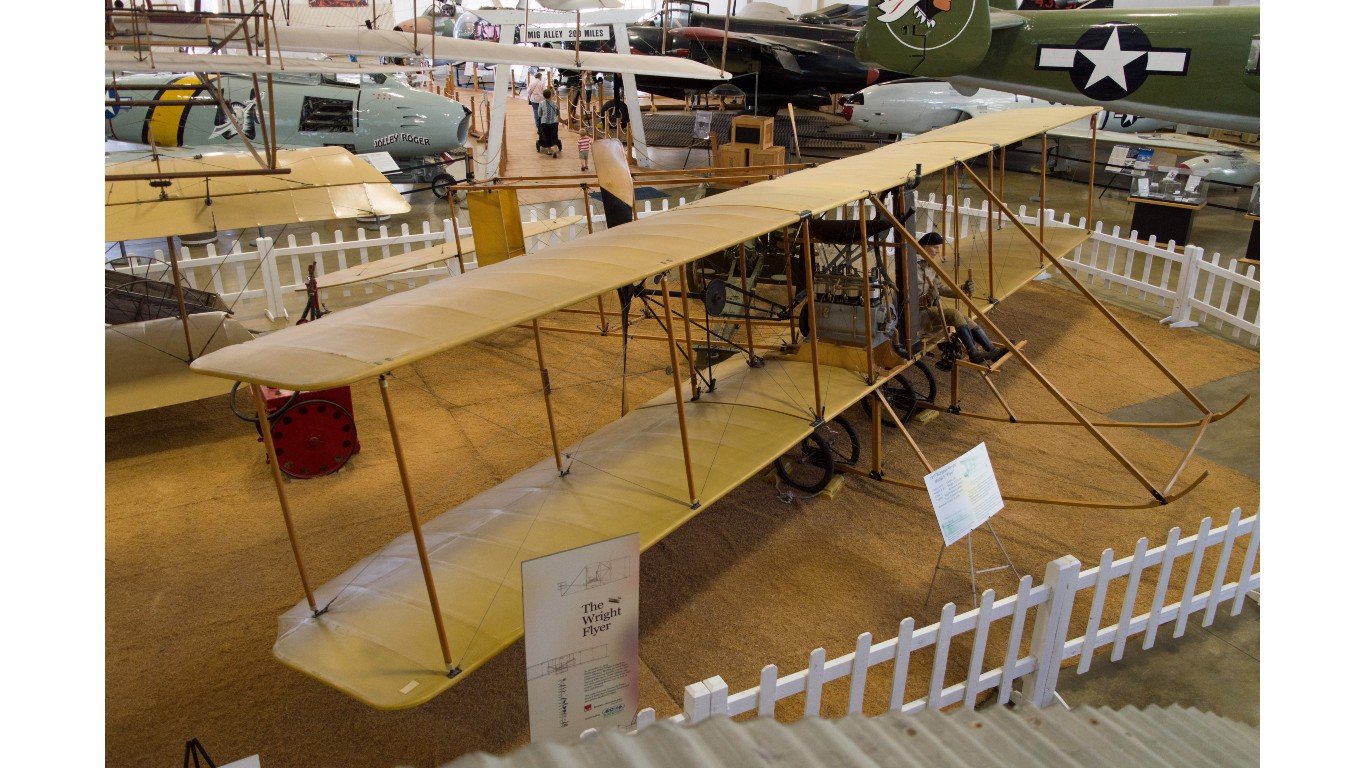
The first military plane developed was the 1909 Wright Military Flyer by the Wright Brothers, and was sold to the US Army Corp. By 1914, the Army and Navy had burgeoning aviation programs for scouting and reconnaissance. Jet propulsion technology was in testing beginning in 1939, and the rest, as they say, is history. Now, almost one hundred years later, it may still be hard to believe we have created a world where planes refuel each other mid-flight, and we have stealth bombers defying even the wildest imaginations.
24/7 Wall St. reviewed former U.S. military aircraft from Military Factory to determine America’s first military war plane and other notable early American military aircraft. Planes are in order according to the year they entered military service. We included supplemental information from Military Factory regarding types of aircraft, maximum speed, crew size, and what roles each aircraft played in the service.
Why Are We Talking About the US Air Force?

The United States Air Force is the largest in the world. It boasts a high level of air superiority, rapid mobility and intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance. The USAF has a long history of developing aircraft while meeting and exceeding technological advancements ahead of competing nations and sharing this technology with other countries. The US has led the charge in military aircraft technology and continues to do so to this day.
Here are the first planes in the United States Air Force.
1. Burgess-Wright Model F Flyer
- Year entered service: 1911
- Type: Biplane aircraft
- Maximum speed: 42 mph
- Crew size: 1
- Role: Surveillance, reconnaissance, trainer
2. Curtiss JN-4
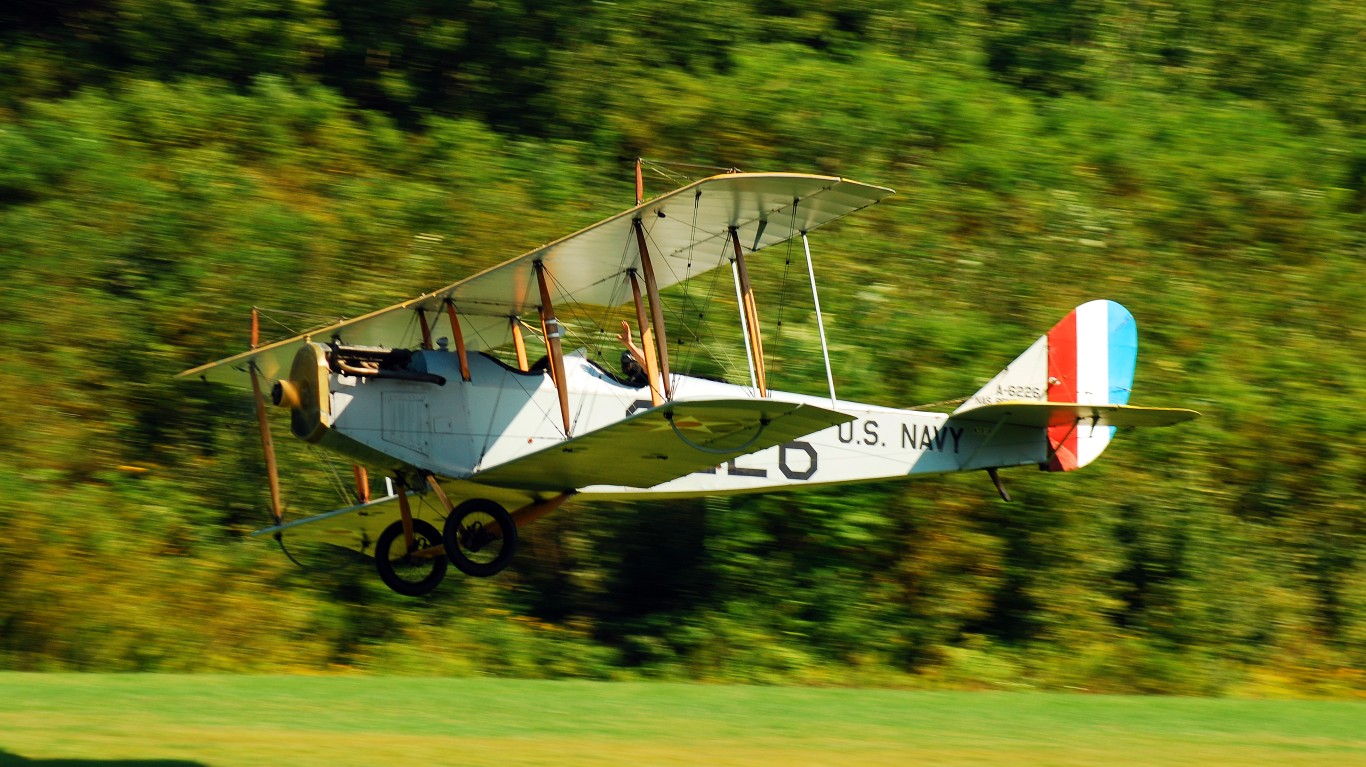

- Year entered service: 1915
- Type: Biplane aircraft
- Maximum speed: 75 mph
- Crew size: 2
- Role: Trainer
3. Thomas-Morse S-4
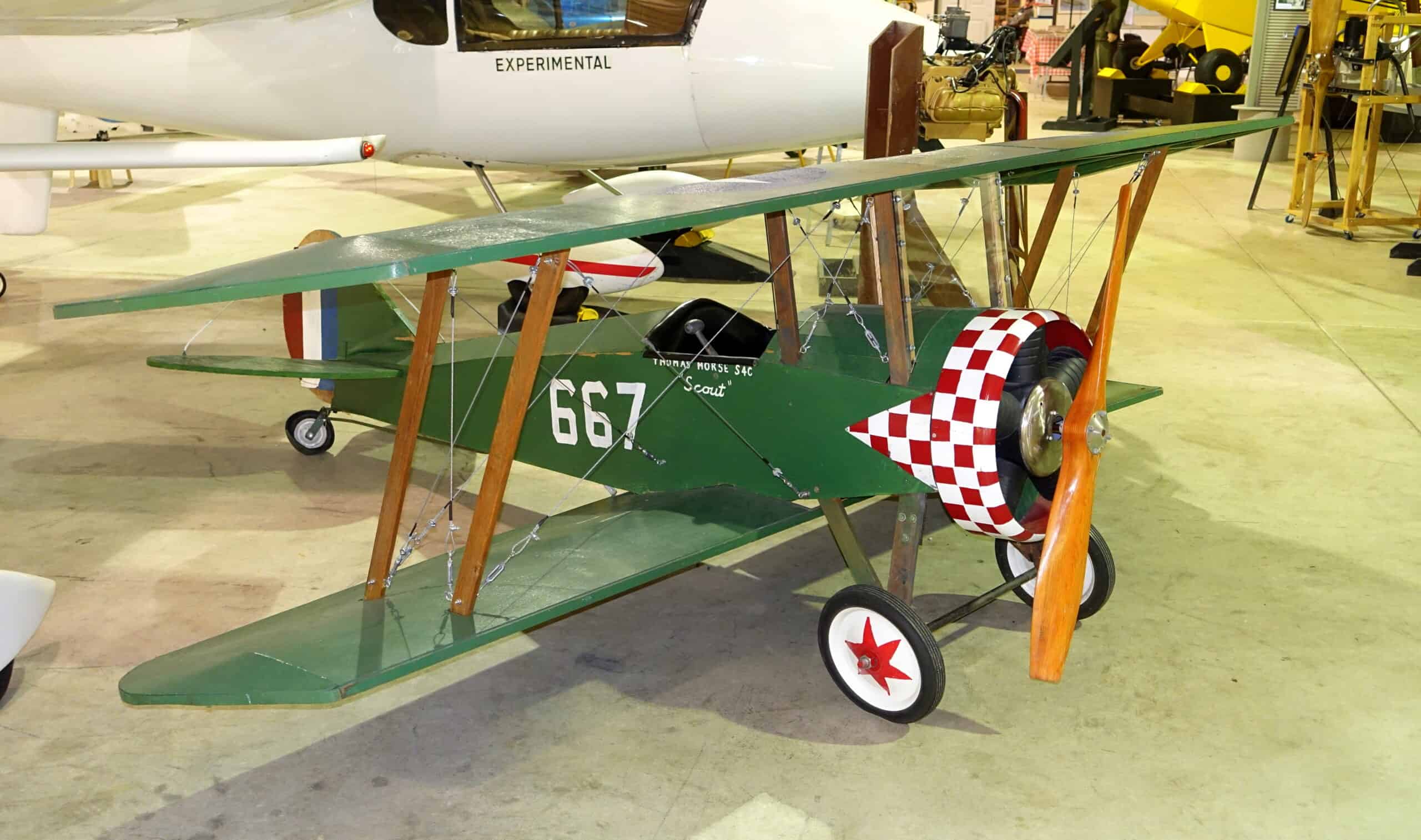

- Year entered service: 1917
- Type: Advanced flight trainer biplane
- Maximum speed: 96 mph
- Crew size: 1
- Role: Trainer
4. Standard J
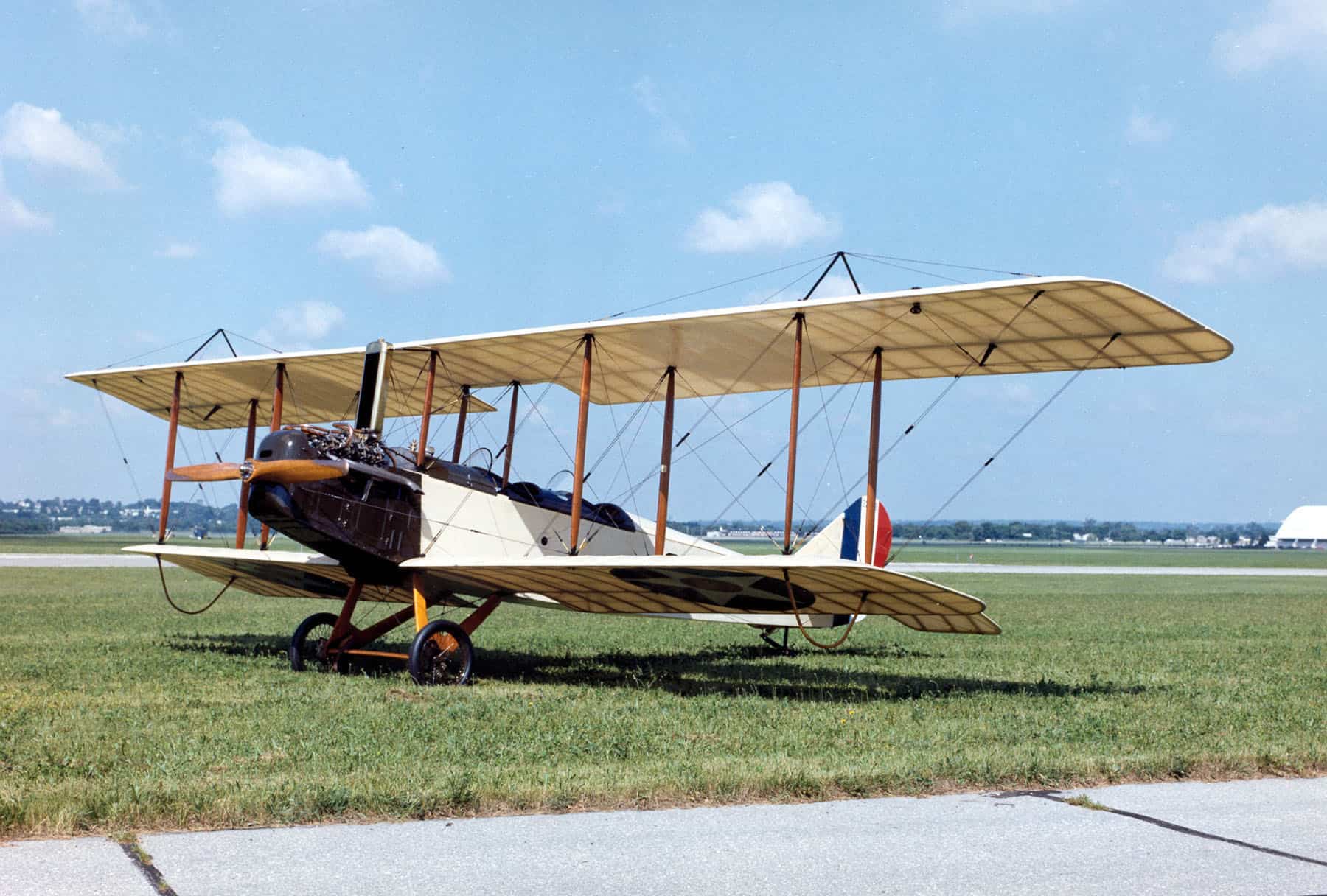

- Year entered service: 1917
- Type: Biplane aircraft
- Maximum speed: 68 mph
- Crew size: 2
- Role: Surveillance, reconnaissance, trainer
5. Curtiss H-16
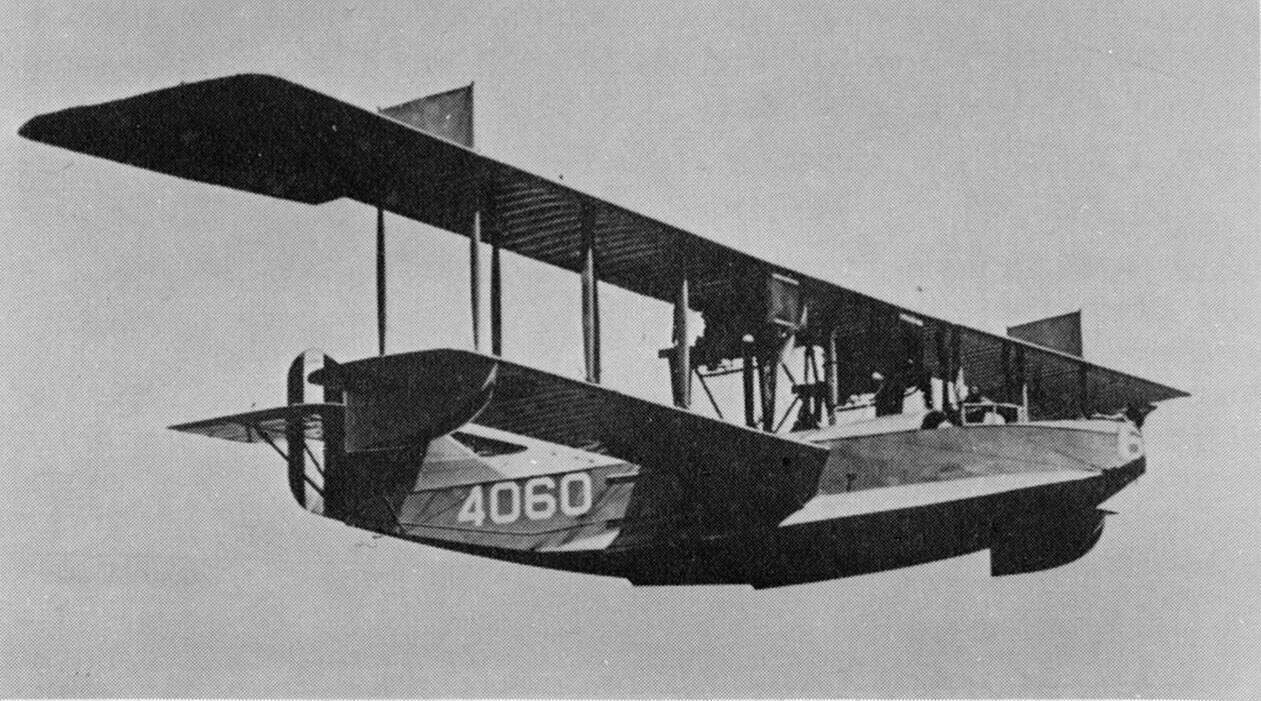
- Year entered service: 1917
- Type: Seaplane
- Maximum speed: 95 mph
- Crew size: 4
- Role: Surveillance & reconnaissance
6. Aeromarine 39
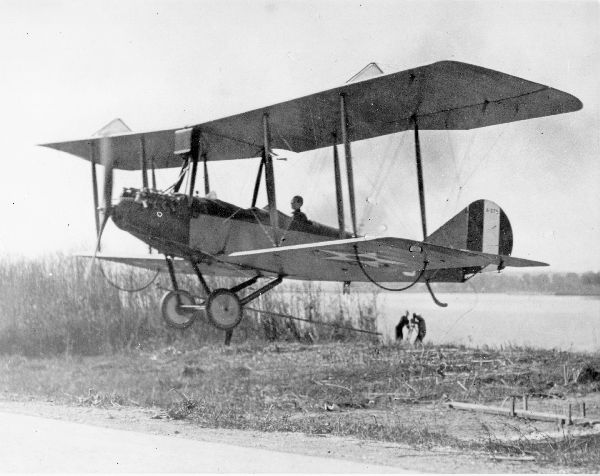

- Year entered service: 1917
- Type: Naval biplane aircraft
- Maximum speed: 73 mph
- Crew size: 2
- Role: Trainer
7. Vought VE-7 Bluebird
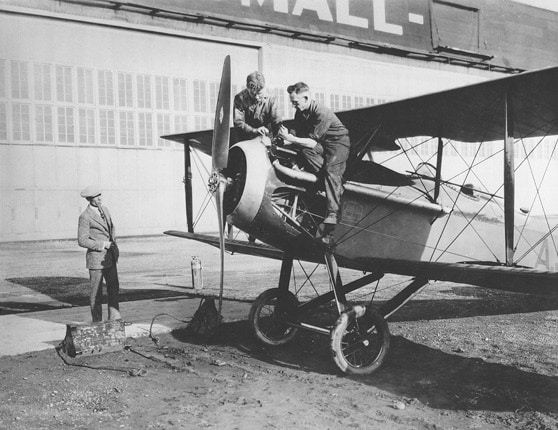

- Year entered service: 1918
- Type: Biplane fighter aircraft
- Maximum speed: 106 mph
- Crew size: 2
- Role: Fighter, trainer
8. Packard-Le Pere LUSAC-11
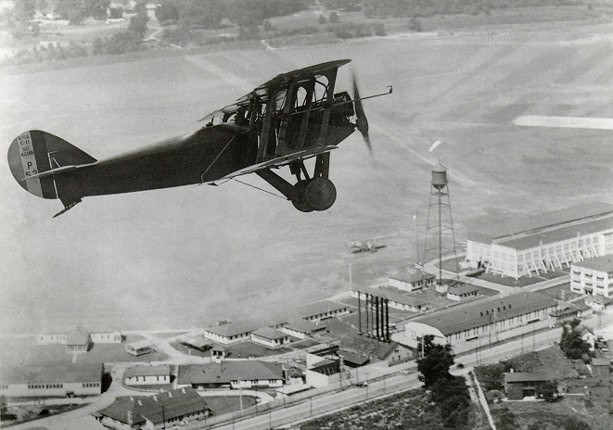

- Year entered service: 1918
- Type: Biplane fighter aircraft
- Maximum speed: 134 mph
- Crew size: 2
- Role: Fighter, bomber, trainer
9. Martin MB-1 (Glenn Martin Bomber)
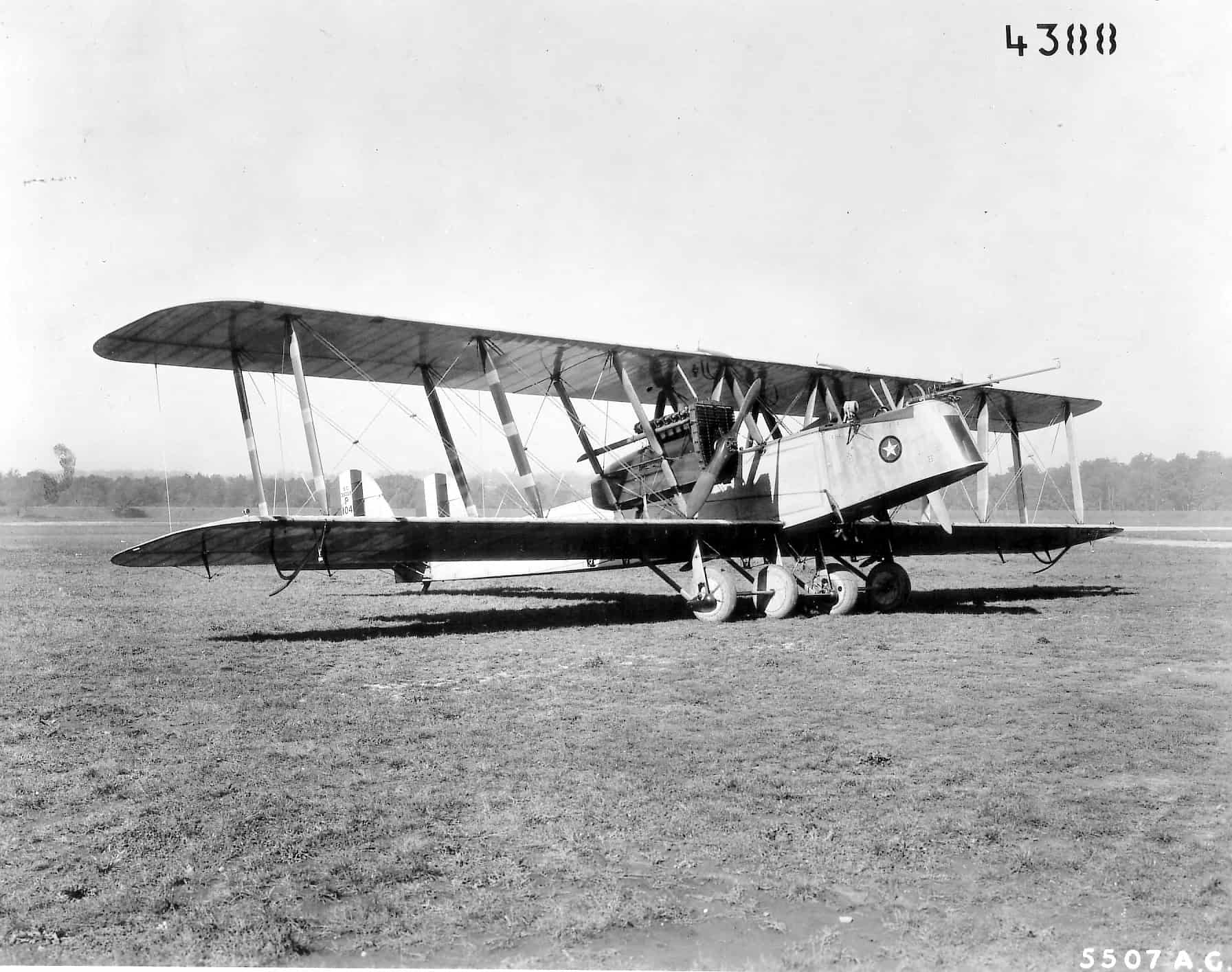

- Year entered service: 1918
- Type: Biplane bomber aircraft
- Maximum speed: 104 mph
- Crew size: 4
- Role: Bomber, surveillance, reconnaissance
10. Aeromarine 40
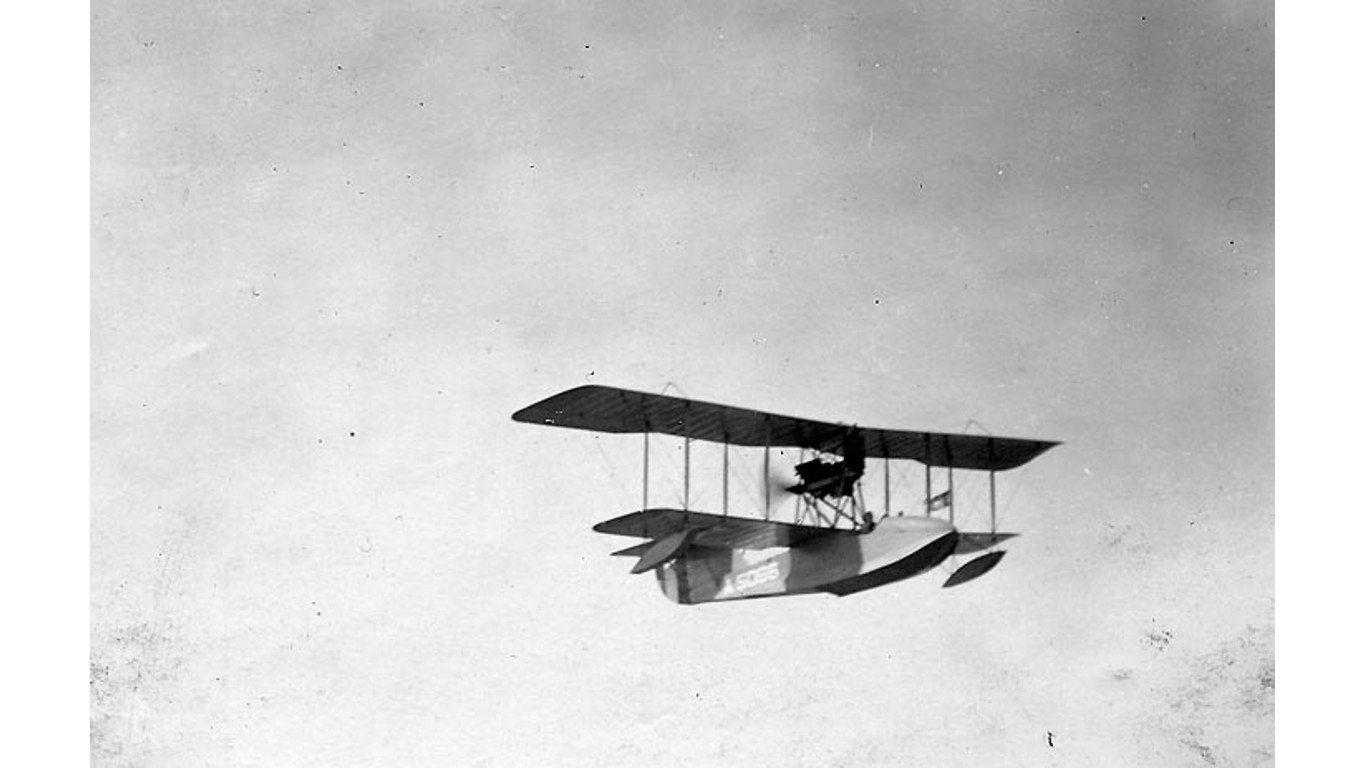

- Year entered service: 1918
- Type: Naval biplane aircraft
- Maximum speed: 71 mph
- Crew size: 2
- Role: Trainer
11. Martin MB-2 / NBS-1
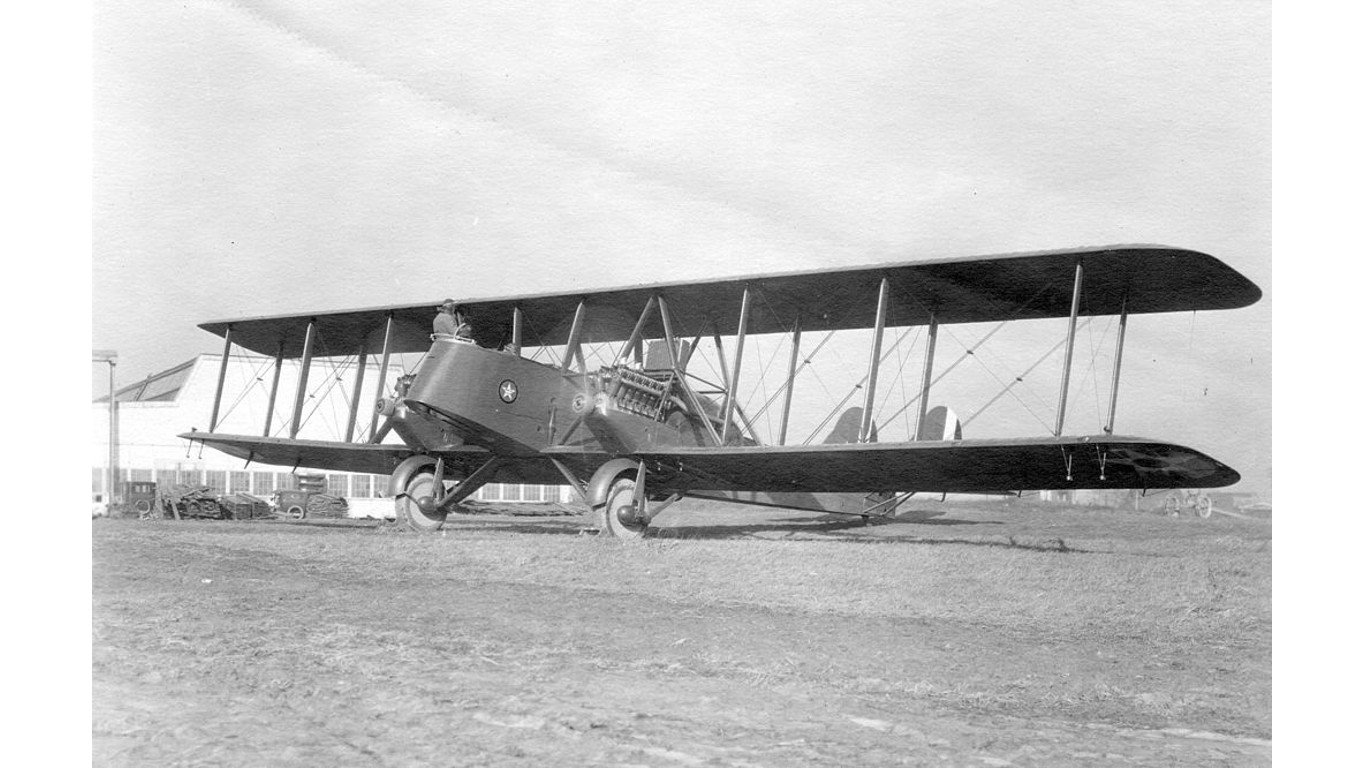

- Year entered service: 1920
- Type: Night bomber aircraft
- Maximum speed: 99 mph
- Crew size: 4
- Role: Bomber
12. Curtiss F6C Hawk
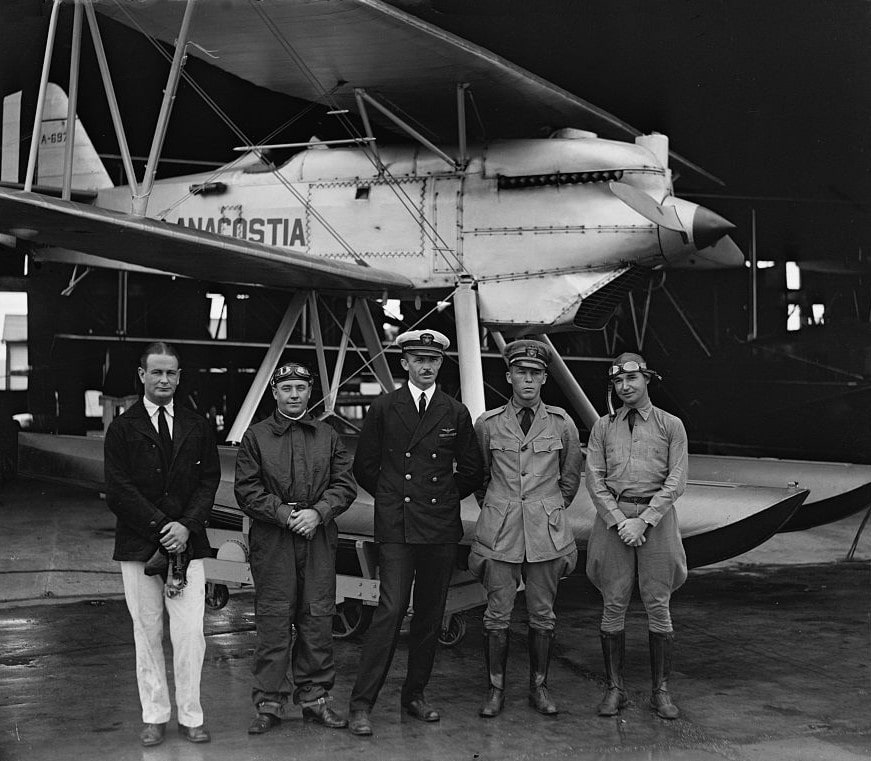

- Year entered service: 1924
- Type: Naval carrier-borne fighter aircraft
- Maximum speed: 154 mph
- Crew size: 1
- Role: Fighter
13. Consolidated PT-1 Trusty
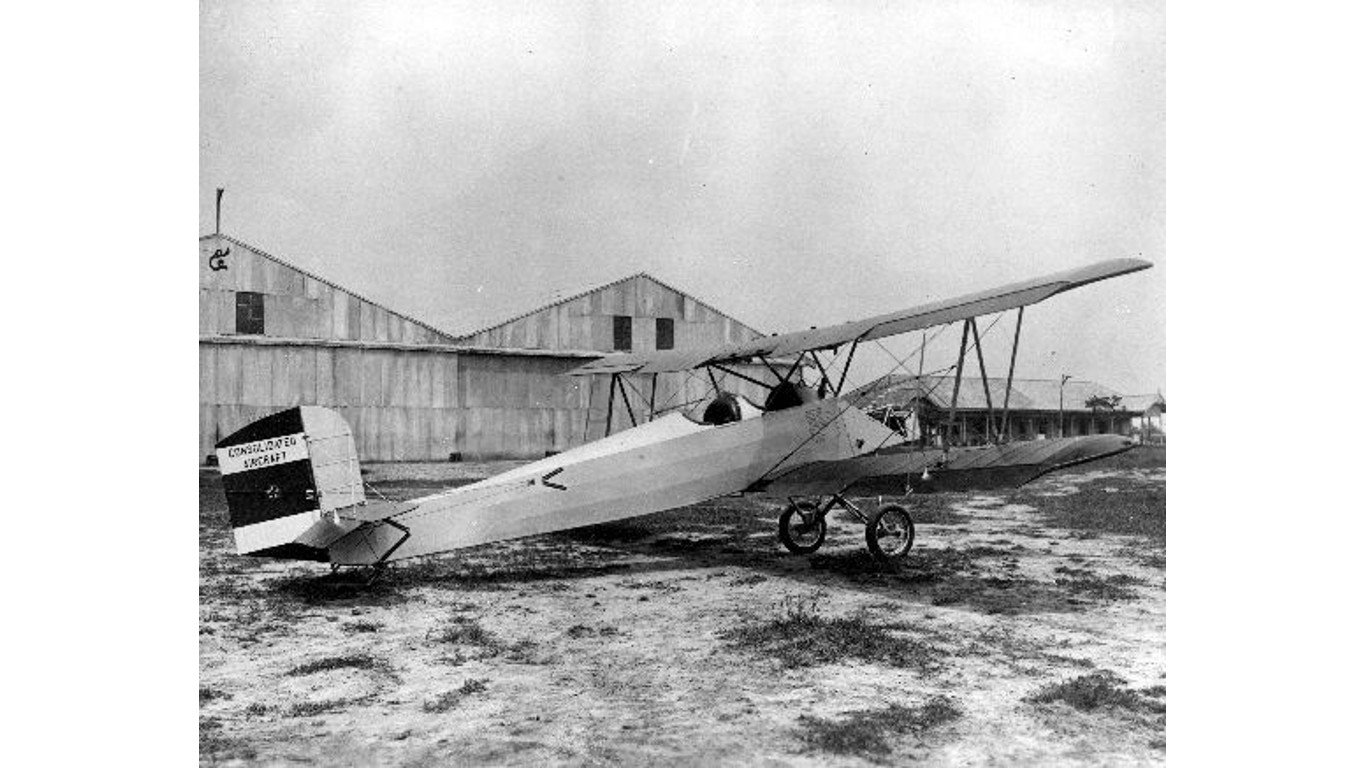

- Year entered service: 1924
- Type: Biplane aircraft
- Maximum speed: 92 mph
- Crew size: 2
- Role: Trainer
14. Boeing PW-9 (FB-5 / Model 15)
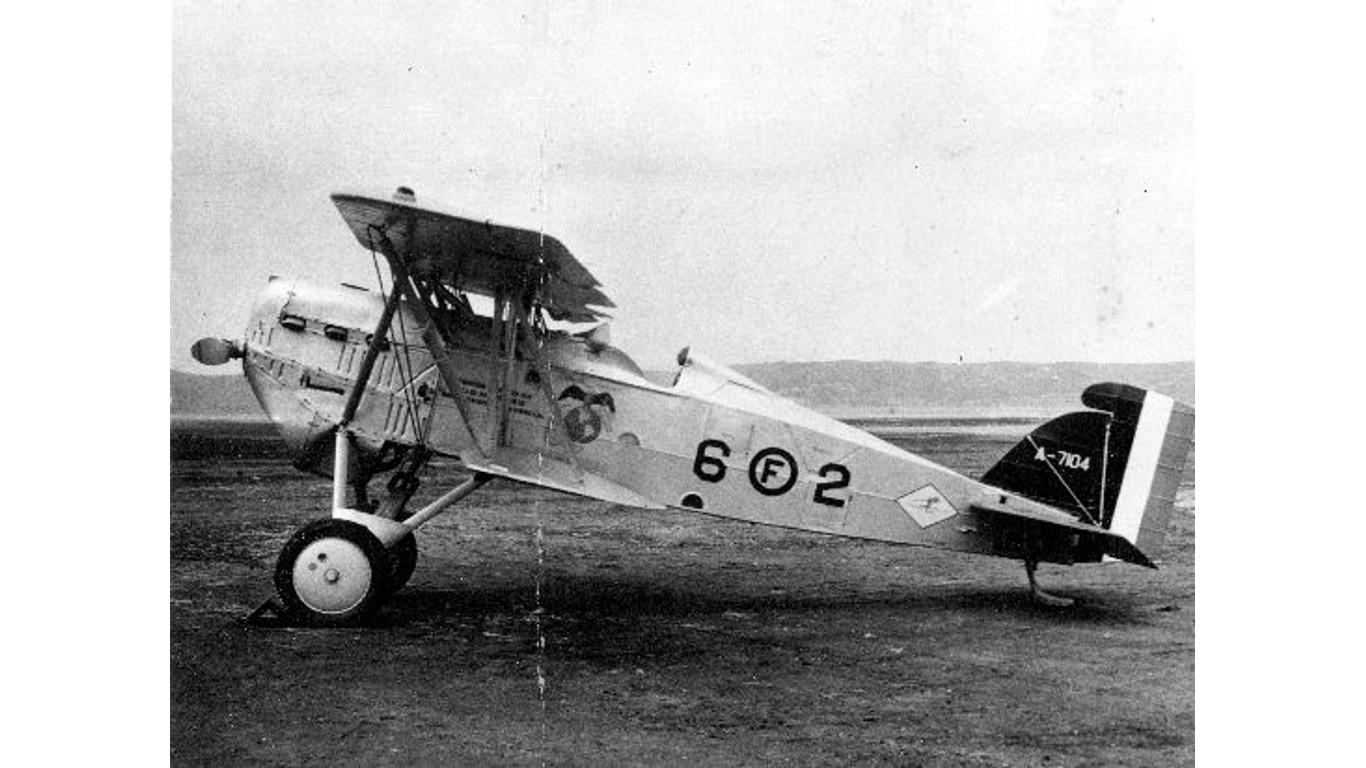

- Year entered service: 1924
- Type: Biplane fighter aircraft
- Maximum speed: 159 mph
- Crew size: 1
- Role: Fighter, interceptor
15. Ford Trimotor
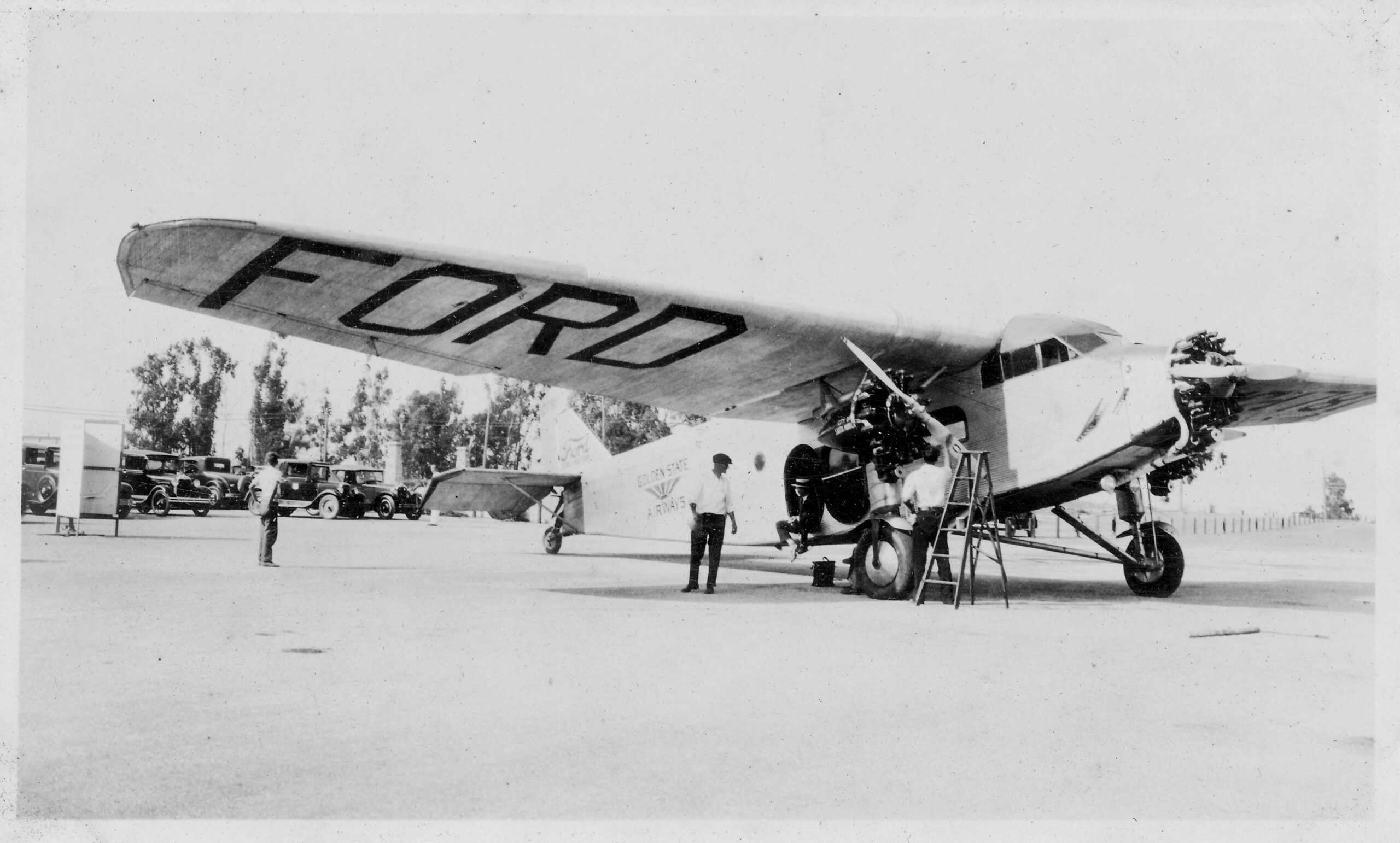

- Year entered service: 1926
- Type: Transport aircraft
- Maximum speed: 149 mph
- Crew size: 2
- Role: Transport
16. Curtiss P-6 Hawk
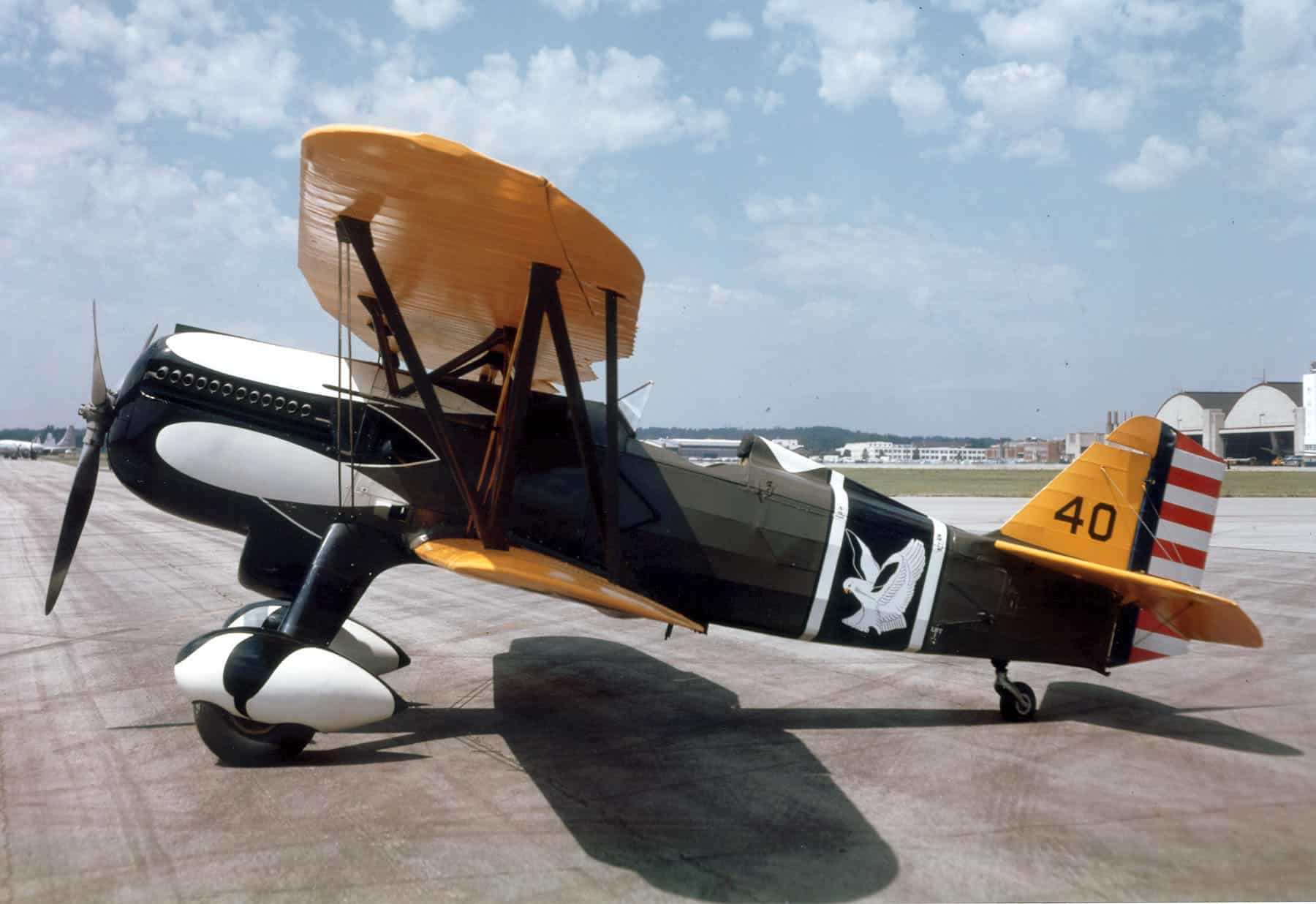

- Year entered service: 1929
- Type: Biplane fighter aircraft
- Maximum speed: 204 mph
- Crew size: 1
- Role: Fighter
17. Boeing F4B / P-12
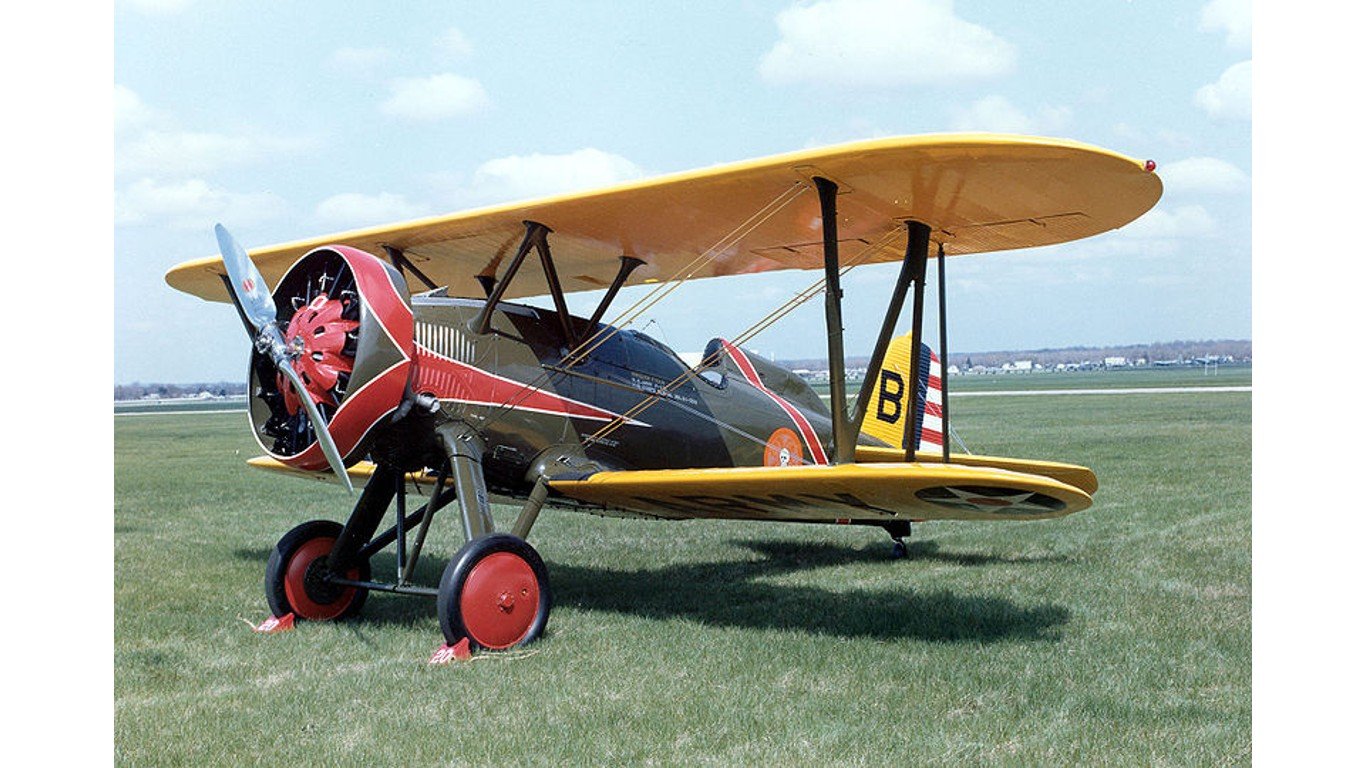

- Year entered service: 1929
- Type: Carrierborne biplane fighter aircraft
- Maximum speed: 189 mph
- Crew size: 1
- Role: Fighter, bomber
18. Northrop Gamma
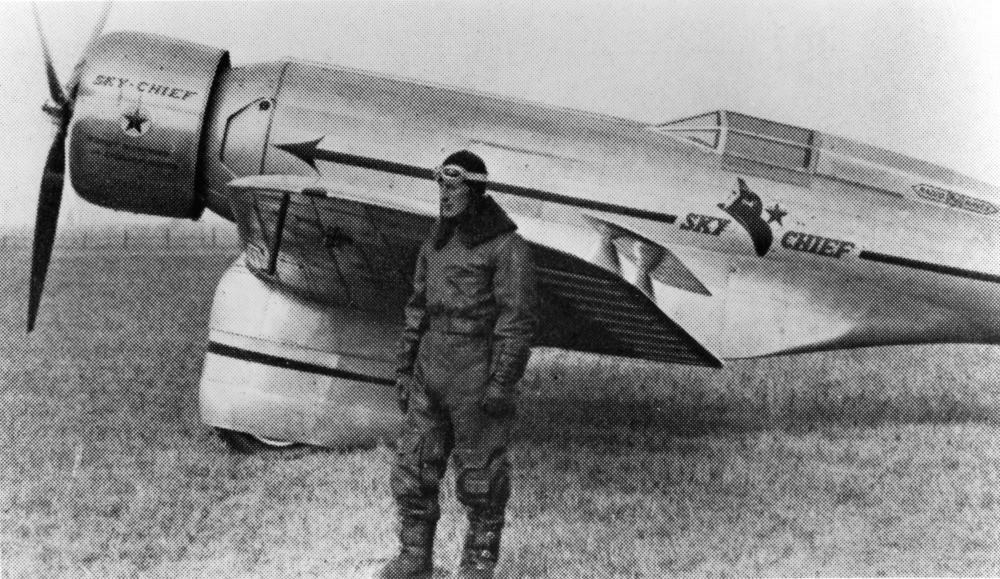
- Year entered service: 1932
- Type: Monoplane aircraft
- Maximum speed: 224 mph
- Crew size: 1
- Role: Fighter, transport
19. Martin B-10
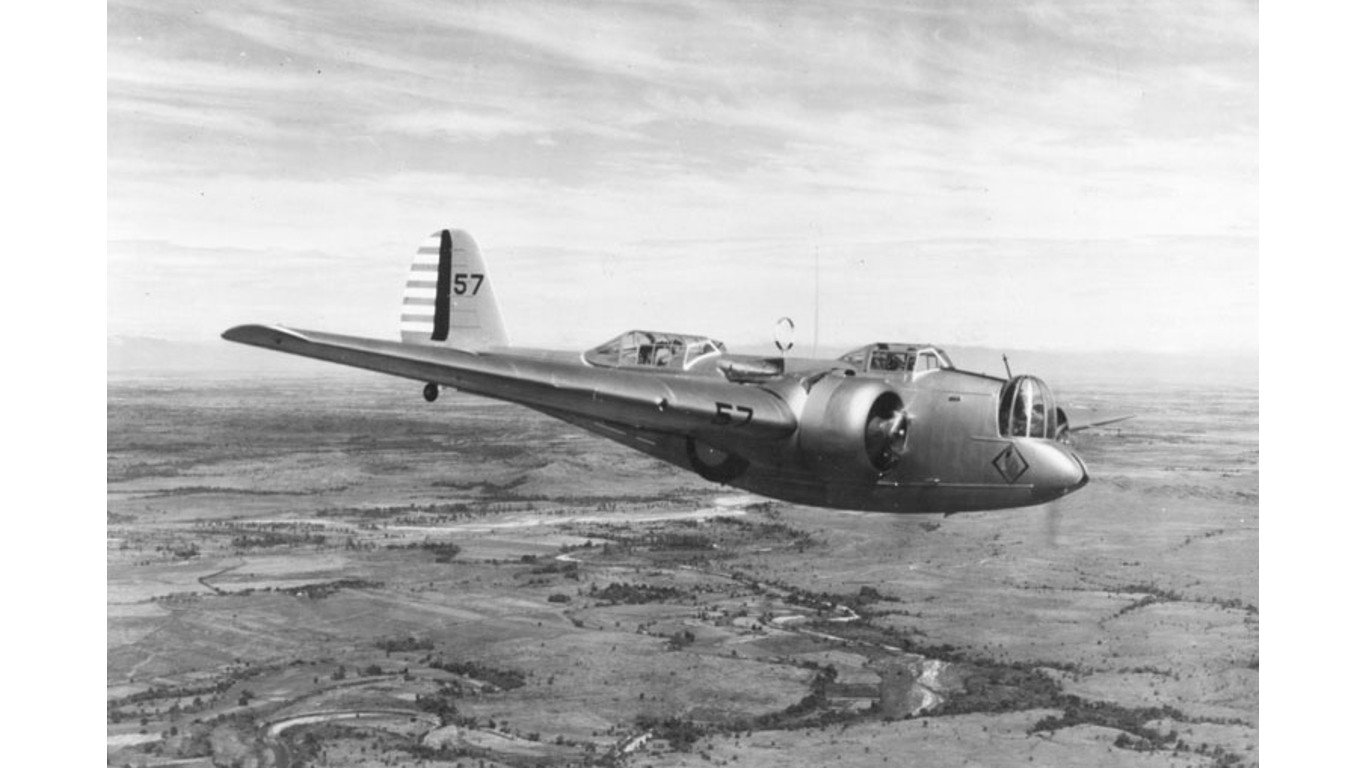

- Year entered service: 1932
- Type: Medium bomber
- Maximum speed: 214 mph
- Crew size: 4
- Role: Bomber
20. Boeing P-26 Peashooter
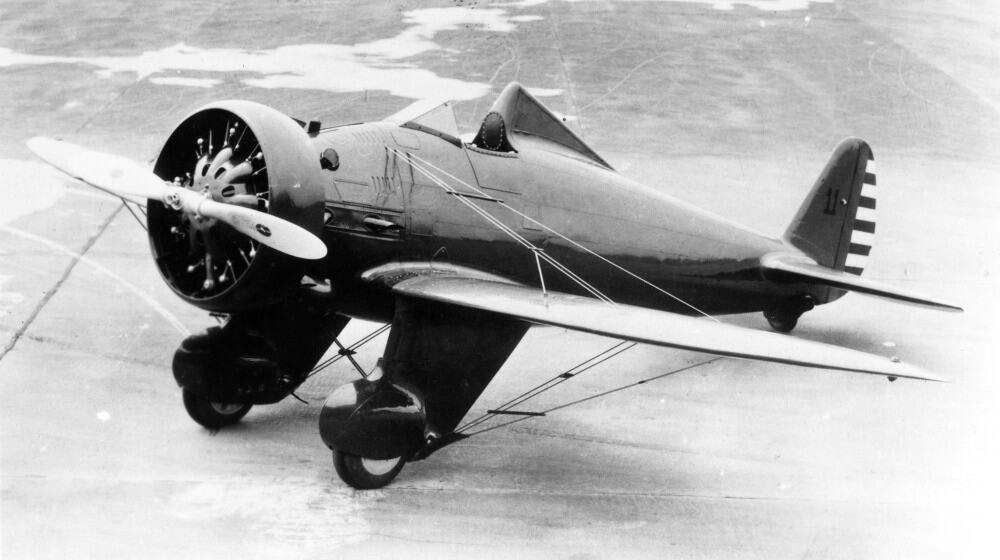

- Year entered service: 1932
- Type: Monoplane fighter aircraft
- Maximum speed: 227 mph
- Crew size: 1
- Role: Fighter
21. Stinson Reliant
- Year entered service: 1933
- Type: Lightweight liason aircraft
- Maximum speed: 177 mph
- Crew size: 1
- Role: Surveillance, reconnaissance, trainer
22. Grumman FF
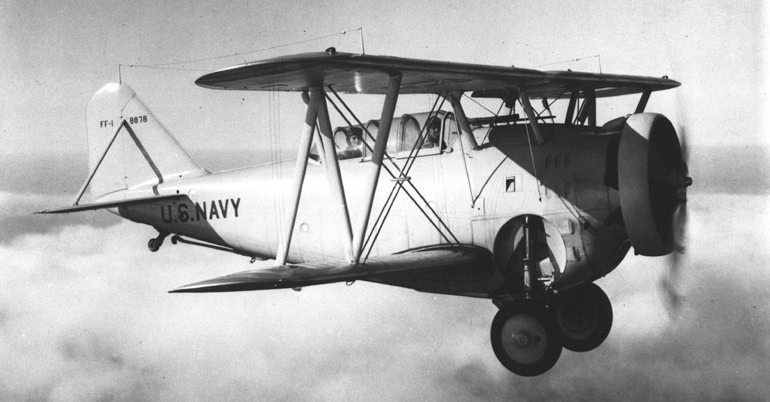

- Year entered service: 1933
- Type: Carrierborne biplane fighter aircraft
- Maximum speed: 207 mph
- Crew size: 2
- Role: Fighter
23. Northrop A-17 (Nomad)
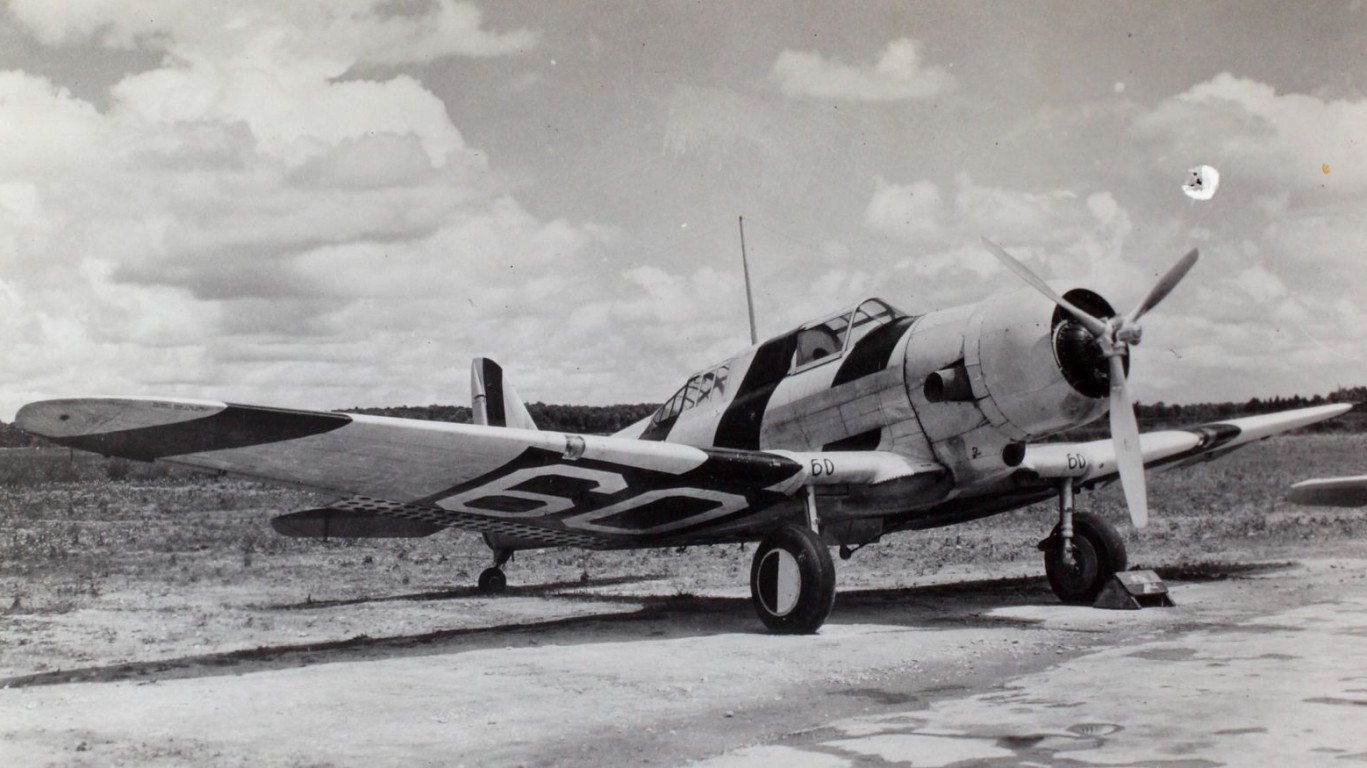

- Year entered service: 1935
- Type: Monoplane aircraft
- Maximum speed: 208 mph
- Crew size: 2
- Role: Bomber, surveillance, reconnaissance
24. Grumman F2F
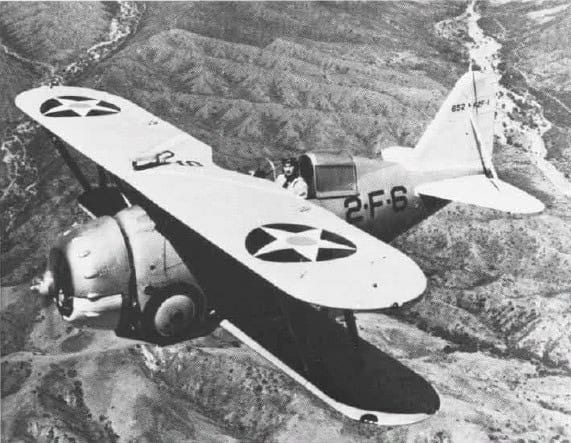

- Year entered service: 1935
- Type: Carrierborne biplane fighter aircraft
- Maximum speed: 238 mph
- Crew size: 1
- Role: Fighter
25. Curtiss SOC Seagull
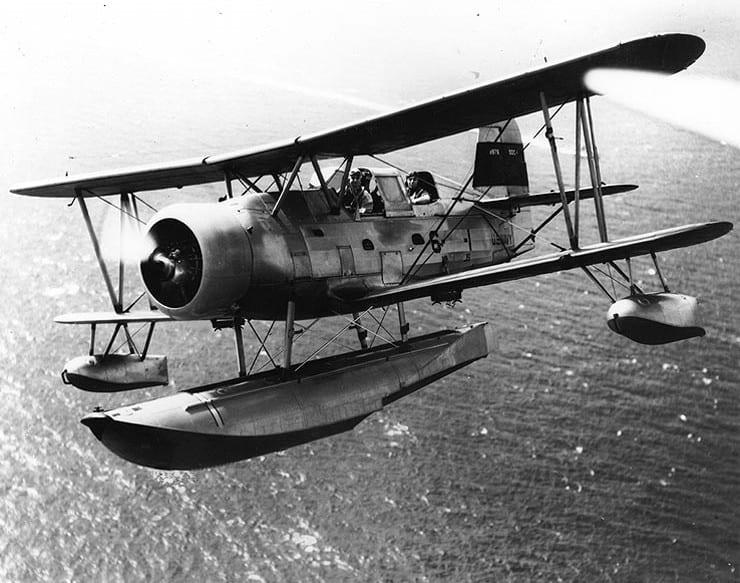

- Year entered service: 1935
- Type: Naval biplane aircraft
- Maximum speed: 165 mph
- Crew size: 2
- Role: Surveillance, reconnaissance, trainer
26. T-6 Texan
- Year entered service: 1936
- Type: Single-engine fighter aircraft
- Maximum speed: 209 mph
- Crew size: 2
- Role: Fighter, close-air-support, trainer
27. Naval Aircraft Factory N3N (Yellow Peril)
- Year entered service: 1936
- Type: Biplane trainer aircraft
- Maximum speed: 127 mph
- Crew size: 2
- Role: Trainer
28. Grumman F3F

- Year entered service: 1936
- Type: Carrierborne biplane fighter aircraft
- Maximum speed: 264 mph
- Crew size: 1
- Role: Fighter
29. Douglas B-18 Bolo
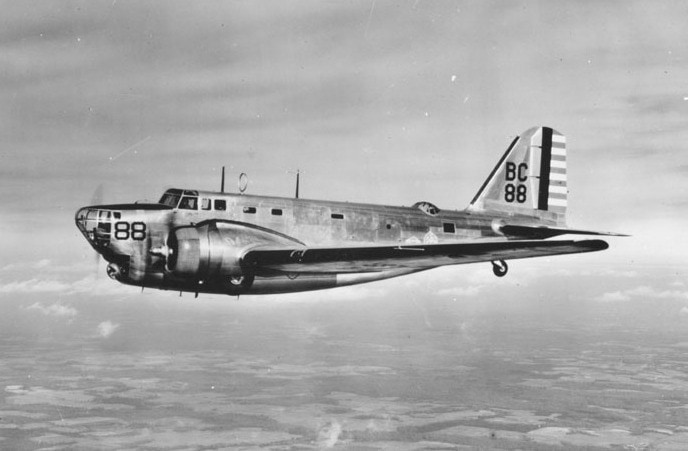

- Year entered service: 1936
- Type: Medium bomber
- Maximum speed: 215 mph
- Crew size: 6
- Role: Bomber, surveillance, reconnaissance, transport
30. Douglas DC-3
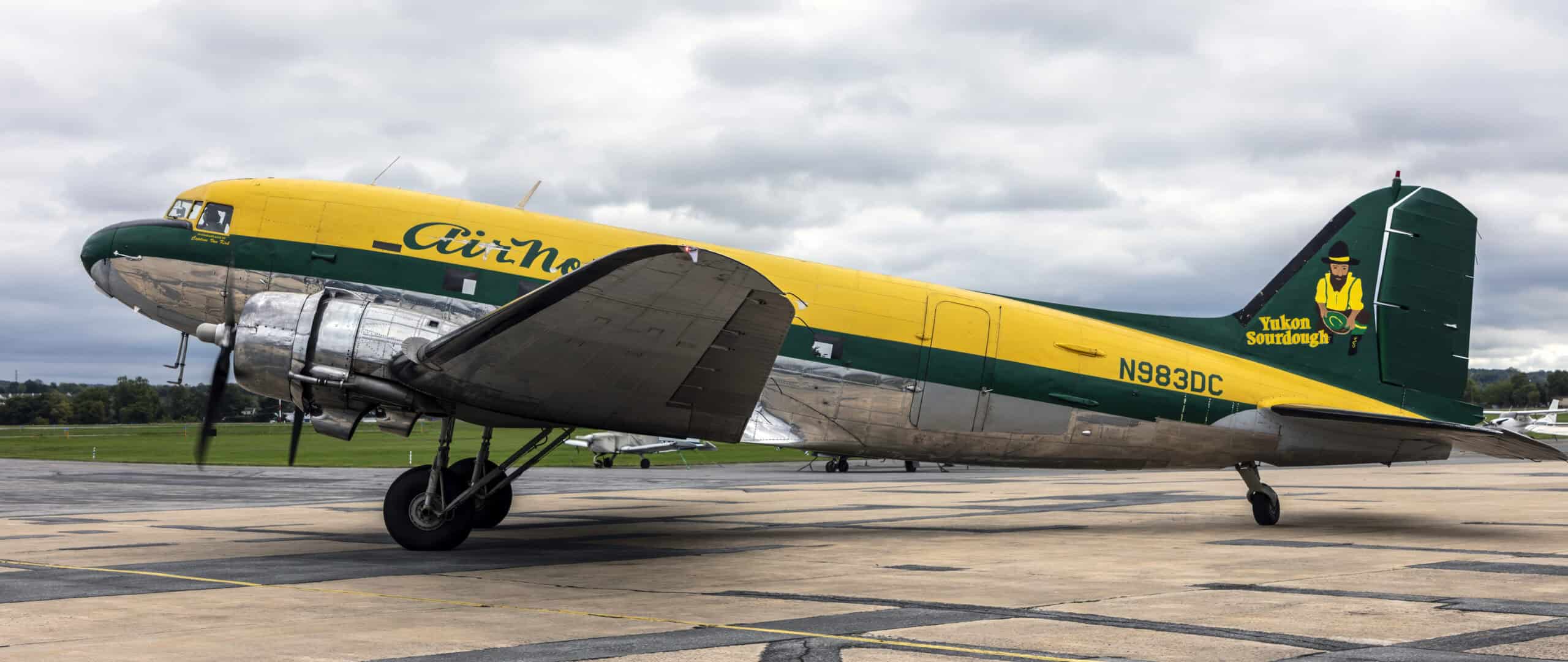

- Year entered service: 1936
- Type: Military transport
- Maximum speed: 237 mph
- Crew size: 5
- Role: Transport
Take This Retirement Quiz To Get Matched With An Advisor Now (Sponsored)
Are you ready for retirement? Planning for retirement can be overwhelming, that’s why it could be a good idea to speak to a fiduciary financial advisor about your goals today.
Start by taking this retirement quiz right here from SmartAsset that will match you with up to 3 financial advisors that serve your area and beyond in 5 minutes. Smart Asset is now matching over 50,000 people a month.
Click here now to get started.
Thank you for reading! Have some feedback for us?
Contact the 24/7 Wall St. editorial team.





